
(a)
Interpretation: The reason of stability of
Concept Introduction: Molecular orbital theory explained the bonding, magnetic and spectral properties of molecule. It is based on the formation of molecular orbitals by the combination of atomic orbitals. On the basis of energy and stability these molecular orbitals can be further classified in three types:
- Bonding molecular orbitals (BMO): They have lesser energy than atomic orbital therefore more stable compare to atomic orbital.
- Antibonding molecular orbitals (ABMO): They have higher energy than atomic orbital therefore less stable compare to atomic orbital.
- Non-bonding molecular orbitals (NBMO): They have same energy as atomic orbital.
Molecular orbital diagrams represents the distribution of electrons in different molecular orbitals in increasing order of their energy. Hence lower energy molecular orbitals occupy first then only electron moves in higher energy orbitals.
(a)
Answer to Problem 39E
Since the bond order of
Explanation of Solution
To draw the energy level and Molecular orbital diagram for
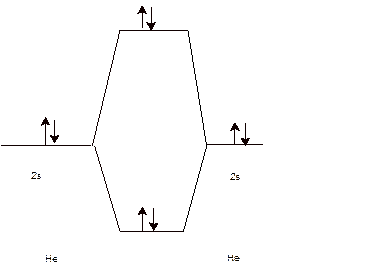
Calculate bond order:
Since the bond order of
(b)
Interpretation: The reason of paramagnetic nature of
Concept Introduction: Molecular orbital theory explained the bonding, magnetic and spectral properties of molecule. It is based on the formation of molecular orbitals by the combination of atomic orbitals. On the basis of energy and stability these molecular orbitals can be further classified in three types:
- Bonding molecular orbitals (BMO): They have lesser energy than atomic orbital therefore more stable compare to atomic orbital.
- Antibonding molecular orbitals (ABMO): They have higher energy than atomic orbital therefore less stable compare to atomic orbital.
- Non-bonding molecular orbitals (NBMO): They have same energy as atomic orbital.
Molecular orbital diagrams represents the distribution of electrons in different molecular orbitals in increasing order of their energy. Hence lower energy molecular orbitals occupy first then only electron moves in higher energy orbitals.
(b)
Answer to Problem 39E
Only
Explanation of Solution
The molecular orbital electronic configuration of
Only
(c)
Interpretation: The reason of large
Concept Introduction: Molecular orbital theory explained the bonding, magnetic and spectral properties of molecule. It is based on the formation of molecular orbitals by the combination of atomic orbitals. On the basis of energy and stability these molecular orbitals can be further classified in three types:
- Bonding molecular orbitals (BMO): They have lesser energy than atomic orbital therefore more stable compare to atomic orbital.
- Antibonding molecular orbitals (ABMO): They have higher energy than atomic orbital therefore less stable compare to atomic orbital.
- Non-bonding molecular orbitals (NBMO): They have same energy as atomic orbital.
Molecular orbital diagrams represents the distribution of electrons in different molecular orbitals in increasing order of their energy. Hence lower energy molecular orbitals occupy first then only electron moves in higher energy orbitals.
(c)
Answer to Problem 39E
Since the bond order for
Explanation of Solution
The molecular orbital electronic configuration of
Calculate bond order:
Since the bond order for
(d)
Interpretation: The reason of more stability of
Concept Introduction: Molecular orbital theory explained the bonding, magnetic and spectral properties of molecule. It is based on the formation of molecular orbitals by the combination of atomic orbitals. On the basis of energy and stability these molecular orbitals can be further classified in three types:
- Bonding molecular orbitals (BMO): They have lesser energy than atomic orbital therefore more stable compare to atomic orbital.
- Antibonding molecular orbitals (ABMO): They have higher energy than atomic orbital therefore less stable compare to atomic orbital.
- Non-bonding molecular orbitals (NBMO): They have same energy as atomic orbital.
Molecular orbital diagrams represents the distribution of electrons in different molecular orbitals in increasing order of their energy. Hence lower energy molecular orbitals occupy first then only electron moves in higher energy orbitals.
(d)
Answer to Problem 39E
Since there are more anti-bonding electrons in
Explanation of Solution
The molecular orbital electronic configuration of
Number of electrons in N = 7
Number of electrons in O = 8
Total number of electrons in
Total number of electrons in
Calculate bond order:
Since there are more anti-bonding electrons in
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
EBK CHEMICAL PRINCIPLES
- Give the chemical equation for the preparation of: -Any aldehyde -Any keytonearrow_forward+ C8H16O2 (Fatty acid) + 11 02 → 8 CO2 a. Which of the above are the reactants? b. Which of the above are the products? H2o CO₂ c. Which reactant is the electron donor? Futty acid d. Which reactant is the electron acceptor? e. Which of the product is now reduced? f. Which of the products is now oxidized? 02 #20 102 8 H₂O g. Where was the carbon initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished? 2 h. Where were the electrons initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished?arrow_forward→ Acetyl-CoA + 3NAD+ + 1FAD + 1ADP 2CO2 + CoA + 3NADH + 1FADH2 + 1ATP a. Which of the above are the reactants? b. Which of the above are the products? c. Which reactant is the electron donor? d. Which reactants are the electron acceptors? e. Which of the products are now reduced? f. Which product is now oxidized? g. Which process was used to produce the ATP? h. Where was the energy initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished? i. Where was the carbon initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished? j. Where were the electrons initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished?arrow_forward
- Rank each of the following substituted benzene molecules in order of which will react fastest (1) to slowest (4) by electrophilic aromatic substitution. OCH 3 (Choose one) OH (Choose one) Br (Choose one) Explanation Check NO2 (Choose one) © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Aarrow_forwardFor each of the substituted benzene molecules below, determine the inductive and resonance effects the substituent will have on the benzene ring, as well as the overall electron-density of the ring compared to unsubstituted benzene. Molecule Inductive Effects O donating O withdrawing O no inductive effects Resonance Effects Overall Electron-Density ○ donating ○ withdrawing O no resonance effects O electron-rich O electron-deficient O similar to benzene Cl O donating O withdrawing ○ donating ○ withdrawing O no inductive effects O no resonance effects O Explanation Check O electron-rich O electron-deficient similar to benzene X © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessarrow_forwardIdentifying electron-donating and For each of the substituted benzene molecules below, determine the inductive and resonance effects the substituent will have on the benzene ring, as well as the overall electron-density of the ring compared to unsubstituted benzene. Molecule Inductive Effects NH2 ○ donating NO2 Explanation Check withdrawing no inductive effects Resonance Effects Overall Electron-Density ○ donating O withdrawing O no resonance effects O donating O withdrawing O donating withdrawing O no inductive effects Ono resonance effects O electron-rich electron-deficient O similar to benzene O electron-rich O electron-deficient O similar to benzene olo 18 Ar 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forward
- Rank each of the following substituted benzene molecules in order of which will react fastest (1) to slowest (4) by electrophilic aromatic substitution. Explanation Check Х (Choose one) OH (Choose one) OCH3 (Choose one) OH (Choose one) © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centerarrow_forwardAssign R or S to all the chiral centers in each compound drawn below porat bg 9 Br Brarrow_forwarddescrive the energy levels of an atom and howan electron moces between themarrow_forward
 General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning





