
(a) Obtain y, z, h, and t parameters for the network shown in Fig. 16.67 using either the defining equations or mesh/nodal equations. (b) Verify your answers using the relationships in Table 16.1.
(a)
The
Answer to Problem 59E
The
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
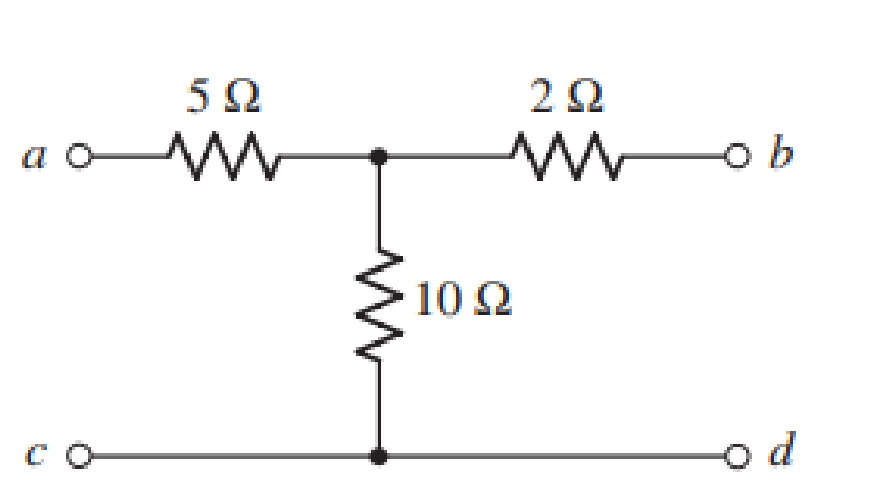
The given diagram is shown in Figure 1.
Calculation:
Mark the branch currents and open circuit voltages.
The required diagram is shown in Figure 2.
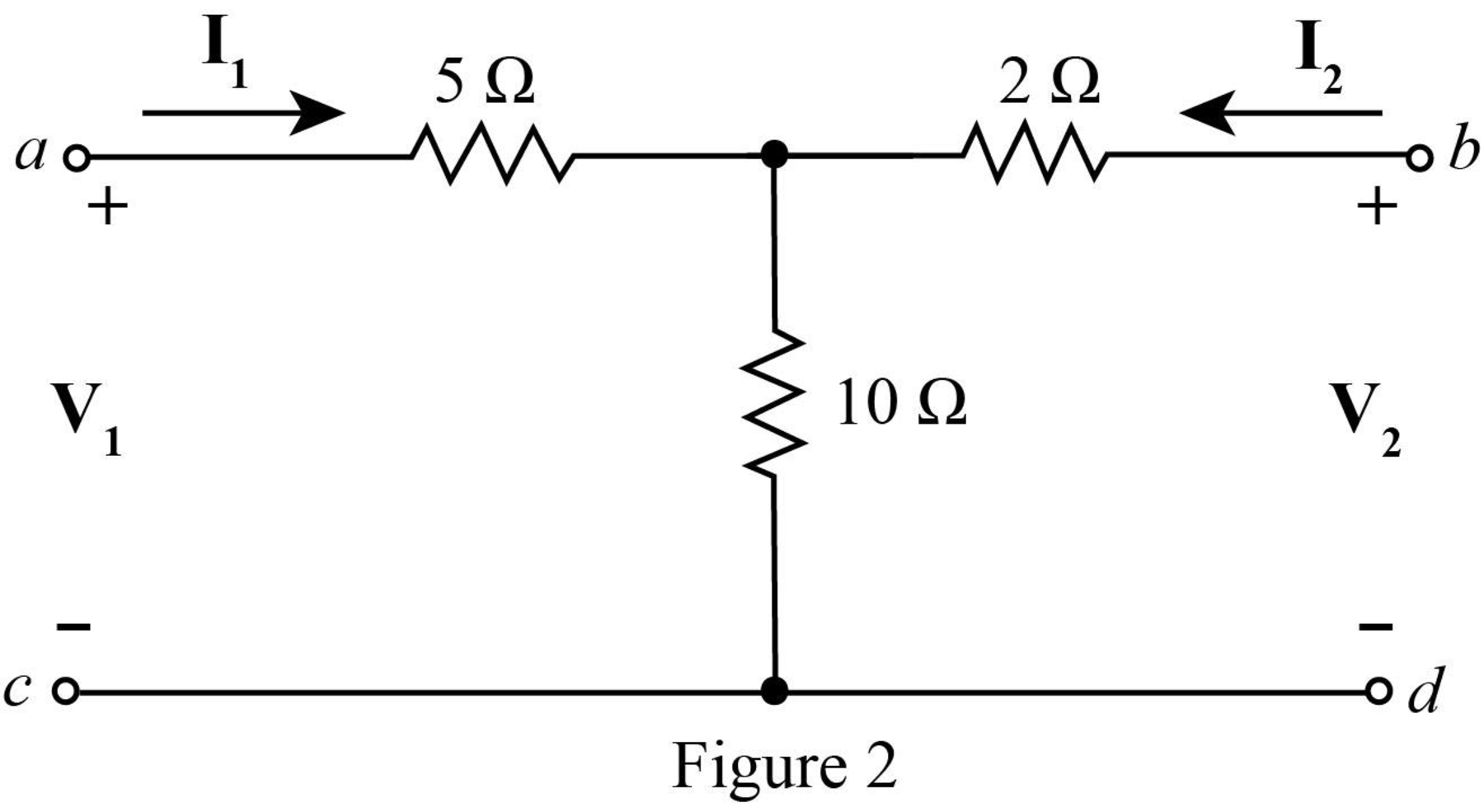
Apply KVL at the input side.
Apply KVL at the output side.
The standard equations for
Compare equation (1) with equation (3).
Compare equation (2) with equation (4).
The
Substitute
Rearrange equation (1) as,
Rearrange equation (2) as,
Substitute
Substitute
The standard equations for
Compare equation (7) with equation (9).
Compare equation (8) with equation (10).
The
Substitute
Substitute
The standard equations for
Compare equation (11) with equation (12).
Compare equation (6) with equation (13).
The
Substitute
Rearrange equation (6) as,
Substitute
The standard equations for
Compare equation (15) with equation (16).
Compare equation (14) with equation (17).
The
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the
(b)
To verify: The value of
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The relation between
The determinant
Substitute
The relation between
Substitute
The relation between
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, within the limits of error the value of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Engineering Circuit Analysis Format: Loose-leaf
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
HEAT+MASS TRANSFER:FUND.+APPL.
- 5.25. Determine the corner frequency resulting from Cin in Fig. 5.47(d). For simplicity, assume C₁ is a short circuit. TVDD C₁ M2 RF Vin H w - Vout Cin M₁arrow_forwardIn the below circuit, find out the value of equivalent Thevenin's voltage and Thevenin's resistance at the terminal. 2000 0.25 A 400 2 800 2 0.1 Aarrow_forwardQ1: For the circuit shown in Figure-1, (a) Calculate the equivalent resistance of the circuit, RAB at the terminals A and B. [10] (b) When 50V dc source is switched at terminals A-B, solve for the voltage V₁ at the location shown. [10] 50V www 12Ω 10Ω 5Ω www www A + B 200 Figure-1 www 10Ω ww 25Ω 100arrow_forward
- a. Write a PLC ladder diagram that allows the teacher to teach AND, OR, and XOR logic gates through using three PLC's digital input points and only one digital output point.arrow_forwardrately by PRACTICE 4.2 For the circuit of Fig. 4.5, compute the voltage across each curren source. 202 ww 3A 30 ww 4Ω S 50 www Reference node FIGURE 4.5 Ans: V3A =5.235 V; 7A = 11.47 V. 7 Aarrow_forwardQ2) a) design and show me your steps to convert the following signal from continuous form to digital form: s(t)=3sin(3πt) -1 373 Colesarrow_forward
- A sequence is defined by the relationship r[n] = [h[m]h[n+m]=hn*h-n where h[n] is a minimum-phase sequence and r[n]= 4 4 (u[n]+ 12" [n-1] 3 (a) Find R(z) and sketch the pole-zero diagram. (b) Determine the minimum-phase sequence h[n] to within a scale factor of ±1. Also, determine the z-transform H(z) of h[n].arrow_forwardusıng j-k and D flipflop design a counter that counts 0,2,1 again as shown below ın the tablearrow_forwardfind the minterms of the followıng boolean expressıon desıgn F's cırcuit using one of the approciate decoders given below and a NOR gateF(A,B,C,D)=(A+'BC)(B 'C+'A 'D + CD)arrow_forward
 Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course ...Electrical EngineeringISBN:9781305632134Author:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. SarmaPublisher:Cengage Learning
Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course ...Electrical EngineeringISBN:9781305632134Author:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. SarmaPublisher:Cengage Learning
