
A cylinder with a circular hole is rolling without slipping on a fixed curved surface as shown. The cylinder would have a weight of 16 lb without the hole, but with the hole it has a weight of 15 lb. Knowing that at the instant shown the disk has an angular velocity of 5 rad/s clockwise, determine (a) the angular acceleration of the disk, (b) the components of the reaction force between the cylinder and the ground at this instant.
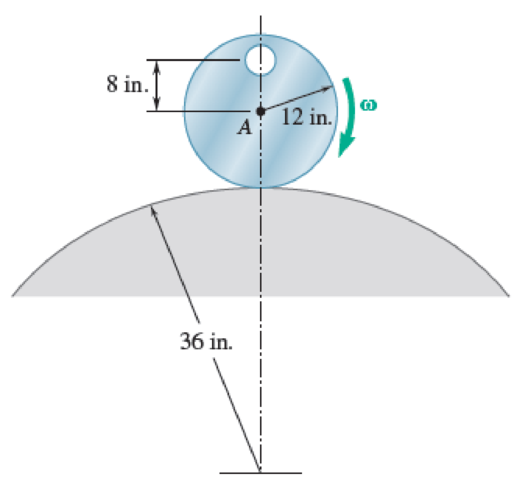
Fig. P16.161
(a)
The angular acceleration of the disk.
Answer to Problem 16.161RP
The angular acceleration of the disk is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The weight of the cylinder without hole is
The weight of the cylinder with hole is
The angular velocity of the disk is
Calculation:
Consider the acceleration due to gravity as
Consider that the mass center of the cylinder is G and it lies at a distance b from center A, and C is the contact point between cylinder and the curved surface is the origin of the coordinate system.
Consider that the radius of cylinder is r and the radius of the curved surface is R.
Sketch the geometry of the cylinder as shown in Figure 1.
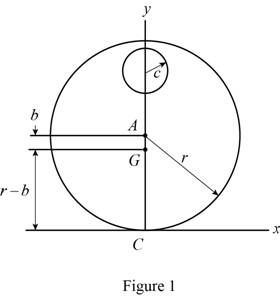
Refer to Figure 1.
Calculate the position vector
The position vector of P with respect to C.
The position vector of G with respect to C.
The position vector of A with respect to C.
The cylinder rolls without slipping on a fixed curved surface hence, the horizontal component of acceleration of point C is
Calculate the acceleration of point C
Substitute 0 for
The acceleration of the disk at A is
Calculate the acceleration of point A
Substitute
Calculate the acceleration of point P
Here,
Substitute
Calculate the acceleration of point G
Substitute
Calculate the acceleration of point A
Substitute
Subtract Equation (2) from Equation (1) as shown below.
Substitute
Calculate the velocity of point A
Calculate the vertical component of acceleration of point A
Substitute
Calculate the acceleration of point G
Substitute
Calculate the effective force at the mass center
Sketch the Free Body Diagram of the cylinder as shown in Figure 2.
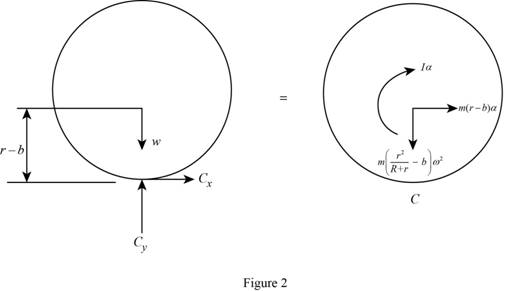
Refer to Figure 2.
Apply the Equilibrium of moment about C as shown below.
Hence, the angular acceleration of the disk is
(b)
The components of the reaction force between the cylinder and the ground.
Answer to Problem 16.161RP
The component of the reaction along x direction is
The component of the reaction along y direction is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The weight of the cylinder without hole is
The weight of the cylinder with hole is
The angular velocity of the disk is
Calculation:
Refer to part (a).
The angular acceleration of the disk is
Refer to Figure 2.
Apply the Equilibrium of force along x direction as shown below.
Substitute 0 for
Hence, the component of the reaction along x direction is
Apply the Equilibrium of force along y direction as shown below.
Sketch the cylinder with hole as shown in Figure 3.
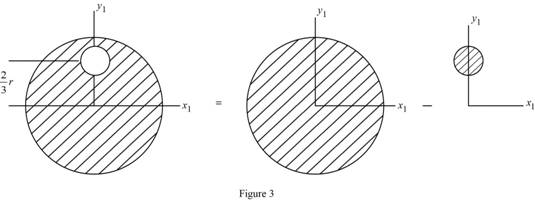
Refer to Figure 3.
Calculate the area of solid cylinder
Calculate the center of gravity of solid cylinder in vertical direction
Calculate the area of hole
Calculate the center of gravity of hole in vertical direction
Calculate the distance
Substitute
Calculate the component of the reaction along y direction as shown below.
Substitute
Therefore, the component of the reaction along y direction is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Connect 1 Semester Access Card for Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Concepts Of Programming Languages
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
- Solve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forwardaversity of Baoyion aculty of Engineering-AIMusyab Automobile Eng. Dep. Year: 2022-2023, st Course, 1st Attempt Stage: 3rd Subject: Heat Transfer I Date: 2023\01\23- Monday Time: 3 Hours Q4: A thick slab of copper initially at a uniform temperature of 20°C is suddenly exposed to radiation at one surface such that the net heat flux is maintained at a constant value of 3×105 W/m². Using the explicit finite-difference techniques with a space increment of Ax = = 75 mm, determine the temperature at the irradiated surface and at an interior point that is 150 mm from the surface after 2 min have elapsed. Q5: (12.5 M) A) A steel bar 2.5 cm square and 7.5 cm long is initially at a temperature of 250°C. It is immersed in a tank of oil maintained at 30°C. The heat-transfer coefficient is 570 W/m². C. Calculate the temperature in the center of the bar after 3 min. B) Air at 90°C and atmospheric pressure flows over a horizontal flat plate at 60 m/s. The plate is 60 cm square and is maintained at a…arrow_forwardUniversity of Baby on Faculty of Engineering-AIMusyab Automobile Eng. Dep. Year: 2022-2023. 1 Course, 1" Attempt Stage 3 Subject Heat Transfer I Date: 2023 01 23- Monday Time: 3 Hours Notes: Q1: • • Answer four questions only Use Troles and Appendices A) A flat wall is exposed to an environmental temperature of 38°C. The wall is covered with a layer of insulation 2.5 cm thick whose thermal conductivity is 1.4 W/m. C, and the temperature of the wall on the inside of the insulation is 315°C. The wall loses heat to the environment by convection. Compute the value of the convection heat-transfer coefficient that must be maintained on the outer surface of the insulation to ensure that the outer-surface temperature does not exceed 41°C. B) A vertical square plate, 30 cm on a side, is maintained at 50°C and exposed to room air at 20°C. The surface emissivity is 0.8. Calculate the total heat lost by both sides of the plate. (12.5 M) Q2: An aluminum fin 1.5 mm thick is placed on a circular tube…arrow_forward
- Solve this and show all of the workarrow_forwardNeed helparrow_forwardY F1 α В X F2 You and your friends are planning to move the log. The log. needs to be moved straight in the x-axis direction and it takes a combined force of 2.9 kN. You (F1) are able to exert 610 N at a = 32°. What magnitude (F2) and direction (B) do you needs your friends to pull? Your friends had to pull at: magnitude in Newton, F2 = direction in degrees, ẞ = N degarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





