
Concept explainers
Write chemical equations, showing all necessary reagents, for the preparation of
by each of the following methods:
Hydroboration–oxidation of an
Use of a Grignard reagent
Use of a Grignard reagent in a way different from part (b)
Reduction of a
Hydrogenation of an
Reduction with sodium borohydride
Interpretation:
The chemical equations showing all necessary reagents for the preparation of
Concept introduction:
Hydroboration-oxidation of an alkene results in overall addition of water molecule across the double bond with a regioselectivity opposite to that of Markovnikov’s rule.
In the overall reaction, a hydrogen atom gets attached to the double bonded carbon atom having fewer hydrogens and the hydroxyl group gets attached to the carbon atom having greater number of hydrogens.
When a Grignard reagent reacts with formaldehyde primary alcohols are produced.
Grignard reagents are nucleophilic and react with oxiranes producing alcohols.
Aldehydes are reduced to the corresponding primary alcohols by using
By a suitable reducing agent like lithium aluminum hydride, carboxylic acids are reduced to the corresponding primary alcohols.
Answer to Problem 16P
Solution:
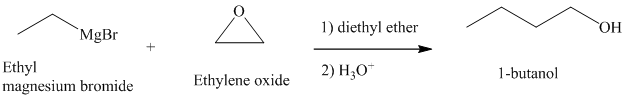

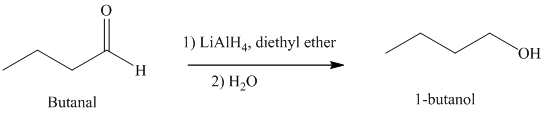
Explanation of Solution
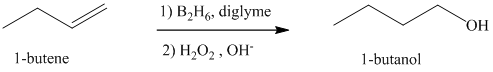
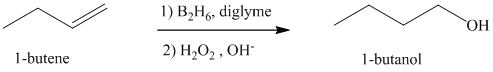
a) Hydroboration-oxidation of an alkene to form
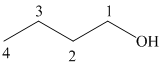
The structure of
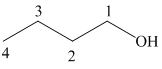
The hydroxyl group is attached to the C1 carbon atom. This alcohol is produced by hydroboration-oxidaton of an alkene. So in the alkene, the C1 carbon atom must be double bonded to the the C2 carbon atom. Thus, the alkene must be
The regioselectivity of hydroboration-oxidation is such that the hydrogen atom will get attached to the C2 carbon atom while the hydroxyl group will get attached to the C1 carbon atom producing
The reaction is shown below:
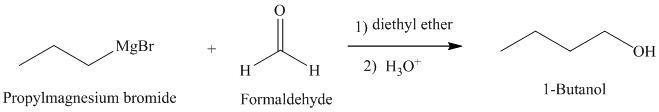
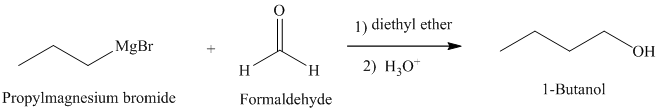
b) Grignard reagent is used to prepare
The structure of
Grignard reagents are nucleophilic and react with carbonyl groups forming a new carbon-carbon bond. An aqueous acid is used to convert the intermediate alkoxy ion to the corresponding alcohol.
In
The reaction is shown below:
c) Different Grignard reagent is used to prepare
The structure of
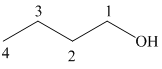
It is a primary alcohol. The hydroxyl group is attached to the C1 carbon atom.
Grignard reagents reacts with ethylene oxide to produce primary alcohol containing two more carbon atoms than the alkyl halide.
Thus, ethyl magnesium bromide, upon reaction with ethylene oxide, will produce
The reaction is shown below:
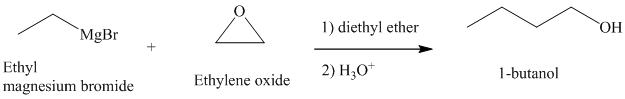
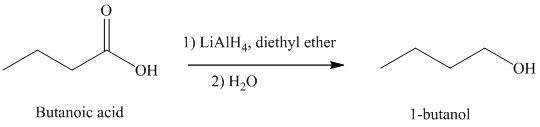
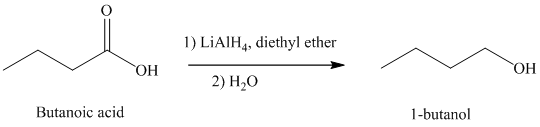
d) The reduction of carboxylic acid to produce

Carboxylic acids, upon reduction, produce the correspionding primary alcohols.
Thus, reduction of butanoic acid with Lithium aluminum hydride will produce
The reaction is shown below:
e) Hydrogenation of an aldehyde to form

Reduction of aldehydes with a suitable reducing agent produces the corresponding primary alcohols.
Thus, reduction of butanal in the presence of Lithium aluminum hydride will produce
The reaction is shown below:
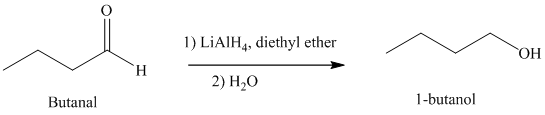
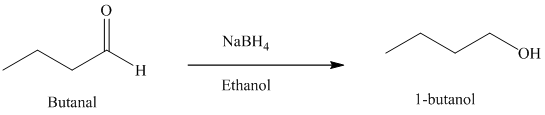
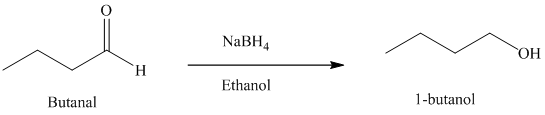
f) Reduction of an aldehyde to form

Sodium borohydride is used for the reduction of aldehydes and ketones to primary and secondary alcohols respectively.
Thus, reduction of butanal with sodium borohydride will produce
The reaction is shown below:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Organic Chemistry - Standalone book
- Question 11 of 18 (1 point) Question Attempt: 3 of How many signals do you expect in the 'H NMR spectrum for this molecule? Br Br Write the answer below. Also, in each of the drawing areas below is a copy of the molecule, with Hs shown. In each copy, one of the H atoms is colored red. Highlight in red all other H atoms that would contribute to the same signal as the H already highlighted red. Note for advanced students: In this question, any multiplet is counted as one signal. Number of signals in the 'H NMR spectrum. 1 For the molecule in the top drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red. If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box at right. No additional Hs to color in top molecule Check For the molecule in the bottom drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red. If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box…arrow_forwardOrganic Chemistry Esterification reactions 1. Write the steps to prepare ester. 2. Write complete reaction of ethanol and acetic acid to make ester. 3. What does ester smell like? What are the uses of ester. 4. What the role of sulfuric acid in the esterification reactionarrow_forward11. Complete the following esterification reaction with names of all the reactants and products under. Hint: Remove the water and end up with ester R-C-OH + ROH R-C-OR + H₂O A carboxylic acid An alcohol An ester Water BYJU'S H-C-C O-H Нин C-C-C-H HAAA H O-C-C-C-H AAA Ethanoic acid Propanol Water Propyl ethanoate By com CH3COOH + CH3CH2CH2CH₂CH₂OH → Practice for alcohols aldehydes and ketones: 12. Draw the structures from the following names mixed of alcohol/aldehyde and ketone: a. 4-methyl cyclohexanone b. 3-methyl-2-pentenal c. 2,3-dimethylcyclohexanone d. 1,3propanediol or Propane 1,3 diol 13. Write systematic names for the following compounds identify functional group: a. b. (CH3)2CH-C OH c) CH(CH₂)-- OH -,-,arrow_forward
- may you please show all steps! i am having a hard time understanding and applying in this format, thank you!arrow_forward10. Complete the substitution reaction of 2 pentanol with these reagents. Reagents & Reaction Conditions use practice sheet. Please write only major products, minor product like water, other gases are not required. Hint: In substitution of alcohol, we generally substitute OH group with Halogens like cl, Br, F using some reagent containing halogens. Ensure to add halogens to the same carbon number where you are removing OH from Examples Alcohols can be converted to Alkyl Halides with HX acids HBr H₂O HCI + H₂O HI + H₂O CH,CH₂OH + SOCI₂ CH,CH₂OH + PCI₁₂ A BBYJU'S CH CHCI + SO₂+ HCI CH₂CH CIP(OH), + HCI CH,CH₂OH + PCI CHCHCI + POCI + HCI CH,CH₂OH + PBr, CH,CH,Br + P(OH), + HBr 1. Reaction with HBr with 2 Pentanol 2.Reaction with HI with 2 pentanol © Byjus.com 3.Reaction with HCI+ZnCl,, with 2 pentanol (Zncl2 is catalyst no role) 4.Reaction with SOCI,, with 2 Pentanol 5.Reaction with PBr; or PCl, with 2 pentanolarrow_forward3. Is 2-methyl-2-propanol a primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol? Write out the structures of 2-methyl-2-propanol and also any oxidation products of 2- methyl-2- propanol. If there is more than one oxidation product, give the structure of each of the products. 4. 2-Propanol is the IUPAC systematic name of this alcohol. It has a common name by which it is much better known (You'll see it in the grocery store or pharmacy). Give that common name 5. Aldehydes can be synthesized by the oxidation of. Please choose from below choices A. Primary alcohols B. Secondary alcohols C. Organic acids D. Inorganic acids 6. Tertiary alcohol Can undergo oxidation. yes or no. ? If yes then answer the product.arrow_forward
- Finish the reactions hand written pleasearrow_forwardPart A Identify each alcohol as primary, secondary, or tertiary Drag the appropriate items to their respective bins. CH₂ H₂C- -C-OH HO CH₂ Primary Он OH CH₂ OH CCH₂OH CH₂ сн Secondary Tertiary Reset Help CH,CH₂ (CH)CHCH,OH CH,CH,CH,CCH, CHOH CH₂ Different types of alcohol groups Alcohol and its reaction: 8. Combing two alcohol molecules below and completing the reaction with Product .( Hint Reaction called etherification as ether is formed and name the ether once you complete the reaction. Hint.: R-O-H+H-O-RR-O-R Do the reaction: CH₂OH + CH₂OH---→ + H-O-H 9. Write the reaction of formation of alcohol from alkene by adding water: Addition reaction also called hydration reaction as we are adding water which occur always in presence of acid Hint: Break the double bond and add H and OH if symmetrical then add anywhere if unsymmetrical then follow Markovnikov rule H should go to that double bone carbon which has more hydrogen CH2=CH2 + H₂O-→arrow_forwardComplete the reaction hand written pleasearrow_forward
- Predict the major products of this organic reaction: HBr (1 equiv) cold ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of this reaction in the drawing area below. • You can draw the products in any arrangement you like. • Pay careful attention to the reaction conditions, and only include the major products. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. • Note that there is only 1 equivalent of HBr reactant, so you need not consider the case of multiple additions. dm Re Explanation Check ©2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Termarrow_forwardb) Use curved arrows to show the reaction of the radical with hydrogen bromide. Br: Br H .. Answer Bankarrow_forwardIndicate the reaction products when CH3COCH2COOCH2COOC2H5 (ethyl acetoacetoacetate) reacts with 1º OH-/H2O and 2º H3O+arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning


