
Concept explainers
The following table contains information concerning four jobs that are awaiting processing at a work center.
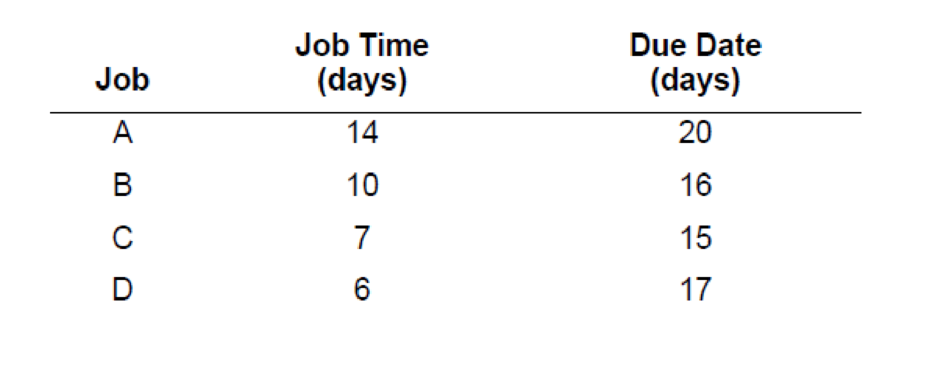
Sequence the jobs using (1) FCFS, (2) SPT, (3) EDD, and (4) CR. Assume the list is by order of arrival.
b. For each of the methods in part a, determine (1) the average job flow time, (2) the average tardiness, and (3) the average number of jobs at the work center.
c. Is one method superior to the others? Explain.
a)
1)
To determine: Sequence of jobs based on decision rule First Come First Served (FCFS).
Introduction: First Come First Served is the scheduling rule, which helps to arrange the sequence in the order. Here, the first come would be served first.
Answer to Problem 6P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) |
| A | 14 | 20 |
| B | 10 | 16 |
| C | 7 | 15 |
| D | 6 | 17 |
Determine the sequence using FCFS:
According to FCFS, the first come would be served first. Hence, the jobs should be sequenced in the order as per its arrival.
Hence, the sequence of jobs using FCFS is A-B-C-D.
1)
To determine: Sequence of jobs based on decision rule First Come First Served (FCFS).
Introduction: First Come First Served is the scheduling rule, which helps to arrange the sequence in the order. Here, the first come would be served first.
Answer to Problem 6P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) |
| A | 14 | 20 |
| B | 10 | 16 |
| C | 7 | 15 |
| D | 6 | 17 |
Determine the sequence using FCFS:
According to FCFS, the first come would be served first. Hence, the jobs should be sequenced in the order as per its arrival.
Hence, the sequence of jobs using FCFS is A-B-C-D.
2)
To determine: Sequence of jobs based on decision rule Shortest Processing Time (SPT).
Introduction: Shortest Processing Tine is the scheduling rule, which helps to arrange the sequence in the order. Here, job with the shortest duration would be served first. Then, the process would be going on from shortest to largest duration.
Answer to Problem 6P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) |
| A | 14 | 20 |
| B | 10 | 16 |
| C | 7 | 15 |
| D | 6 | 17 |
Determine the sequence using SPT:
According to SPT, the job that has the shortest processing would be served first and it goes on as the processing time increase. Duration should be assembled in the ascending order
Hence, the sequence of jobs using SPT is D-C-B-A.
3)
To determine: Sequence of jobs based on decision rule Earliest Due Date (EDD).
Introduction: Earliest Due Date is the scheduling rule, which helps to arrange the sequence in the order. Here, job with the earliest due date would be served first. Then, the process would be going on from earliest due date to latest due date.
Answer to Problem 6P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) |
| A | 14 | 20 |
| B | 10 | 16 |
| C | 7 | 15 |
| D | 6 | 17 |
Determine the sequence using EDD:
According to EDD, the job that has the earliest due date would be served first and it goes on as the due date increases. The job should be arranged based on due date. Due date should be assembled in the ascending order
Hence, the sequence of jobs using EDD is C-B-D-A.
4)
To determine: Sequence of jobs based on decision rule critical ratio.
Introduction: Critical ratio is kind of scheduling rule that helps to identify that, the task or job is on the correct track. It would help to identify if the task is behind or ahead of the schedule.
Answer to Problem 6P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) |
| A | 14 | 20 |
| B | 10 | 16 |
| C | 7 | 15 |
| D | 6 | 17 |
Determine the sequence using critical ratio:
Initial critical ratio should be determined at day 0:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Critical ratio |
| A | 14 | 20 | 1.43 |
| B | 10 | 16 | 1.6 |
| C | 7 | 15 | 2.14 |
| D | 6 | 17 | 2.83 |
Critical ratio for Job A:
It is can be determined by dividing the value attained by subtracting the completion day of previous job from the due date of current job with the processing time.
Critical ratio for Job B:
It is can be determined by dividing the value attained by subtracting the completion day of previous job from the due date of current job with the processing time.
Critical ratio for Job C:
It is can be determined by dividing the value attained by subtracting the completion day of previous job from the due date of current job with the processing time.
Critical ratio for Job D:
It is can be determined by dividing the value attained by subtracting the completion day of previous job from the due date of current job with the processing time.
Job A has the lowest critical ratio. Thus, it will be completed first. Hence, Job A would be completed first in the sequence of jobs.
Determine the critical ratio after the completion of Job A:
As the processing time of job A is 14 days, completion day of completed day would be 14.
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Critical ratio |
| A | - | - | - |
| B | 10 | 16 | 0.20 |
| C | 7 | 15 | 0.14 |
| D | 6 | 17 | 0.50 |
Critical ratio for Job B:
It is can be determined by dividing the value attained by subtracting the completion day of completed job from the due date of current job with the processing time.
Critical ratio for Job C:
It is can be determined by dividing the value attained by subtracting the completion day of completed job from the due date of current job with the processing time.
Critical ratio for Job D:
It is can be determined by dividing the value attained by subtracting the completion day of completed job from the due date of current job with the processing time.
Job C has the lowest critical ratio. Hence, Job C would be completed next in the sequence of jobs after Job A.
Determine the critical ratio after the completion of Job A and Job C:
As the processing time of job A is 14 days and Job C is 7, completion day of completed day would be 21 (14+7).
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Critical ratio |
| A | - | - | - |
| B | 10 | 16 | -0.50 |
| C | |||
| D | 6 | 17 | -0.67 |
Critical ratio for Job B:
It is can be determined by dividing the value attained by subtracting the completion day of completed job from the due date of current job with the processing time.
Critical ratio for Job D:
It is can be determined by dividing the value attained by subtracting the completion day of completed job from the due date of current job with the processing time.
Job D has the lowest critical ratio. Hence, Job D would be completed next in the sequence of jobs after Job A and Job C.
As Job B is the remaining job, it will be completed next.
Hence, the sequence of jobs using critical ratio is A-C-D-B.
b)
To determine: Average flow time, average tardiness, and average number of jobs for each method.
Introduction: Rules that are framed for providing the order in which the jobs need to be performed are termed as priority rules. These rules are more suitable for process-oriented facilities. The main purpose of priority rules are on-time completion of jobs, efficient utilization of services, and the maximizing the customer services.
Answer to Problem 6P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) |
| A | 14 | 20 |
| B | 10 | 16 |
| C | 7 | 15 |
| D | 6 | 17 |
First Come First Served:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Flow time | Tardiness |
| A | 14 | 20 | 14 | 0 |
| B | 10 | 16 | 24 | 8 |
| C | 7 | 15 | 31 | 16 |
| D | 6 | 17 | 37 | 20 |
| Total | 37 | 68 | 106 | 44 |
| Average | 9.3 | 17.0 | 26.5 | 11.0 |
Supporting calculation:
Processing time and due date are given for each job. Flow time is the cumulative of the processing time.
Tardiness of Job A:
Flow time of Job A is less than its respective due date. Hence, there would be no tardiness.
Tardiness of Job B:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job B is 8.
Tardiness of Job C:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job C is 16.
Tardiness of Job D:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job D is 20.
Average flow time:
It is calculated by dividing the total flow time and number of jobs.
Hence, average flow time is 26.5 days.
Average tardiness:
It is calculated by dividing the total tardiness and number of jobs.
Hence, average tardiness is 11.0 days
Average number of jobs:
It can be determined by dividing the total flow time and total processing time.
Hence, average number of jobs is 2.86 jobs.
Shortest processing time:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Flow time | Tardiness |
| D | 6 | 17 | 6 | |
| C | 7 | 15 | 13 | |
| B | 10 | 16 | 23 | 7 |
| A | 14 | 20 | 37 | 17 |
| Total | 37 | 68 | 79 | 24 |
| Average | 9.3 | 17.0 | 19.8 | 12.0 |
Supporting calculation:
Processing time and due date are given for each job. Flow time is the cumulative of the processing time.
Tardiness of Job D and Job C:
Flow time of Job D and Job C is less than its respective due date. Hence, there would be no tardiness.
Tardiness of Job B:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job B is 7.
Tardiness of Job A:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job A is 17.
Average flow time:
It is calculated by dividing the total flow time and number of jobs.
Hence, average flow time is 19.75 days.
Average tardiness:
It is calculated by dividing the total tardiness and number of jobs.
Hence, average tardiness is 6.0 days
Average number of jobs:
It can be determined by dividing the total flow time and total processing time.
Hence, average number of jobs is 2.14 jobs.
Earliest Due Date:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Flow time | Tardiness |
| C | 7 | 15 | 7 | |
| B | 10 | 16 | 17 | 1 |
| D | 6 | 17 | 23 | 6 |
| A | 14 | 20 | 37 | 17 |
| Total | 37 | 68 | 84 | 24 |
| Average | 9.3 | 17.0 | 21.0 | 8.0 |
Supporting calculation:
Processing time and due date are given for each job. Flow time is the cumulative of the processing time.
Tardiness of Job C:
Flow time of Job C is less than its respective due date. Hence, there would be no tardiness.
Tardiness of Job B:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job B is 1.
Tardiness of Job D:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job D is 6.
Tardiness of Job A:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job A is 17.
Average flow time:
It is calculated by dividing the total flow time and number of jobs.
Hence, average flow time is 21.00 days.
Average tardiness:
It is calculated by dividing the total tardiness and number of jobs.
Hence, average tardiness is 6.0 days
Average number of jobs:
It can be determined by dividing the total flow time and total processing time.
Hence, average number of jobs is 2.27 jobs.
Critical ratio:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Flow time | Tardiness |
| A | 14 | 20 | 14 | 0 |
| C | 7 | 15 | 21 | 6 |
| D | 6 | 17 | 27 | 10 |
| B | 10 | 16 | 37 | 21 |
| Total | 37 | 68 | 99 | 37 |
| Average | 9.3 | 17.0 | 24.8 | 9.3 |
Supporting calculation:
Processing time and due date are given for each job. Flow time is the cumulative of the processing time.
Tardiness of Job A:
Flow time of Job A is less than its respective due date. Hence, there would be no tardiness.
Tardiness of Job C:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job C is 6.
Tardiness of Job D:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job D is 10.
Tardiness of Job B:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job B is 21.
Average flow time:
It is calculated by dividing the total flow time and number of jobs.
Hence, average flow time is 24.75 days.
Average tardiness:
It is calculated by dividing the total tardiness and number of jobs.
Hence, average tardiness is 9.25 days
Average number of jobs:
It can be determined by dividing the total flow time and total processing time.
Hence, average number of jobs is 2.68 jobs.
c)
To determine: The method which is superior to others.
Introduction: Rules that are framed for providing the order in which the jobs need to be performed are termed as priority rules. These rules are more suitable for process-oriented facilities. The main purpose of priority rules are on-time completion of jobs, efficient utilization of services, and the maximizing the customer services.
Answer to Problem 6P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) |
| A | 14 | 20 |
| B | 10 | 16 |
| C | 7 | 15 |
| D | 6 | 17 |
Determine the method which is superior to other:
Shortest Processing Time (SPT) is the method which is superior to other, as it is the method which would provide lowest value when compare to others.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Loose-leaf for Operations Management (The Mcgraw-hill Series in Operations and Decision Sciences)
- in the MABE: learning to be multinational case report, what is the reccomended course of action?arrow_forwardIn the MABE case report what would be the reccomened course of action?arrow_forwardQuestion 6. An electrical engineering company is designing two types of solar panel systems: Standard Panels (S) and High-Efficiency Panels (H). The company has certain constraints regarding the hours of labor and material available for production each week. Each Standard Panel requires 4 hours of labor and 2 units of material and each High-Efficiency Panel requires 3 hours of labor and 5 units of material. The company has a maximum of 60 hours of labor and 40 units of material available per week. The profit from each Standard Panel is GH¢80, and the profit from each High-Efficiency Panel is GH¢100. The company wants to determine how many of each type of panel to produce in order to maximize profit. i) Solve this LPP by using graphical analysis ii) What will be the slack at the optimal solution point? Show calculation.arrow_forward
- qusestion 6. An electrical engineering company is designing two types of solar panel systems: Standard Panels (S) and High-Efficiency Panels (H). The company has certain constraints regarding the hours of labor and material available for production each week. Each Standard Panel requires 4 hours of labor and 2 units of material and each High-Efficiency Panel requires 3 hours of labor and 5 units of material. The company has a maximum of 60 hours of labor and 40 units of material available per week. The profit from each Standard Panel is GH¢80, and the profit from each High-Efficiency Panel is GH¢100. The company wants to determine how many of each type of panel to produce in order to maximize profit. i. Formulate a linear programming model of the problem for the company. ii Convert the linear programming model formulated in (a) to a standard form.arrow_forwardG ווח >>> Mind Tap Cengage Learning 1- CENGAGE MINDTAP Chapter 09 Excel Activity: Exponential Smoothing Question 1 3.33/10 e Submit 自 A ng.cengage.com C Excel Online Student Work G A retail store records customer demand during each sales period. 1. What is the f... Q Search this course ? ✓ Co Excel Online Tutorial Excel Online Activity: Exponential Smoothing A-Z A retail store records customer demand during each sales period. The data has been collected in the Microsoft Excel Online file below. Use the Microsoft Excel Online file below to develop the single exponential smoothing forecast and answer the following questions. Office Video X Open spreadsheet Questions 1. What is the forecast for the 13th period based on the single exponential smoothing? Round your answer to two decimal places. 25.10 2. What is the MSE for the single exponential smoothing forecast? Round your answer to two decimal places. 21.88 Activity Frame ? 3. Choose the correct graph for the single exponential…arrow_forwardNot use ai pleasearrow_forward
- Items removed from the work area (5S) were taken to a storage area called ___________. Choose from: SORT, STORD, KNUJ, STUFF, FUDG SORT STORD KNUJ STUFF FUDGarrow_forwardCould you please help explain How was the poor strategic decisions lead to economic downturns of Circuit City Company? What are the sequences of key events and problems that contribute to its collapse. Could you please explain each one them and give the examples If Circuit City would apply Lean Six Sigma. would it helped prevent businesses from collapsed?? How Qualitative and quantitative Research Methodology in Case Study Research would affect Circuit City?arrow_forwardApple is a global technology company renowned for its innovation and design. To create its products, Apple has established a world class global supply chain to bring their products to market. What strategies is Apple using to source and manufacture its products? How does Apple view its responsibility to its suppliers and those who build its products?arrow_forward
- Critical Path Method (CPM) is an important Project Management Tool that has wide industry application in modern day Project Management. By using an example of the project of your choice, critically examine the practical application of CPM as a Project Management Tool.arrow_forwardwhat is an other difination for principle?arrow_forwardNeed help or ideas to design out two slides as my script and writing quite long to squeese into two slides. But can just point form in slides with correct title and a good script for me to present two slides in only 2.5 mins. Following is my draft, pls guide me step by step on powerpoint creation and good script to present findings. My draft: Slide 1: Foreign Labor Exploitation in Dyson's Supply Chain Introduction Dyson's former Malaysian supplier, ATA IMS Bhd, became embroiled in serious labor exploitation allegations in 2021. These concerns surfaced when whistleblowers exposed unethical labor practices affecting migrant workers, primarily from Nepal and Bangladesh. Key Forms of Exploitation Debt Bondage Due to Recruitment Fees Workers were forced to pay exorbitant recruitment fees before securing employment, often taking loans at high interest rates. This financial burden trapped them in debt bondage, leaving them with little choice but to accept exploitative working…arrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing

