
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The complete equation for the reaction between an acid chloride and ammonia is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
In secondary amines, two of the hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
In tertiary amines, all hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
Answer to Problem 16.25E
The complete reaction between an acid chloride and ammonia is given below.
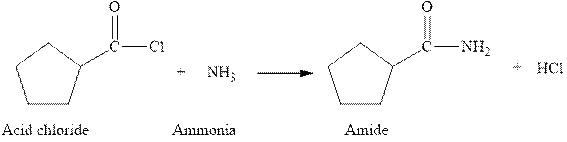
Explanation of Solution
The reaction between an acid chloride and ammonia gives amide and hydrochloric acid. This happens by the attack of lone pair of electrons of nitrogen in ammonia on the carbonyl carbon of acid chloride. The intermediate then rearranges to give amide and hydrochloric acid.
The complete reaction between an acid chloride and ammonia is given below.

Figure 1
The complete reaction between an acid chloride and ammonia is shown in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation:
The complete equation for the reaction between an amine and
Concept introduction:
Amines are nitrogen-containing organic compounds. The general formula of amines is
In secondary amines, two of the hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
In tertiary amines, all hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
Answer to Problem 16.25E
The complete reaction between an amine and carboxylic acid is given below.
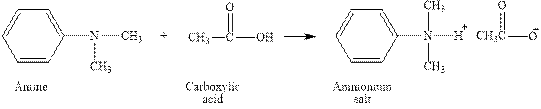
Explanation of Solution
The reaction between an amine and carboxylic acid gives ammonium salt of carboxylic acid. This happens by the abstraction of proton by lone pair of electrons of nitrogen in amine from the carboxylic acid. The intermediate then rearranges to give ammonium salt of carboxylic acid.
The complete reaction between an amine and carboxylic acid is given below.
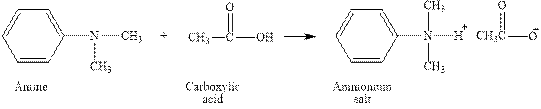
Figure 2
The complete reaction between an amine and carboxylic acid is shown in Figure 2.
(c)
Interpretation:
The complete equation for the reaction between a tertiary amine and acid chloride is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Amines are nitrogen-containing organic compounds. The general formula of amines is
In secondary amines, two of the hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
In tertiary amines, all hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
Answer to Problem 16.25E
The reaction between a tertiary amine and acid chloride does not occur and this is shown below.
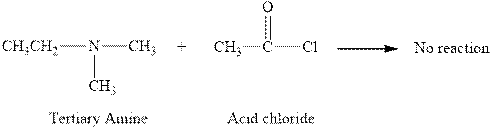
Explanation of Solution
The reaction between a tertiary amine and acid chloride does not occur. This happens due to the absence of hydrogen atom in the tertiary amine. The complete reaction between a tertiary amine and acid chloride can be written as given below.

Figure 3
The reaction between a tertiary amine and acid chloride does not occur and this is shown in Figure 3.
(d)
Interpretation:
The complete equation for the reaction between a secondary amine and hydrochloric acid is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Amines are nitrogen-containing organic compounds. The general formula of amines is
In secondary amines, two of the hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
In tertiary amines, all hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
Answer to Problem 16.25E
The complete reaction between a secondary amine and hydrochloric acid is given below.

Explanation of Solution
The reaction between a secondary amine and hydrochloric acid gives salt of amine. This happens by the abstraction of proton by lone pair of electrons of nitrogen in amine from the hydrochloric acid. The intermediate then rearranges to give salt of amine.
The complete reaction between a secondary amine and hydrochloric acid is given below.

Figure 4
The complete reaction between a secondary amine and hydrochloric acid is shown in Figure 4.
(e)
Interpretation:
The complete equation for the reaction between a secondary amine and water is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Amines are nitrogen-containing organic compounds. The general formula of amines is
In secondary amines, two of the hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
In tertiary amines, all hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
Answer to Problem 16.25E
The complete reaction between a secondary amine and water is given below.
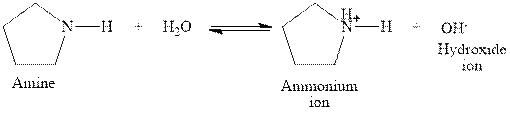
Explanation of Solution
The reaction between a secondary amine and water gives ammonium ion and hydroxide ion. This happens by the abstraction of proton by lone pair of electrons of nitrogen in amine from the water. The intermediate then rearranges to give ammonium ion and hydroxide ion.
The complete reaction between a secondary amine and water is given below.

Figure 5
The complete reaction between a secondary amine and water is shown in Figure 5.
(f)
Interpretation:
The complete equation for the reaction between an amine salt and sodium hydroxide is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Amines are nitrogen-containing organic compounds. The general formula of amines is
In secondary amines, two of the hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
In tertiary amines, all hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
Answer to Problem 16.25E
The complete reaction between an amine salt and sodium hydroxide is given below.
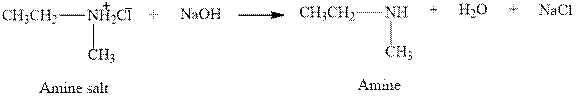
Explanation of Solution
The reaction between an amine salt and sodium hydroxide gives amine, water and sodium chloride. This happens by the abstraction of proton by lone pair of electrons of oxygen in sodium hydroxide from the amine salt. The intermediate then rearranges to give amine, water and sodium chloride.
The complete reaction between an amine salt and sodium hydroxide is given below.
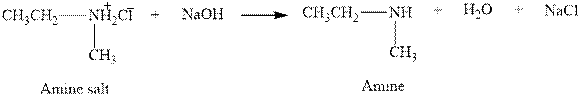
Figure 6
The complete reaction between an amine salt and sodium hydroxide is shown in Figure 6.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Chemistry For Today: General, Organic, And Biochemistry, Loose-leaf Version
- Show work with explanation needed. Don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forwardA Elschboard Part of SpeechT-D Alt Leaming App app.aktiv.com Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided resonance structures, draw the curved electron- pushing arrows to show the interconversion between resonance hybrid contributors. Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. Include all lone pairs and formal charges in the structures. Problem 45 of 10 I Select to Add Arrows N Please selarrow_forwardSo I'm working on molecular geometry. Can you help me with this stuff here and create three circles: one that's 120, one that’s 180, and one that’s 109.5?arrow_forward
- Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. Problem 164 of N Select to Add Arrows CHI CH 1 1 1 Parrow_forwardusing these can you help me , I guess convert them to lewis dit structures or full drawn out skeletal and I guess is that what would help me depict the bond angle.arrow_forwardShow reaction mechanism with explanation.don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forward
- Please answer the questions and provide detailed explanations.arrow_forwardShow reaction mechanism. Don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forwardPlease answer the questions and provide detailed explanation. Please also include the Hydrogens that are on the molecule to show how many signals there are.arrow_forward
- Capp aktiv.com Part of Speech Table for Assi x Aktiv Learning App K Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. Problem 232 of 10 10: Mg Select to Add Arrows Br O H :0 CI:O H Mg THE + dy Undo Reset Done Brarrow_forwardPlease answer the question and provide a detailed drawing of the structure. If there will not be a new C – C bond, then the box under the drawing area will be checked. Will the following reaction make a molecule with a new C – C bond as its major product: Draw the major organic product or products, if the reaction will work. Be sure you use wedge and dash bonds if necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry.arrow_forwardNeed help with witharrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning

