
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The number of carbon atoms with
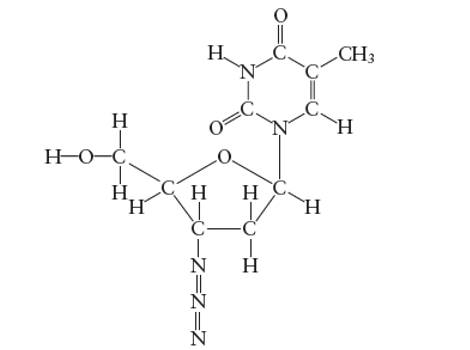
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
(a)
Answer to Problem 29E
There are 6 carbon atoms in
Explanation of Solution
A
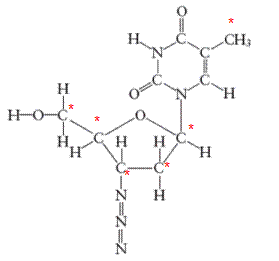
All the asterisk C atoms are
(b)
Interpretation: The number of carbon atoms with
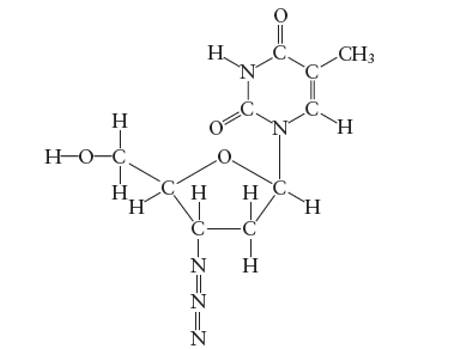
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
(b)
Answer to Problem 29E
There are 4 carbon atoms in
Explanation of Solution
A
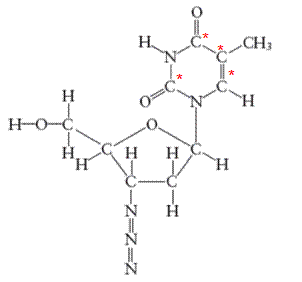
All the asterisk C atoms are
(c)
Interpretation: The number of carbon atoms with
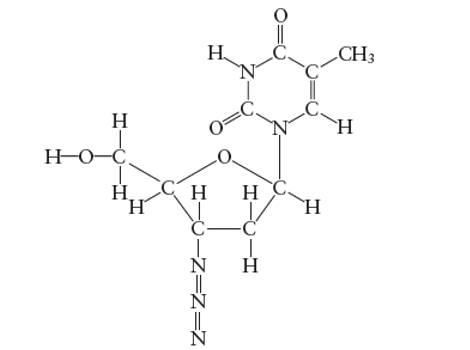
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
(c)
Answer to Problem 29E
The N atoms which forms two double covalent bond is sp-hybridized only.
Explanation of Solution
A
There is no
(d)
Interpretation: The number of σ-bonds in AZT molecule needs to be determined.
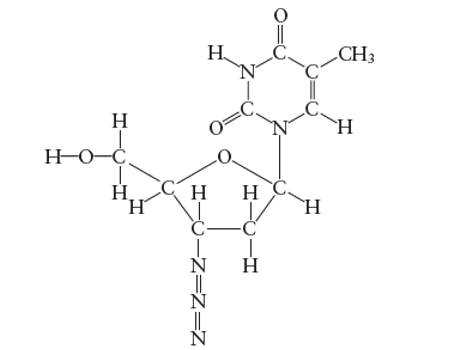
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
(d)
Answer to Problem 29E
The total number of σ bonds are 33 in AZT molecule
Explanation of Solution
There are two types of covalent bonds; σ bond and π-bonds. A σ-bond is formed by head-to head overlapping of hybridized orbitals. It is a strong bond and can exist between two bonded atoms. On the contrary, a π-bond is a weak covalent bond as it forms by side-way-overlapping of un-hybridized orbitals.
Since it is a weak bond therefore it is always exist with σ-bond in a double and triple covalent bond. A double covalent bond is formed by 1σ and 1 π bond whereas a triple covalent bond is formed by 1σ and two π bonds. In the given molecule, all single bonds are σ-bonds and all double bonds have 1 σ bonds. Therefore total number of σ bonds are 33 in AZT molecule.
(e)
Interpretation: The number of π-bonds in AZT molecule needs to be determined.
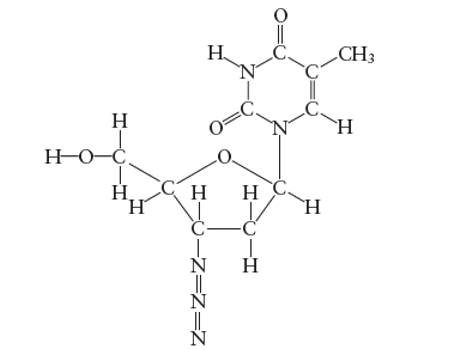
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
(e)
Answer to Problem 29E
The total number of π bonds are 5 in AZT molecule
Explanation of Solution
There are two types of covalent bonds; σ bond and π-bonds. A σ-bond is formed by head-to head overlapping of hybridized orbitals. It is a strong bond and can exist between two bonded atoms. On the contrary, a π-bond is a weak covalent bond as it forms by side-way-overlapping of un-hybridized orbitals.
Since it is a weak bond therefore it is always exist with σ-bond in a double and triple covalent bond. A double covalent bond is formed by 1σ and 1 π bond whereas a triple covalent bond is formed by 1σ and two π bonds. In the given molecule, total number of π bonds are 5 in AZT molecule.
(f)
Interpretation: The bond angle in the N-N-N (azide group) of AZT molecule needs to be determined.
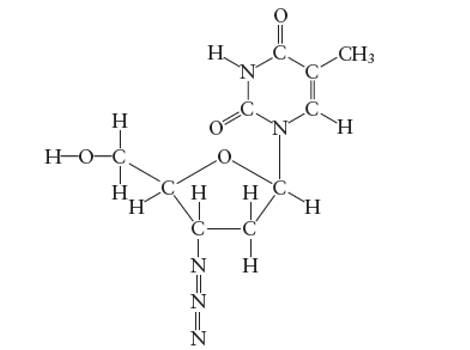
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
(f)
Answer to Problem 29E
With sp-hybridization, the bond angle must be 180°.
Explanation of Solution
Hybridization of central N atom in azide group is:
With sp-hybridization, the bond angle must be 180°.
(g)
Interpretation: The bond angle in the H-O-C in the side group attached to the five membered ring of AZT molecule needs to be determined.
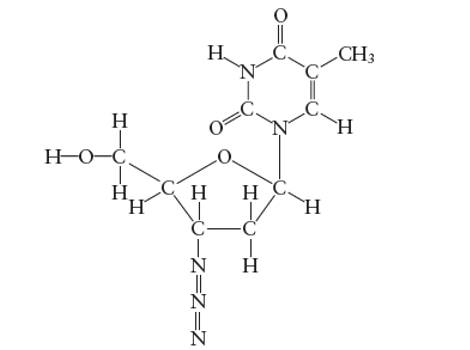
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
(g)
Answer to Problem 29E
With
Explanation of Solution
Hybridization of central C atom in −CH2OH group attached to the five membered ring:
With
(h)
Interpretation: The hybridization of O atom in −CH2OH group attached to the five membered ring of AZT molecule needs to be determined.
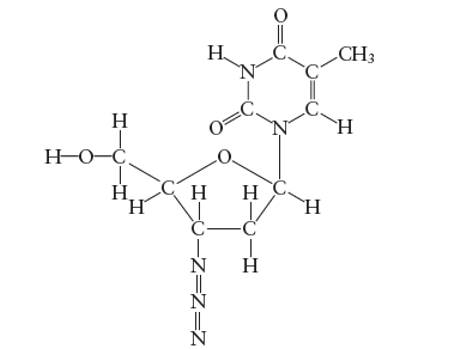
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
The sum of valence electrons must be arranged in such a way that all atoms must get octet configuration (8 electrons).
(h)
Answer to Problem 29E
The hybridization of O atom in −CH2OH group attached to the five membered ring is
Explanation of Solution
Hybridization of O atom in −CH2OH group attached to the five membered ring:
The hybridization of O atom in −CH2OH group attached to the five membered ring is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
EBK CHEMICAL PRINCIPLES
- drawing, no aiarrow_forwarddrawing, no aiarrow_forwardDraw the major organic product when each of the bellow reagents is added to 3,3-dimethylbutere. ✓ 3rd attempt Part 1 (0.3 point) H.C CH CH + 1. BHG THF 210 NaOH NJ 10000 Part 2 (0.3 point) HC- CH HC 2741 OH a Search 1. He|DA HO 2. NIBH さ 士 Ju See Periodic Table See Hint j = uz C H F F boxarrow_forward
- Indicate the product formed in each reaction. If the product exhibits tautomerism, draw the tautomeric structure. a) о + CH3-NH-NH2 CO2C2H5 b) + CoH5-NH-NH2 OC2H5arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the compound, that is the result of the N- alquilación (nucleofílic substitution), in which an additional lateral chain was formed (NH-CH2-COOMe). F3C. CF3 NH NH2 Br о OMe K2CO3, DABCO, DMFarrow_forwardSynthesis of 1-metilbenzotriazole from 1,2-diaminobenceno.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





