
In an alternative design for the structure of Prob. 1.55, a pin of 10-mm-diameter is to be used at A. Assuming that all other specifications remain unchanged, determine the allowable load P if an overall factor of safety of 3.0 is desired.
1.55 In the structure shown, an 8-mm-diameter pin is used at A, and 12-mm-diameter pins are used at B and D. Knowing that the ultimate shearing stress is 100 MPa at all connections and that the ultimate normal stress is 250 MPa in each of the two links joining B and D, determine the allowable load P if an overall factor of safety of 3.0 is desired.
Fig. P1.55
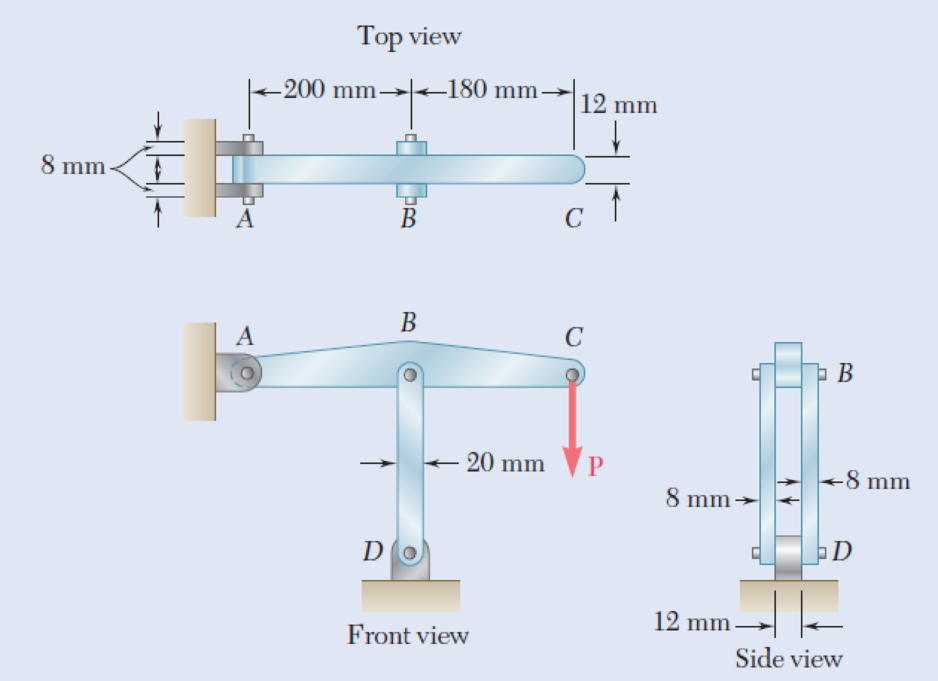
The allowable load P when an overall factor of safety of 3.0 is desired.
Answer to Problem 56P
The allowable load P when an overall factor of safety of 3.0 is desired is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The diameter (d) of each pin B and D is
The diameter (d) of pin A is
The ultimate shearing stress
The ultimate normal stress
Calculation:
Sketch the free body diagram of ABC as shown in Figure 1.
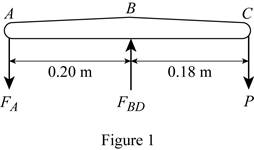
Refer to figure 1.
Take a moment about B.
Take a moment about A.
Find the area of pin at A using the relation:
Substitute
Find the value of
Here, A is the double shear pin A.
Substitute
Find the value of P using the relation:
Substitute
Find the area of double shear pin at B and D using the relation:
Substitute
Find the force in member BD based on double shear in pins at B and D using the relation:
Substitute
Find the value of P using the relation:
Substitute
Find the area based on compression in links BD for one link as follows:
Here, d is the diameter of pin and b is the width of the section.
Substitute
Find the force in member BD of pin at B and D for one link using the relation:
Here, A is the area based on compression in links BD.
Substitute
Find the value of P using the relation:
Substitute
Based on results,
Select the smaller value of P is
Thus, the allowable load P when an overall factor of safety of 3.0 is desired is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
EBK MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
- 1.55 In the structure shown, an 8-mm-diameter pin is used at A, and 12-mm-diameter pins are used at B and D. Knowing that the ulti- mate shearing stress is 100 MPa at all connections and that the ultimate normal stress is 250 MPa in each of the two links joining B and D, determine the allowable load P if an overall factor of safety of 3.0 is desired. Тоp view 200 mm +180 mm - 12 mm 8 mm A В C A 20 mm P 8 mm 8 mm - DO 12 mm - Front view Side view Fig. P1.55arrow_forward1.55 In the structure shown, an 8-mm-diameter pin is used at A, and 12-mm-diameter pins are used at Band D. Knowing that the ulti- mate shearing stress is 100 MPa at all connections and that the ultimate normal stress is 250 MPa in each of the two links joining B and D. determine the allowable load P if an overall factor of safety of 3.0 is desired. Top siew 12 20 12 mm Front view Side view Fig. P1.55arrow_forward250 mm 400 mm 1.53 Each of the two vertical links CF connecting the two horizontal members AD and EG has a 10 x 40-mm uniform rectangular cross section and is made of a steel with an ultimate strength in tension of 400 MPa, while each of the pins at C and F has a 20-mm diameter and are made of a steel with an ultimate strength in shear of 150 MPa. Determine the overall factor of safety for the links CF and the pins connecting them to the horizontal members. A 250 mm D E F 24 kNarrow_forward
- Solve fast pleasearrow_forwardTwo loads are applied to the bracket BCD as shown. (a) Knowing that the control rod AB is to be made of a steel having an ultimate normal stress of 600 MPa, determine the diameter of the rod for which the factor of safetywith respect to failure will be 3.3. (b) The pin at C is to be made of a steelhaving an ultimate shearing stress of 350 MPa. Determine the diameter ofthe pin C for which the factor of safety with respect to shear will also be 3.3.(c) Determine the required thickness of the bracket supports at C, knowingthat the allowable bearing stress of the steel used is 300 MPa.arrow_forwardAn annular washer distributes the load P applied to a steel rod to a timber support. The rod's diameter is 22 mm, and the washer's inner diameter is 25 mm, which is larger than the hole's permissible outer diameter. Knowing that the axial normal stress in the steel rod is 35 MPa and the average bearing stress between the washer and the timber must not exceed 5 MPa, examine the smallest allowed outer diameter, d, of the washer. %3D %3D +22 mm P Figure 4arrow_forward
- 15. In the steel structure shown, a 6-mm-diamter pin is used at C and 10-mm-diameter pins are used at B and D. The ultimate shearing stress is 150 MPa at all connections, and the ultimate normal stress is 400 MPa in link BD. Knowing that a factor of safety is 3.0 is desired, determine the largest load P that can be applied at A. Note that link BD is not reinforced around the pin holes. Front view 18 mm 6 mm 120 mm- Side view 160 mm Top viewarrow_forwardTwo links BF are made of steel with a 450-MPa ultimate normal stress and has a 6x12–mm uniform rectangular cross section. Links BF are connected to members ABD and CDEF by 8-mm diameter pins; ABD and CDEF are connected together by a 10-mm diameter pin; CDEF is connected to the support by a 10-mm diameter pin; all of the pins are made of steel with a 170 MPa ultimate shearing stress. Knowing that a factor of safety of 3 is desired, determine the largest load P that may be appliedarrow_forward12 in. E 12 in. A steel loop ABCD of length 5 ft and of -in. diameter is placed as shown around a l-in.-diameter aluminum rod AC. Cables BE and DF, each of -in. diameter, are used to apply the load Q. Knowing that the ultimate strength of the steel used for the loop and the cables is 70 ksi, and that the ultimate strength of the aluminum used for the rod is 38 ksi, determine the largest load Q that can be applied if an overall factor of safety of 3 is desired. 9 in. 1 in. 9 in. in. 응 in. Farrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





