
Concept explainers
A foreman has determined processing times at a work center for a set of jobs and now wants to sequence them. Given the information shown, do the following:
a. Determine the processing sequence using (1) FCFS, (2) SPT, (3) EDD, and (4) CR. For each sequence, compute the average job tardiness, the average flow time, and the average number of jobs at the work center. The list is in FCFS order.
b. Using the results of your calculations in part a, show that the ratio of average flow time and the average number of jobs measures are equivalent for all four sequencing rules.
c. Determine the processing sequence that would result using the S/O rule.
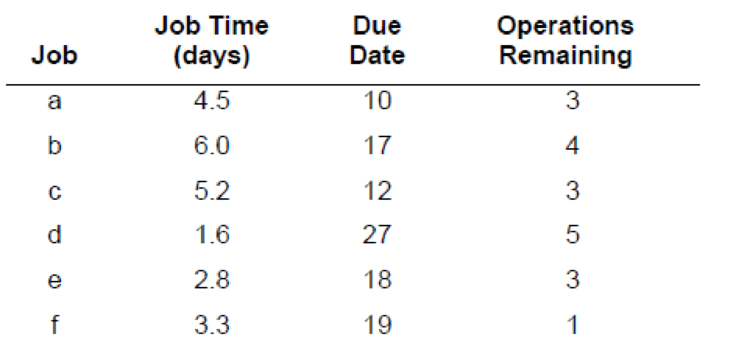
a)
1)
To determine: The processing sequence based on First Come First Served (FCFS).
Introduction: First Come First Served is the scheduling rule, which helps to arrange the sequence in the order. Here, the first come would be served first.
Answer to Problem 15P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Remaining number of operations |
| a | 4.5 | 10 | 3 |
| b | 6 | 17 | 4 |
| c | 5.2 | 12 | 3 |
| d | 1.6 | 27 | 5 |
| e | 2.8 | 18 | 3 |
| f | 3.3 | 19 | 1 |
Determine the sequence using FCFS:
According to FCFS, the first come would be served first. Hence, the jobs should be sequenced in the order as per its arrival.
Hence, the sequence of jobs using FCFS is a-b-c-d-e-f.
Determine average flow time, average tardiness, and average number of jobs for FCFS:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Flow time (days) | Due date (days) | Tardiness |
| a | 4.5 | 4.5 | 10 | 0 |
| b | 6 | 10.5 | 17 | 0 |
| c | 5.2 | 15.7 | 12 | 3.7 |
| d | 1.6 | 17.3 | 27 | 0 |
| e | 2.8 | 20.1 | 18 | 2.1 |
| f | 3.3 | 23.4 | 19 | 4.4 |
| Total | 23.4 | 91.5 | 10.2 |
Supporting calculation:
Processing time and due date are given for each job. Flow time is the cumulative of the processing time.
Tardiness of Job a:
Flowtime is less than the due date. Hence, there would be tardiness.
Tardiness of Job b:
Flowtime is less than the due date. Hence, there would be tardiness.
Tardiness of Job c:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job c is 3.7.
Note: The procedure continues for all the jobs.
Average flow time:
It is calculated by dividing the total flow time and number of jobs.
Hence, average flow time is 15.25 days.
Average tardiness:
It is calculated by dividing the total tardiness and number of jobs.
Hence, average tardiness is 1.7 days.
Average number of jobs:
It can be determined by dividing the total flow time and total processing time.
Hence, average number of jobs is 3.9 jobs.
1)
To determine: The processing sequence based on First Come First Served (FCFS).
Introduction: First Come First Served is the scheduling rule, which helps to arrange the sequence in the order. Here, the first come would be served first.
Answer to Problem 15P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Remaining number of operations |
| a | 4.5 | 10 | 3 |
| b | 6 | 17 | 4 |
| c | 5.2 | 12 | 3 |
| d | 1.6 | 27 | 5 |
| e | 2.8 | 18 | 3 |
| f | 3.3 | 19 | 1 |
Determine the sequence using FCFS:
According to FCFS, the first come would be served first. Hence, the jobs should be sequenced in the order as per its arrival.
Hence, the sequence of jobs using FCFS is a-b-c-d-e-f.
Determine average flow time, average tardiness, and average number of jobs for FCFS:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Flow time (days) | Due date (days) | Tardiness |
| a | 4.5 | 4.5 | 10 | 0 |
| b | 6 | 10.5 | 17 | 0 |
| c | 5.2 | 15.7 | 12 | 3.7 |
| d | 1.6 | 17.3 | 27 | 0 |
| e | 2.8 | 20.1 | 18 | 2.1 |
| f | 3.3 | 23.4 | 19 | 4.4 |
| Total | 23.4 | 91.5 | 10.2 |
Supporting calculation:
Processing time and due date are given for each job. Flow time is the cumulative of the processing time.
Tardiness of Job a:
Flowtime is less than the due date. Hence, there would be tardiness.
Tardiness of Job b:
Flowtime is less than the due date. Hence, there would be tardiness.
Tardiness of Job c:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job c is 3.7.
Note: The procedure continues for all the jobs.
Average flow time:
It is calculated by dividing the total flow time and number of jobs.
Hence, average flow time is 15.25 days.
Average tardiness:
It is calculated by dividing the total tardiness and number of jobs.
Hence, average tardiness is 1.7 days.
Average number of jobs:
It can be determined by dividing the total flow time and total processing time.
Hence, average number of jobs is 3.9 jobs.
2)
To determine: Sequence of jobs based on decision rule Shortest Processing Time (SPT).
Introduction: Shortest Processing Tine is the scheduling rule, which helps to arrange the sequence in the order. Here, job with the shortest duration would be served first. Then, the process would be going on from shortest to largest duration.
Answer to Problem 15P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Remaining number of operations |
| a | 4.5 | 10 | 3 |
| b | 6 | 17 | 4 |
| c | 5.2 | 12 | 3 |
| d | 1.6 | 27 | 5 |
| e | 2.8 | 18 | 3 |
| f | 3.3 | 19 | 1 |
Determine the sequence using SPT:
According to SPT, the job that has the shortest processing would be served first and it goes on as the processing time increase. Duration should be assembled in the ascending order
Hence, the sequence of jobs using SPT is d-e-f-a-c-b.
Determine average flow time, average tardiness, and average number of jobs for SPT:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Flow time (days) | Due date (days) | Tardiness |
| d | 1.6 | 1.6 | 27 | |
| e | 2.8 | 4.4 | 18 | |
| f | 3.3 | 7.7 | 19 | |
| a | 4.5 | 12.2 | 10 | 2.2 |
| c | 5.2 | 17.4 | 12 | 5.4 |
| b | 6 | 23.4 | 17 | 6.4 |
| Total | 23.4 | 66.7 | 14 |
Supporting calculation:
Processing time and due date are given for each job. Flow time is the cumulative of the processing time.
Tardiness of Job d, Job e, and Job f:
Flow time of Job d, Job e, and Job f is less than its respective due date. Hence, there would be no tardiness.
Tardiness of Job a:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job a is 2.2.
Tardiness of Job c:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job c is 5.4.
Tardiness of Job b:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job b is 6.4.
Average flow time:
It is calculated by dividing the total flow time and number of jobs.
Hence, average flow time is 11.12 days.
Average tardiness:
It is calculated by dividing the total tardiness and number of jobs.
Hence, average tardiness is 2.33 days.
Average number of jobs:
It can be determined by dividing the total flow time and total processing time.
Hence, average number of jobs is 2.85 jobs.
3)
To determine: Sequence of jobs based on decision rule Earliest Due Date (EDD).
Introduction: Earliest Due Date is the scheduling rule, which helps to arrange the sequence in the order. Here, job with the earliest due date would be served first. Then, the process would be going on from earliest due date to latest due date.
Answer to Problem 15P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Remaining number of operations |
| a | 4.5 | 10 | 3 |
| b | 6 | 17 | 4 |
| c | 5.2 | 12 | 3 |
| d | 1.6 | 27 | 5 |
| e | 2.8 | 18 | 3 |
| f | 3.3 | 19 | 1 |
Determine the sequence using EDD:
According to EDD, the job that has the earliest due date would be served first and it goes on as the due date increases. The job should be arranged based on due date. Due date should be assembled in the ascending order
Hence, the sequence of jobs using EDD is a-c-b-e-f-d.
Determine average flow time, average tardiness, and average number of jobs for EDD:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Flow time (days) | Due date (days) | Tardiness |
| a | 4.5 | 4.5 | 10 | 0 |
| c | 5.2 | 9.7 | 12 | 0 |
| b | 6 | 15.7 | 17 | 0 |
| e | 2.8 | 18.5 | 18 | 0.5 |
| f | 3.3 | 21.8 | 19 | 2.8 |
| d | 1.6 | 23.4 | 27 | 0 |
| Total | 23.4 | 93.6 | 3.3 |
Supporting calculation:
Processing time and due date are given for each job. Flow time is the cumulative of the processing time.
Tardiness of Job a, Job c, Job b, and Job d:
Flow time of Job a, Job c, Job b, and Job d is less than its respective due date. Hence, there would be no tardiness.
Tardiness of Job e:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job e is 0.5.
Tardiness of Job f:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job f is 2.8.
Average flow time:
It is calculated by dividing the total flow time and number of jobs.
Hence, average flow time is 15.6 days.
Average tardiness:
It is calculated by dividing the total tardiness and number of jobs.
Hence, average tardiness is 0.55 days.
Average number of jobs:
It can be determined by dividing the total flow time and total processing time.
Hence, average number of jobs is 4 jobs.
4)
To determine: Sequence of jobs based on decision rule critical ratio.
Introduction: Critical ratio is kind of scheduling rule that helps to identify that, the task or job is on the correct track. It would help to identify if the task is behind or ahead of the schedule.
Answer to Problem 15P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Remaining number of operations |
| a | 4.5 | 10 | 3 |
| b | 6 | 17 | 4 |
| c | 5.2 | 12 | 3 |
| d | 1.6 | 27 | 5 |
| e | 2.8 | 18 | 3 |
| f | 3.3 | 19 | 1 |
Determine the sequence using critical ratio:
Initial critical ratio should be determined at day 0:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Critical ratio |
| a | 4.5 | 10 | 2.22 |
| b | 6 | 17 | 2.83 |
| c | 5.2 | 12 | 2.31 |
| d | 1.6 | 27 | 16.88 |
| e | 2.8 | 18 | 6.43 |
| f | 3.3 | 19 | 5.76 |
Critical ratio for Job a:
It is can be determined by dividing the value attained by subtracting the completion day of previous job from the due date of current job with the processing time.
Note: Process continues for all the jobs.
Job a has the lowest critical ratio. Thus, it will be completed first. Hence, Job a would be completed first in the sequence of jobs.
Determine the critical ratio after the completion of Job a:
As the processing time of job a is 4.5 days, completion day of completed day would be 4.5.
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Critical ratio |
| a | |||
| b | 6 | 17 | 2.08 |
| c | 5.2 | 12 | 1.44 |
| d | 1.6 | 27 | 14.06 |
| e | 2.8 | 18 | 4.82 |
| f | 3.3 | 19 | 4.39 |
Critical ratio for Job b:
It is can be determined by dividing the value attained by subtracting the completion day of completed job from the due date of current job with the processing time.
Note: Process continues for all the jobs.
Job c has the lowest critical ratio. Hence, Job c would be completed next in the sequence of jobs.
Determine the critical ratio after the completion of Job a and Job c:
As the processing time of job a is 4.5 days and Job c is 5.2, completion day of completed day would be 9.7 (4.5+5.2).
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Ratio |
| a | |||
| b | 6 | 17 | 1.22 |
| c | |||
| d | 1.6 | 27 | 10.81 |
| e | 2.8 | 18 | 2.96 |
| f | 3.3 | 19 | 2.82 |
Critical ratio for Job b:
It is can be determined by dividing the value attained by subtracting the completion day of completed job from the due date of current job with the processing time.
Job b has the lowest critical ratio. Hence, Job b would be completed next in the sequence of jobs after Job a and Job c.
Determine the critical ratio after the completion of Job a, Job c and Job b:
As the processing time of job a is 4.5 days, Job b is 6.0, and Job c is 5.2 days. Completion day of completed day would be 15.7 (4.5+5.2+6).
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Ratio |
| a | |||
| b | |||
| c | |||
| d | 1.6 | 27 | 7.06 |
| e | 2.8 | 18 | 0.82 |
| f | 3.3 | 19 | 1 |
Critical ratio for Job d:
It is can be determined by dividing the value attained by subtracting the completion day of completed job from the due date of current job with the processing time.
Job e has the lowest critical ratio. Hence, Job e would be completed next in the sequence of jobs after Job a, Job c, and Job b.
Determine the critical ratio after the completion of Job a, Job c, Job b, and job e:
As the processing time of job a is 4.5 days, Job b is 6.0, Job c is 5.2 days, and job e is 2.8. Completion day of completed day would be 18.5 (4.5+5.2+6+2.8).
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Ratio |
| a | |||
| b | |||
| c | |||
| d | 1.6 | 27 | 5.31 |
| e | |||
| f | 3.3 | 19 | 0.15 |
Critical ratio for Job d:
It is can be determined by dividing the value attained by subtracting the completion day of completed job from the due date of current job with the processing time.
Job f has the lowest critical ratio. Hence, Job f would be completed next in the sequence of jobs after Job a, Job c, Job b, and Job e.
As Job d is the remaining job, it will be completed next.
Hence, the sequence of jobs using critical ratio is a-c-b-e-f-d.
Determine average flow time, average tardiness, and average number of jobs for critical ratio:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Flow time (days) | Due date (days) | Tardiness |
| a | 4.5 | 4.5 | 10 | 0 |
| c | 5.2 | 9.7 | 12 | 0 |
| b | 6 | 15.7 | 17 | 0 |
| e | 2.8 | 18.5 | 18 | 0.5 |
| f | 3.3 | 21.8 | 19 | 2.8 |
| d | 1.6 | 23.4 | 27 | 0 |
| Total | 23.4 | 93.6 | 3.3 |
Supporting calculation:
Processing time and due date are given for each job. Flow time is the cumulative of the processing time.
Tardiness of Job a, Job c, Job b, and Job d:
Flow time of Job a, Job c, Job b, and Job d is less than its respective due date. Hence, there would be no tardiness.
Tardiness of Job e:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job e is 0.5.
Tardiness of Job f:
It is calculated by subtracting the flow time of the job from the due date of the project. Hence, the lateness of Job f is 2.8.
Average flow time:
It is calculated by dividing the total flow time and number of jobs.
Hence, average flow time is 15.6 days.
Average tardiness:
It is calculated by dividing the total tardiness and number of jobs.
Hence, average tardiness is 0.55 days.
Average number of jobs:
It can be determined by dividing the total flow time and total processing time.
Hence, average number of jobs is 4 jobs.
b)
To determine: Whether the average flow time and average number of jobs are equivalent for four sequencing rules.
Introduction: Sequencing is the process of arranging the jobs in certain order in which it should be performed.
Answer to Problem 15P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date (days) | Remaining number of operations |
| a | 4.5 | 10 | 3 |
| b | 6 | 17 | 4 |
| c | 5.2 | 12 | 3 |
| d | 1.6 | 27 | 5 |
| e | 2.8 | 18 | 3 |
| f | 3.3 | 19 | 1 |
Determine whether the average flow time and average number of jobs are equivalent for four sequencing rules:
| Rule | Average flow time | Average number of jobs | Ratio |
| FCFS | 15.25 | 3.91 | 3.9 |
| SPT | 11.12 | 2.85 | 3.9 |
| EDD | 15.6 | 4 | 3.9 |
| CR | 15.6 | 4 | 3.9 |
Calculate ratio for FCFS:
It is calculated by dividing average flow time and average number of jobs.
Calculate ratio for SPT:
It is calculated by dividing average flow time and average number of jobs.
Calculate ratio for EDD:
It is calculated by dividing average flow time and average number of jobs.
Calculate ratio for CR:
It is calculated by dividing average flow time and average number of jobs.
c)
To determine: The processing sequence of the jobs using Slack per Operation (S/O) rule
Introduction: Slack per operation is a scheduling method that helps to determine the sequence of the operation. Slack is the difference between the due date and the required time to process certain job.
Answer to Problem 15P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The following information is given:
| Job | Processing time (days) | Due date | Remaining number of operations |
| a | 5 | 8 | 2 |
| b | 6 | 5 | 4 |
| c | 9 | 10 | 4 |
| d | 7 | 12 | 3 |
| e | 8 | 10 | 2 |
Determine the processing sequence of the jobs using Slack per Operation:
| Job | Job time (days) | Due date (days) | Operations remaining | Slack | Slack per operation (S/O) | Rank |
| a | 4.5 | 10 | 3 | 5.5 | 1.83 | 1 |
| b | 6 | 17 | 4 | 11 | 2.75 | 3 |
| c | 5.2 | 12 | 3 | 6.8 | 2.27 | 2 |
| d | 1.6 | 27 | 5 | 25.4 | 5.08 | 5 |
| e | 2.8 | 18 | 3 | 15.2 | 5.07 | 4 |
| f | 3.3 | 19 | 1 | 15.7 | 15.7 | 6 |
Supporting calculation:
Processing time, due date, and remaining number of operation is given. Rank should be assigned according to the slack per operation.
Calculate slack:
It can be calculated by subtracting the processing time from the due date.
Note: The process continues for all the jobs:
Calculate slack per operation:
It can be calculated by dividing the slack value and the remaining number of operations.
Note: The process continues for all the jobs:
Hence, the sequence of jobs using S/O is a-c-b-e-d-f.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Operations Management
- Please assist in writing a complete reasearch project of the following title: Title of research: Study on the impact of Technology in the Work Place.arrow_forwardIntuition is both an emotional experience and a nonconscious analytic process. One problem, however, is that not all emotions signaling that there is a problem or opportunity represent intuition. Please in your Personal opinion how we would know if our “gut feelings” are intuition or not, and if not intuition, suggest what might be causing them.arrow_forwardA coworker suggests that the company where you both work would be much more effective if there were no organizational politics. Please in your personal and detailed opinion, What would you say to this person in reply?arrow_forward
- What is a bottleneck? Would you try to reduce a bottleneck? Why or why not? Please provide a referencearrow_forwardYour firm has been the auditor of Caribild Products, a listed company, for a number of years. The engagement partner has asked you to describe the matters you would consider when planning the audit for the year ended 31January 2022. During recent visit to the company you obtained the following information: (a) The management accounts for the 10 months to 30 November 2021 show a revenue of $260 million and profit before tax of $8 million. Assume sales and profits accrue evenly throughout the year. In the year ended 31 January 2021 Caribild Products had sales of $220 million and profit before tax of $16 million. (b) The company installed a new computerised inventory control system which has operated from 1 June 2021. As the inventory control system records inventory movements and current inventory quantities, the company is proposing: (i) To use the inventory quantities on the computer to value the inventory at the year-end (ii) Not to carry out an inventory count at the year-end (c)…arrow_forwardDevelop and implement a complex and scientific project for an organisation of your choice. please include report include the following: Introduction Background research to the project The 5 basic phases in the project management process Project Initiation Project Planning Project Execution Project Monitoring and Controlling Project Closing Conclusionarrow_forward
- Not use ai pleasearrow_forwardSam's Pet Hotel operates 51 weeks per year, 6 days per week, and uses a continuous review inventory system. It purchases kitty litter for $11.00 per bag. The following information is available about these bags: > Demand 95 bags/week > Order cost $52.00/order > Annual holding cost = 25 percent of cost > Desired cycle-service level = 80 percent >Lead time 4 weeks (24 working days) > Standard deviation of weekly demand = 15 bags > Current on-hand inventory is 320 bags, with no open orders or backorders. a. Suppose that the weekly demand forecast of 95 bags is incorrect and actual demand averages only 75 bags per week. How much higher will total costs be, owing to the distorted EOQ caused by this forecast error? The costs will be $ higher owing to the error in EOQ. (Enter your response rounded to two decimal places.)arrow_forwardSam's Pet Hotel operates 50 weeks per year, 6 days per week, and uses a continuous review inventory system. It purchases kitty litter for $10.50 per bag. The following information is available about these bags: > Demand = 95 bags/week > Order cost = $55.00/order > Annual holding cost = 35 percent of cost > Desired cycle-service level = 80 percent > Lead time = 4 weeks (24 working days) > Standard deviation of weekly demand = 15 bags > Current on-hand inventory is 320 bags, with no open orders or backorders. a. Suppose that the weekly demand forecast of 95 bags is incorrect and actual demand averages only 75 bags per week. How much higher will total costs be, owing to the distorted EOQ caused by this forecast error? The costs will be $ 10.64 higher owing to the error in EOQ. (Enter your response rounded to two decimal places.) b. Suppose that actual demand is 75 bags but that ordering costs are cut to only $13.00 by using the internet to automate order placing. However, the buyer does…arrow_forward
- BUS-660 Topic 4: Intege... W Midterm Exam - BUS-66... webassign.net b Answered: The binding c... × W Topic 4 Assignment - BU... how to get more chegg... b My Questions | bartleby + macbook screenshot - G... C Consider the following m... As discussed in Section 8.3, the Markowitz model uses the variance of the portfolio as the measure of risk. However, variance includes deviations both below and above the mean return. Semivariance includes only deviations below the mean and is considered by many to be a better measure of risk. (a) Develop a model that minimizes semivariance for the Hauck Financial data given in the file HauckData with a required return of 10%. Assume that the five planning scenarios in the Hauck Financial Services model are equally likely to occur. Hint: Modify model (8.10)-(8.19). Define a variable d for each 5 - scenario and let d≥ Ŕ – R¸ with d¸ ≥ 0. Then make the objective function: Min 1 5 Σας Let Min s.t. 15 FS = proportion of portfolio invested in the foreign…arrow_forwardOn a daily basis, the van is dispatched from Maplewood Hospital to pickup blood and platelet donations made at its local donation centers. The distances in miles between all locations may be found in the table below. Click the icon to view mileage data for Vampire Van. a. The van travels from the Hospital (A) to (B) to (C) to (D) to (E) and then returns to the Hospital (A). What is the total number of miles that the van must travel using this route? Route ABCDEA requires a total distance of miles. (Enter your response rounded to one decimal place.) More Info Maplewood City Center Westbrook Hospital (A) Donation Site (B) Donation Site (C) Municipal Park Donation Site (D) Valley Hills Donation Site (E) Maplewood 3.1 5.3 3.2 4.4 Hospital (A) City Center 3.1 6.7 2.2 4.3 Donation Site (B) Westbrook 5.3 Donation Site (C) 19 6.7 | 6.2 2.5 Municipal Park 3.2 2.2 6.2 | 4.6 Donation Site (D) Valley Hills 4.4 4.3 2.5 4.6 Donation Site (E) - ☑arrow_forwardThe Harvey Motorcycle Company produces three models: the Tiger, a sure-footed dirt bike; the LX2000, a nimble cafe racer; and the Golden, a large interstate tourer. The month's master production schedule calls for the production of 32 Goldens, 31 LX2000s, and 38 Tigers per 10-hour shift. What average cycle time is required for the assembly line to achieve the production quota in 10 hours? 0.099 hours per motorcycle. (Enter your response rounded to three decimal places.) If mixed-model scheduling is used, how many of each model will be produced before the production cycle is repeated? The greatest common divisor of the production requirements is Therefore, the Harvey Motorcycle Company will produce Goldens, LX2000s, and Tigers. (Enter your responses as integers.)arrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Understanding Management (MindTap Course List)ManagementISBN:9781305502215Author:Richard L. Daft, Dorothy MarcicPublisher:Cengage Learning
Understanding Management (MindTap Course List)ManagementISBN:9781305502215Author:Richard L. Daft, Dorothy MarcicPublisher:Cengage Learning


