
EBK MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
7th Edition
ISBN: 8220100257063
Author: BEER
Publisher: YUZU
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 1.5, Problem 58P
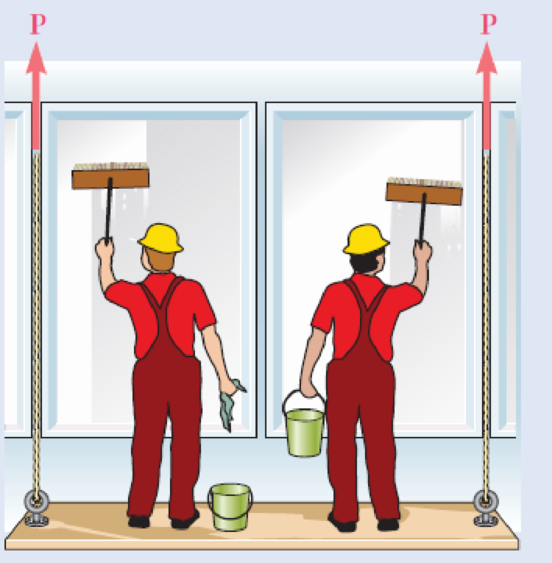
The Load and Resistance Factor Design method is to be used to select the two cables that will raise and lower a platform supporting two window washers. The platform weighs 160 lb and each of the window washers is assumed to weigh 195 lb with equipment. Since these workers are free to move on the platform, 75% of their total weight and the weight of their equipment will be used as the design live load of each cable. (a) Assuming a resistance factor ϕ = 0.85 and load factors γD = 1.2 and γL = 1.5, determine the required minimum ultimate load of one cable. (b) What is the corresponding conventional factor of safety for the selected cables?
Fig. P1.58
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
An ideal gas, occupying a volume of 0.02 m3 , has a temperature of 25 0C and is at 1.2 bar. The gas is compressed reversibly and adiabatically to a final pressure of 8 bar. Assuming the gas has an adiabatic index of γ = 1.4, calculate (a) the final temperature, (b) the final volume, (c) the work performed during the compression and (d) the heat transferred.
attached is a past paper question in which we werent given the solution. a solution with clear steps and justification would be massively appreciated thankyou.
in this scenario, when it comes to matrix iterations it states this system is assumed out of phase. why is this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
EBK MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
Ch. 1.2 - Two solid cylindrical rods AB and BC are welded...Ch. 1.2 - Two solid cylindrical rods AB and BC are welded...Ch. 1.2 - Two solid cylindrical rods AB and BC are welded...Ch. 1.2 - Two solid cylindrical rods AB and BC are welded...Ch. 1.2 - A strain gage located at C on the surface of bone...Ch. 1.2 - Two brass rods AB and BC, each of uniform...Ch. 1.2 - Each of the four vertical links has an 8 36-mm...Ch. 1.2 - Link AC has a uniform rectangular cross section 18...Ch. 1.2 - Three forces, each of magnitude P = 4 kN, are...Ch. 1.2 - Link BD consists of a single bar 1 in. wide and 12...
Ch. 1.2 - For the Pratt bridge truss and loading shown,...Ch. 1.2 - The frame shown consists of four wooden members,...Ch. 1.2 - An aircraft tow bar is positioned by means of a...Ch. 1.2 - Two hydraulic cylinders are used to control the...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the diameter of the largest circular...Ch. 1.2 - Two wooden planks, each 12 in. thick and 9 in....Ch. 1.2 - When the force P reached 1600 lb, the wooden...Ch. 1.2 - A load P is applied to a steel rod supported as...Ch. 1.2 - The axial force in the column supporting the...Ch. 1.2 - Three wooden planks are fastened together by a...Ch. 1.2 - A 40-kN axial load is applied to a short wooden...Ch. 1.2 - An axial load P is supported by a short W8 40...Ch. 1.2 - Link AB, of width b = 2 in. and thickness t=14...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the largest load P that can be applied...Ch. 1.2 - Knowing that = 40 and P = 9 kN, determine (a) the...Ch. 1.2 - The hydraulic cylinder CF, which partially...Ch. 1.2 - For the assembly and loading of Prob. 1.7,...Ch. 1.2 - Two identical linkage-and-hydraulic-cylinder...Ch. 1.5 - Two wooden members of uniform rectangular cross...Ch. 1.5 - Two wooden members of uniform rectangular cross...Ch. 1.5 - The 1.4-kip load P is supported by two wooden...Ch. 1.5 - Two wooden members of uniform cross section are...Ch. 1.5 - A centric load P is applied to the granite block...Ch. 1.5 - A 240-kip load P is applied to the granite block...Ch. 1.5 - A steel pipe of 400-mm outer diameter is...Ch. 1.5 - A steel pipe of 400-mm outer diameter is...Ch. 1.5 - A steel loop ABCD of length 5 ft and of 38-in....Ch. 1.5 - Link BC is 6 mm thick, has a width w = 25 mm, and...Ch. 1.5 - Link BC is 6 mm thick and is made of a steel with...Ch. 1.5 - Members AB and BC of the truss shown are made of...Ch. 1.5 - Members AB and BC of the truss shown are made of...Ch. 1.5 - Link AB is to be made of a steel for which the...Ch. 1.5 - Two wooden members are joined by plywood splice...Ch. 1.5 - For the joint and loading of Prob. 1.43, determine...Ch. 1.5 - Three 34-in.-diameter steel bolts are to be used...Ch. 1.5 - Three steel bolts are to be used to attach the...Ch. 1.5 - A load P is supported as shown by a steel pin that...Ch. 1.5 - A load P is supported as shown by a steel pin that...Ch. 1.5 - A steel plate 14 in. thick is embedded in a...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the factor of safety for the cable...Ch. 1.5 - Link AC is made of a steel with a 65-ksi ultimate...Ch. 1.5 - Solve Prob. 1.51, assuming that the structure has...Ch. 1.5 - Each of the two vertical links CF connecting the...Ch. 1.5 - Solve Prob. 1.53, assuming that the pins at C and...Ch. 1.5 - In the structure shown, an 8-mm-diameter pin is...Ch. 1.5 - In an alternative design for the structure of...Ch. 1.5 - Prob. 57PCh. 1.5 - The Load and Resistance Factor Design method is to...Ch. 1 - In the marine crane shown, link CD is known to...Ch. 1 - Two horizontal 5-kip forces are applied to pin B...Ch. 1 - For the assembly and loading of Prob. 1.60,...Ch. 1 - Two steel plates are to be held together by means...Ch. 1 - A couple M of magnitude 1500 N m is applied to...Ch. 1 - Knowing that link DE is 18 in. thick and 1 in....Ch. 1 - A 58-in.-diameter steel rod AB is fitted to a...Ch. 1 - In the steel structure shown, a 6-mm-diameter pin...Ch. 1 - Prob. 67RPCh. 1 - A force P is applied as shown to a steel...Ch. 1 - The two portions of member AB are glued together...Ch. 1 - The two portions of member AB are glued together...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Q1. A curved beam of a circular cross section of diameter "d" is fixed at one end and subjected to a concentrated load P at the free end (Fig. 1). Calculate stresses at points A and C. Given: P = 800 N, d = 30 mm, a 25 mm, and b = 15 mm. Fig.1 P b B (10 Marks)arrow_forwardYou are working as an engineer in a bearing systems design company. The flow of lubricant inside a hydrodynamic bearing (p = 0.001 kg m-1 s-1) can be approximated as a parallel, steady, two-dimensional, incompressible flow between two parallel plates. The top plate, representing the moving part of the bearing, travels at a constant speed, U, while the bottom plate remains stationary (Figure Q1). The plates are separated by a distance of 2h = 1 cm and are W = 20 cm wide. Their length is L = 10 cm. By applying the above approximations to the Navier-Stokes equations and assuming that end effects can be neglected, the horizontal velocity profile can be shown to be y = +h I 2h = 1 cm x1 y = -h u(y) 1 dP 2μ dx -y² + Ay + B moving plate stationary plate U 2 I2 L = 10 cm Figure Q1: Flow in a hydrodynamic bearing. The plates extend a width, W = 20 cm, into the page.arrow_forwardQuestion 1 You are working as an engineer in a bearing systems design company. The flow of lubricant inside a hydrodynamic bearing (µ = 0.001 kg m¯¹ s¯¹) can be approximated as a parallel, steady, two-dimensional, incompressible flow between two parallel plates. The top plate, representing the moving part of the bearing, travels at a constant speed, U, while the bottom plate remains stationary (Figure Q1). The plates are separated by a distance of 2h = 1 cm and are W = 20 cm wide. Their length is L = 10 cm. By applying the above approximations to the Navier-Stokes equations and assuming that end effects can be neglected, the horizontal velocity profile can be shown to be 1 dP u(y) = 2μ dx -y² + Ay + B y= +h Ꮖ 2h=1 cm 1 x1 y = −h moving plate stationary plate 2 X2 L = 10 cm Figure Q1: Flow in a hydrodynamic bearing. The plates extend a width, W = 20 cm, into the page. (a) By considering the appropriate boundary conditions, show that the constants take the following forms: U U 1 dP A =…arrow_forward
- Question 2 You are an engineer working in the propulsion team for a supersonic civil transport aircraft driven by a turbojet engine, where you have oversight of the design for the engine intake and the exhaust nozzle, indicated in Figure Q2a. The turbojet engine can operate when provided with air flow in the Mach number range, 0.60 to 0.80. You are asked to analyse a condition where the aircraft is flying at 472 m/s at an altitude of 14,000 m. For all parts of the question, you can assume that the flow path of air through the engine has a circular cross section. (a) ← intake normal shock 472 m/s A B (b) 50 m/s H 472 m/s B engine altitude: 14,000 m exhaust nozzle E F exit to atmosphere diameter: DE = 0.30 m E F diameter: DF = 0.66 m Figure Q2: Propulsion system for a supersonic aircraft. a) When the aircraft is at an altitude of 14,000 m, use the International Standard Atmosphere in the Module Data Book to state the local air pressure and tempera- ture. Thus show that the aircraft speed…arrow_forwardيكا - put 96** I need a detailed drawing with explanation or in wake, and the top edge of im below the free surface of the water. Determine the hydrothed if hydrostatic on the Plot the displacement diagram for a cam with roller follower of diameter 10 mm. The required motion is as follows; 1- Rising 60 mm in 135° with uniform acceleration and retardation motion. 2- Dwell 90° 3- Falling 60 mm for 135° with Uniform acceleration-retardation motion. Then design the cam profile to give the above displacement diagram if the minimum circle diameter of the cam is 50 mm. =--20125 7357 750 X 2.01arrow_forwardYou are working as an engineer in a bearing systems design company. The flow of lubricant inside a hydrodynamic bearing (µ = 0.001 kg m¯¹ s¯¹) can be approximated as a parallel, steady, two-dimensional, incompressible flow between two parallel plates. The top plate, representing the moving part of the bearing, travels at a constant speed, U, while the bottom plate remains stationary (Figure Q1). The plates are separated by a distance of 2h = 1 cm and are W = 20 cm wide. Their length is L = 10 cm. By applying the above approximations to the Navier-Stokes equations and assuming that end effects can be neglected, the horizontal velocity profile can be shown to be U y = +h У 2h = 1 cm 1 x1 y=-h u(y) = 1 dP 2μ dx -y² + Ay + B moving plate - U stationary plate 2 I2 L = 10 cm Figure Q1: Flow in a hydrodynamic bearing. The plates extend a width, W = 20 cm, into the page. (a) By considering the appropriate boundary conditions, show that the constants take the following forms: A = U 2h U 1 dP…arrow_forward
- Question 2 You are an engineer working in the propulsion team for a supersonic civil transport aircraft driven by a turbojet engine, where you have oversight of the design for the engine intake and the exhaust nozzle, indicated in Figure Q2a. The turbojet engine can operate when provided with air flow in the Mach number range, 0.60 to 0.80. You are asked to analyse a condition where the aircraft is flying at 472 m/s at an altitude of 14,000 m. For all parts of the question, you can assume that the flow path of air through the engine has a circular cross section. (a) normal shock 472 m/s A B (b) intake engine altitude: 14,000 m D exhaust nozzle→ exit to atmosphere 472 m/s 50 m/s B diameter: DE = 0.30 m EX diameter: DF = 0.66 m Figure Q2: Propulsion system for a supersonic aircraft. F a) When the aircraft is at an altitude of 14,000 m, use the International Standard Atmosphere in the Module Data Book to state the local air pressure and tempera- ture. Thus show that the aircraft speed of…arrow_forwardgiven below: A rectangular wing with wing twist yields the spanwise circulation distribution kbV1 roy) = kbv. (2) where k is a constant, b is the span length and V. is the free-stream velocity. The wing has an aspect ratio of 4. For all wing sections, the lift curve slope (ag) is 2 and the zero-lift angle of attack (a=0) is 0. a. Derive expressions for the downwash (w) and induced angle of attack a distributions along the span. b. Derive an expression for the induced drag coefficient. c. Calculate the span efficiency factor. d. Calculate the value of k if the wing has a washout and the difference between the geometric angles of attack of the root (y = 0) and the tip (y = tb/2) is: a(y = 0) a(y = ±b/2) = /18 Hint: Use the coordinate transformation y = cos (0)arrow_forward۳/۱ العنوان O не شكا +91x PU + 96852 A heavy car plunges into a lake during an accident and lands at the bottom of the lake on its wheels as shown in figure. The door is 1.2 m high and I m wide, and the top edge of Deine the hadrostatic force on the Plot the displacement diagram for a cam with roller follower of diameter 10 mm. The required motion is as follows; 1- Rising 60 mm in 135° with uniform acceleration and retardation motion. 2- Dwell 90° 3- Falling 60 mm for 135° with Uniform acceleration-retardation motion. Then design the cam profile to give the above displacement diagram if the minimum circle diameter of the cam is 50 mm. = -20125 750 x2.01arrow_forward
- Plot the displacement diagram for a cam with roller follower of diameter 10 mm. The required motion is as follows; 1- Rising 60 mm in 135° with uniform acceleration and retardation motion. 2- Dwell 90° 3- Falling 60 mm for 135° with Uniform acceleration-retardation motion. Then design the cam profile to give the above displacement diagram if the minimum circle diameter of the cam is 50 mm.arrow_forwardQ1/ A vertical, circular gate with water on one side as shown. Determine the total resultant force acting on the gate and the location of the center of pressure, use water specific weight 9.81 kN/m³ 1 m 4 marrow_forwardI need handwritten solution with sketches for eacharrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Ch 2 - 2.2.2 Forced Undamped Oscillation; Author: Benjamin Drew;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6Tb7Rx-bCWE;License: Standard youtube license