Problem 1PE: Which of the following are conjugate acid-base pairs? Describe why the others are not true conjugate... Problem 2PE: Write the formula of the conjugate base for each of the following Bronsted-Lowry acids:... Problem 3PE: Sodium cyanide solution, when poured into excess hydrochloric acid, releases hydrogen cyanide as a... Problem 4PE: One kind of baking powder contains sodium bicarbonate and calcium dihydrogen phosphate. When water... Problem 5PE: Which of the following are amphoteric and which are not? Provide reasons for your decisions: (a)... Problem 6PE: The anion of sodium monohydrogen phosphate, Na2HPO4, is amphoteric. Using H3O+ and OH-, write net... Problem 7PE:
Given that is a stronger acid than what is the chemical reaction if solutions containing these... Problem 8PE: Given that HClO is a weaker acid than determine whether the substances on the left of the arrows or... Problem 9PE: Order the following groups of acids from the weakest to the strongest: (a) HI, HF, HBr;
(b) (c) ... Problem 10PE: Using only the periodic cable, choose the stronger acid of each pair: (a) H2SeorHBr, (b) H2SeorH2Te,... Problem 11PE Problem 12PE: Explain why one acid is weaker than the other in the following pairs: (a) H3PO4 and H3AsO4, (b)... Problem 13PE: In each pair, explain why one is a stronger acid than the other: (a) (b) and (c) . (Hint: This... Problem 14PE: In each pair, explain why one is a weaker acid than the other: (a) H2SO4andHC1O4, (b)... Problem 15PE: How would you expect the acidities of the following molecules to compare? (Hint. How does the... Problem 16PE: List these acids in terms of increasing acidity: CF3CO2H,CH3CO2H,CHF2CO2H,CH2FCO2H Problem 17PE: Identify the Lewis acid and Lewis base in each reaction. (a) NH3+H+NH4+ (b) SeO3+Na2ONa2SeO4 (c)... Problem 18PE: Is the fluoride ion more likely to behave as a Lewis acid or a Lewis base? Explain. Is the BeCl2... Problem 1RQ: Brnsted-Lowry Acids and Bases How is a Brnsted-Lowry acid defined? How is a Brnsted- Lowry base... Problem 2RQ: Brnsted-Lowry Acids and Bases How are the formulas of the members of a conjugate acid-base pair... Problem 3RQ: Brnsted-Lowry Acids and Bases Is H2SO4 the conjugate acid of SO24 ? Explain your answer. Problem 4RQ: Brnsted-Lowry Acids and Bases What is meant by the term amphoteric? Give two chemical equations that... Problem 5RQ: Brnsted-Lowry Acids and Bases Define the term amphiprotic. Problem 6RQ: Strengths of Bronsted-Lowry Acids and Bases
15.6 Explain why is the strongest acid found in water.... Problem 7RQ: Strengths of Brønsted-Lowry Acids and Bases
15.7 In an acid-base equilibrium, can the stronger acid... Problem 8RQ: Strengths of Brnsted-Lowry Acids and Bases The position of equilibrium in the equation below lies... Problem 9RQ: Strengths of Brnsted-Lowry Acids and Bases Consider the following: CO/ is a weaker base than... Problem 10RQ: Strengths of Brnsted-Lowry Acids and Bases Acetic acid, HC2H3O2, is a weaker acid than nitrous acid,... Problem 11RQ: Strengths of Brnsted-Lowry Acids and Bases Nitric acid, HNO3, is a very strong acid. It is 100%... Problem 12RQ: Strengths of Brnsted-Lowry Acids and Bases HCIO4 is a stronger proton donor than HNO3 but in water... Problem 13RQ: Strengths of Brnsted-Lowry Acids and Bases Formic acid, HCHO2, and acetic acid, HC2H3O2, are... Problem 14RQ: Periodic Trends in the Strength of Acids Explain how the strength of the bond between the molecule... Problem 15RQ: Periodic Trends in the Strength of Acids What are the two properties that have an effect on the... Problem 16RQ: Periodic Trends in the Strength of Acids Within the periodic table, how do the strengths of the... Problem 17RQ: Periodic Trends in the Strength of Acids Explain why H2S is a stronger acid than H2O. Problem 18RQ: Periodic Trends in the Strength of Acids Within the periodic table, how do the strengths of the... Problem 19RQ: Periodic Trends in the Strength of Acids Explain why nitric acid is a stronger acid than nitrous... Problem 20RQ: Periodic Trends in the Strength of Acids Astatine, atomic number 85, is radioactive and does not... Problem 21RQ: Periodic Trends in the Strength of Acids
15.21 Which is the stronger Brønsted-Lowry base, ? What is... Problem 22RQ: Periodic Trends in the Strength of Acids
15.22 Explain why is a stronger acid than
Problem 23RQ: Periodic Trends in the Strength of Acids Which of the molecules below is expected to be the stronger... Problem 24RQ: Periodic Trends in the Strength of Acids Which of the molecules below has the stronger conjugate... Problem 25RQ: Lewis Acids and Bases Define Lewis acid and Lewis base. Problem 26RQ: Lewis Acids and Bases In terms of atomic orbitals, what is required for Lewis acids and Lewis bases? Problem 27RQ: Lewis Acids and Bases
15.27 Explain why the addition of a proton to a water molecule to give can be... Problem 28RQ: Lewis Acids and Bases Methylamine has the formula CH3NH2 and the structure Use Lewis structures to... Problem 29RQ: Use Lewis structures to show the Lewis acid-base reaction between SO3andH2OtogiveH2SO4. Identify the... Problem 30RQ: Lewis Acids and Bases
15.30 Explain why the oxide ion, , can function as a Lewis base but not as a... Problem 31RQ: Lewis Acids and Bases The molecule SbF5 is able to function as a Lewis acid. Explain why it is able... Problem 32RQ: Lewis Acids and Bases In the reaction of calcium with oxygen to form calcium oxide, each calcium... Problem 33RQ: Acid-Base Properties of the Elements and Their Oxides Why do nonmetals oxides tend to form acids and... Problem 34RQ: Acid-Base Properties of the Elements and Their Oxides Suppose that a new element was discovered.... Problem 35RQ Problem 36RQ: Acid-Base Properties of the Elements and Their Oxides
15.36 Boric acid is very poisonous and is used... Problem 37RQ: Acid-Base Properties of the Elements and Their Oxides Why do small highly charged hydrated metal... Problem 38RQ: Acid-Base Properties of the Elements and Their Oxides
15.38 Many chromium salts crystallize as... Problem 39RQ: Acid-Base Properties of the Elements and Their Oxides Which ion is expected to give the more acidic... Problem 40RQ Problem 41RQ: Acid-Base Properties of the Elements and Their Oxides What acid is formed when the following oxides... Problem 42RQ: Acid-Base Properties of the Elements and Their Oxides
15.42 Consider the following oxides: .
Which... Problem 43RQ Problem 44RQ: Advanced Ceramics and Acid-Base Chemistry What is a ceramic? How are ceramics formed from their raw... Problem 45RQ: Advanced Ceramics and Acid-Base Chemistry What is sintering? Problem 46RQ: Advanced Ceramics and Acid-Base Chemistry
15.46 What type of reaction is used in the sol-gel... Problem 47RQ: Advanced Ceramics and Acid-Base Chemistry How does the sol-gel process work and how does it make... Problem 48RQ: Advanced Ceramics and Acid-Base Chemistry
15.48 How can a xerogel be convened into an aerogel? Why... Problem 49RQ: Brønsted-Lowry Acids and Bases
15.49 Write the formula for the conjugate acid of each of the... Problem 50RQ: Brønsted-Lowry Acids and Bases
15.50 Write the formula for the conjugate acid of each of the... Problem 51RQ: Brønsted-Lowry Acids and Bases
15.51 Write the formula for the conjugate base of each of the... Problem 52RQ: Brnsted-Lowry Acids and Bases Write the formula for the conjugate base of each of the following.... Problem 53RQ: Brønsted-Lowry Acids and Bases
15.53 Identify the conjugate acid-base pairs in the following... Problem 54RQ: Brønsted-Lowry Acids and Bases
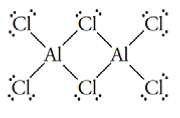
15.54 Identify the conjugate acid-base pairs in the following... Problem 55RQ: Periodic Trends in the Strengths of Acids Choose the stronger acid:... Problem 56RQ: Periodic Trends in the Strengths of Acids Choose the stronger acid:... Problem 57RQ: Choose the stronger acid and give your reason: (a)HOClorHClO2,(b)H2SeO4orH2SeO3. Problem 58RQ: Choose the stronger acid and give your reason: (a)HIO3orHIO4,(b)H3ASO4orH3AsO3. Problem 59RQ: Choose the stronger acid: (a)HClO3orHIO3,(b)HIO2orHCIO3,(c)H2SeO3orHBrO4. Give your reasons. Problem 60RQ: Choose the stronger acid: (a)H3AsO4orH3PO4,(b)H2CO3orHNO3,(c)H2SeO4orHClO4. Give your reasons. Problem 61RQ: Lewis Acids and Bases Use Lewis symbols co diagram the reaction NH2-+H+NH3 Identify the Lewis acid... Problem 62RQ: Lewis Acids and Bases Use Lewis symbols to diagram the reaction BF3+F-BF4- Problem 63RQ: *15.63 Beryllium chloride, , exists in the solid as a polymer composed of long chains of units... Problem 64RQ: Aluminum chloride, AlCl3, forms molecules with itself with the formula Al2Cl6. Its structure is Use... Problem 65RQ: Use Lewis structures to diagram the reaction CO2+H2OH2CO3 Identify the Lewis acid and Lewis base in... Problem 66RQ: Use Lewis structures to diagram the reaction CO2+O2CO32 Identify the Lewis acid and Lewis base in... Problem 67RQ: Use Lewis structures to show how the following reaction involves the transfer of a Lewis base from... Problem 68RQ: *15.68 Use Lewis structures to show how the following reaction can be viewed as the displacement of... Problem 69RQ: Acid-Base Properties of Elements and Their Oxides
15.69 The ion is weakly acid. Write an equation... Problem 70RQ: Acid-Base Properties of Elements and Their Oxides The ion Hg(H2O)62+ acts as an acid. Write an... Problem 71RQ Problem 72RQ Problem 73RQ: What is the formula of the conjugate acid of dimethyl- amine, (CH3)2NH? What is the formula of its... Problem 74RQ: *15.74 Using liquid ammonia as a solvent, sodium amide reacts with ammonium chloride in an acid-base... Problem 75RQ: In liquid SO2asasolvent,SOCl2reactswithNa2SO3 in a reaction that can be classified as neutralization... Problem 76RQ: *15.76 The following space-filling model depicts the structure of a compound called ethanamide.
How... Problem 77RQ: Which of the following compounds is the stronger base? Explain. Problem 78RQ: Which of the two molecules below is the stronger Brnsted-Lowry acid? Why? Problem 79RQ: 15.79 Write equations that illustrate the amphiprotic nature of the bicarbonate ion.
Problem 80RQ: Hydrogen peroxide is a stronger Brnsted-Lowry acid than water. Explain why this is so. Is an aqueous... Problem 81RQ: Sodium hydroxide, NaOH, is basic. Aluminum hydroxide, A1(H2O)3(OH)3, is amphoteric. The compound... Problem 82RQ: Hydrazine, N2H4, is a weaker Brnsted-Lowry base than ammonia. In the following reaction, would the... Problem 83RQ: Identify the two Brnsted-Lowry acids and two bases in the reaction NH2OH+CH3N+NH3OH++CH3NH2 Problem 84RQ: In the reaction in the preceding exercise, the position of equilibrium lies to left. Identify the... Problem 85RQ: How would you expect the degree of ionization of HClO3 to compare in the solvents H2O(l) and HF(l)?... Problem 86RQ Problem 87RQ: A mixture is prepared containing 0.10 M of each of the following: arsenic acid, sodium arsenate,... Problem 88RQ: 15.88 Are all Arrhenius acids Brønsted-Lowry acids? Are they all Lewis acids? Give examples if they... Problem 89RQ: How could you determine whether HBr is a stronger acid than HI? Problem 90RQ: 15.90 Alcohols are organic compounds that have an —OH group. Are alcohols acids or bases? Sugars... Problem 91RQ: Acid rain, acid mine runoff, and acid leaching of metals from soils are important environmental... Problem 92RQ: 15.92 Using just Figure 7.30, find the five most acidic cations. Explain your methods. Where would... format_list_bulleted


 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning



