
University Physics with Modern Physics (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780321973610
Author: Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 14, Problem 14.88P
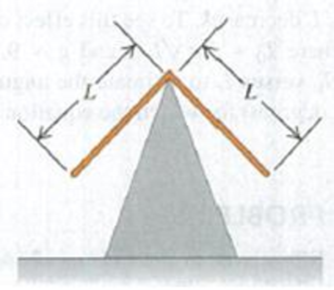
Two identical thin rods, each with mass m and length L, are joined at right angles to form an L-shaped object. This object is balanced on top of a sharp edge (Fig. P14.88). If the L-shaped object is deflected slightly, it oscillates. Find the frequency of oscillation.
Figure P14.88
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 14 Solutions
University Physics with Modern Physics (14th Edition)
Ch. 14.1 - A body like that shown in Fig. 14.2 oscillates...Ch. 14.2 - A glider is attached to a spring as shown in Fig....Ch. 14.3 - (a) To double the total energy for a mass-spring...Ch. 14.4 - A block attached to a hanging ideal spring...Ch. 14.5 - When a body oscillating on a horizontal spring...Ch. 14.6 - The center of gravity of a simple pendulum of mass...Ch. 14.7 - An airplane is flying in a straight line at a...Ch. 14.8 - When driven at a frequency near its natural...Ch. 14 - An object is moving with SHM of amplitude A on the...Ch. 14 - Think of several examples in everyday life of...
Ch. 14 - Does a tuning fork or similar tuning instrument...Ch. 14 - A box containing a pebble is attached to an ideal...Ch. 14 - If a uniform spring is cut in half, what is the...Ch. 14 - A glider is attached to a fixed ideal spring and...Ch. 14 - Two identical gliders on an air track are...Ch. 14 - You are captured by Martians, taken into their...Ch. 14 - The system shown in Fig. 14.17 is mounted in an...Ch. 14 - If a pendulum has a period of 2.5 s on earth, what...Ch. 14 - A simple pendulum is mounted in an elevator. What...Ch. 14 - What should you do to the length of the string of...Ch. 14 - If a pendulum clock is taken to a mountaintop,...Ch. 14 - When the amplitude of a simple pendulum increases,...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.15DQCh. 14 - At what point in the motion of a simple pendulum...Ch. 14 - Could a standard of time be based on the period of...Ch. 14 - For a simple pendulum, clearly distinguish between...Ch. 14 - In designing structures in an earthquake-prone...Ch. 14 - BIO (a) Music. When a person sings, his or her...Ch. 14 - If an object on a horizontal, frictionless surface...Ch. 14 - The tip of a tuning fork goes through 440 complete...Ch. 14 - The displacement of an oscillating object as a...Ch. 14 - A machine part is undergoing SUM with a frequency...Ch. 14 - BIO The wings of the blue-throated hummingbird...Ch. 14 - A 2.40-kg ball is attached to an unknown spring...Ch. 14 - In a physics lab, you attach a 0.200-kg air-track...Ch. 14 - When a body of unknown mass is attached to an...Ch. 14 - When a 0.750-kg mass oscillates on an ideal...Ch. 14 - An object is undergoing SHM with period 0.900 s...Ch. 14 - A small block is attached to an ideal spring and...Ch. 14 - A 2.00-kg. frictionless block is attached to an...Ch. 14 - Repeat Exercise 14.13, but assume that at t = 0...Ch. 14 - The point of the needle of a sewing machine moves...Ch. 14 - A small block is attached to an ideal spring and...Ch. 14 - BIO Weighing Astronauts. This procedure has been...Ch. 14 - A 0.400-kg object undergoing SHM has ax = 1.80...Ch. 14 - On a frictionless, horizontal air track, a glider...Ch. 14 - A 0.500-kg mass on a spring has velocity as a...Ch. 14 - A 1.50-kg mass on a spring has displacement as a...Ch. 14 - BIO Weighing a Virus. In February 2004, scientists...Ch. 14 - CALC Jerk. A guitar string vibrates at a frequency...Ch. 14 - For the oscillating object in Fig. E14.4, what are...Ch. 14 - A small block is attached to an ideal spring and...Ch. 14 - A small block is attached to an ideal spring and...Ch. 14 - A 0.150-kg toy is undergoing SHM on the end of a...Ch. 14 - A harmonic oscillator has angular frequency and...Ch. 14 - A 0.500-kg glider, attached to the end of an ideal...Ch. 14 - A cheerleader waves her pom-pom in SHM with an...Ch. 14 - CP For the situation described in part (a) of...Ch. 14 - A block with mass m = 0.300 kg is attached to one...Ch. 14 - You are watching an object that is moving in SHM....Ch. 14 - A 2.00-kg frictionless block is attached to an...Ch. 14 - A 2.00-kg frictionless block attached to an ideal...Ch. 14 - A mass is oscillating with amplitude A at the end...Ch. 14 - A 175-g glider on a horizontal, frictionless air...Ch. 14 - A proud deep-sea fisherman hangs a 65.0-kg fish...Ch. 14 - A thrill-seeking cat with mass 4.00 kg is attached...Ch. 14 - A uniform, solid metal disk of mass 6.50 kg and...Ch. 14 - A certain alarm clock ticks four times each...Ch. 14 - A thin metal disk with mass 2.00 103 kg and...Ch. 14 - You want to find the moment of inertia of a...Ch. 14 - CALC The balance wheel of a watch vibrates with an...Ch. 14 - You pull a simple pendulum 0.240 m long to the...Ch. 14 - An 85.0-kg mountain climber plans to swing down,...Ch. 14 - A building in San Francisco has light fixtures...Ch. 14 - A Pendulum on Mars. A certain simple pendulum has...Ch. 14 - After landing on an unfamiliar planet, a space...Ch. 14 - In the laboratory, a student studies a pendulum by...Ch. 14 - A simple pendulum 2.00 m long swings through a...Ch. 14 - A small sphere with mass m is attached to a...Ch. 14 - Two pendulums have the same dimensions (length L)...Ch. 14 - We want to hang a thin hoop on a horizontal nail...Ch. 14 - A 1.80-kg connecting rod from a car engine is...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.56ECh. 14 - The two pendulums shown in Fig. E14.57 each...Ch. 14 - CP A holiday ornament in the shape of a hollow...Ch. 14 - A 1.35-kg object is attached to a horizontal...Ch. 14 - A 50.0-g hard-boiled egg moves on the end of a...Ch. 14 - An unhappy 0.300-kg rodent, moving on the end of a...Ch. 14 - A mass is vibrating at the end of a spring of...Ch. 14 - A sinusoidally varying driving force is applied to...Ch. 14 - An object is undergoing SHM with period 0.300 s...Ch. 14 - An object is undergoing SHM with period 1.200 s...Ch. 14 - Four passengers with combined mass 250 kg compress...Ch. 14 - At the end of a ride at a winter-theme amusement...Ch. 14 - CP A block with mass M rests on a frictionless...Ch. 14 - A 1.50-kg, horizontal, uniform tray is attached to...Ch. 14 - CP A 10.0-kg mass is traveling to the right with a...Ch. 14 - An apple weighs 1.00 N. When you hang it from the...Ch. 14 - CP SHM of a Floating Object. An object with height...Ch. 14 - CP A square object of mass m is constructed of...Ch. 14 - An object with mass 0.200 kg is acted on by an...Ch. 14 - CALC A 2.00-kg bucket containing 10.0 kg of water...Ch. 14 - A uniform beam is suspended horizontally by two...Ch. 14 - A 5.00-kg partridge is suspended from a pear tree...Ch. 14 - A 0.0200-kg bolt moves with SHM that has an...Ch. 14 - CP SHM of a Butchers Scale. A spring of negligible...Ch. 14 - A 40.0-N force stretches a vertical spring 0.250...Ch. 14 - Dont Miss the Boat. While on a visit to Minnesota...Ch. 14 - CP An interesting, though highly impractical...Ch. 14 - CP A rifle bullet with mass 8.00 g and initial...Ch. 14 - CP Two uniform solid spheres, each with mass M =...Ch. 14 - CP In Fig. P14.85 the upper ball is released from...Ch. 14 - The Silently Ringing Bell. A large, 34.0-kg bell...Ch. 14 - CALC A slender, uniform, metal rod with mass M is...Ch. 14 - Two identical thin rods, each with mass m and...Ch. 14 - DATA A mass m is attached to a spring of force...Ch. 14 - DATA You hang various masses m from the end of a...Ch. 14 - DATA Experimenting with pendulums, you attach a...Ch. 14 - The Effective Force Constant of Two Springs. Two...Ch. 14 - CALC A Spring with Mass. The preceding problems in...Ch. 14 - BIO SEEING SURFACES AT THE NANOSCALE. One...Ch. 14 - In the model of Problem 14.94, what is the...Ch. 14 - By what percentage does the frequency of...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
26. Why are most of the world's deserts found in the area known as the horse latitudes?
Conceptual Physical Science (6th Edition)
A mole is approximately the number of protons in a gram of protons. The mass of a neutron is about the same as ...
An Introduction to Thermal Physics
60. You are 9.0 m from the door of your bus, behind the bus, when it pulls away with an acceleration of 1.0 m/...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
A Carnot engine extracts 745 J from a 592-K reservoir during each cycle and rejects 458 J to a cooler reservoir...
Essential University Physics: Volume 1 (3rd Edition)
(II) Light of wavelength 750 nm passes through a slit 1.0 μm wide and a single-slit diffraction pattern is form...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
Description of Motion: Move toward the detector with decreasing speed, then just as you have come to rest, move...
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A very light rigid rod of length 0.500 m extends straight out from one end of a meter-stick. The combination is suspended from a pivot at the upper end of the rod as shown in Figure P12.31. The combination is then pulled out by a small angle and released. (a) Determine the period of oscillation of the system. (b) By what percentage does the period differ from the period of a simple pendulum 1.00 m long? Figure P12.31arrow_forwardA uniform annular ring of mass m and inner and outer radii a and b, respectively, is pivoted around an axis perpendicular to the plane of the ring at point P (Fig. P16.35). Determine its period of oscillation. FIGURE P16.35arrow_forwardConsider the simplified single-piston engine in Figure CQ12.13. Assuming the wheel rotates with constant angular speed, explain why the piston rod oscillates in simple harmonic motion. Figure CQ12.13arrow_forward
- Determine the angular frequency of oscillation of a thin, uniform, vertical rod of mass m and length L pivoted at the point O and connected to two springs (Fig. P16.78). The combined spring constant of the springs is k(k = k1 + k2), and the masses of the springs are negligible. Use the small-angle approximation (sin ). FIGURE P16.78arrow_forwardA watch balance wheel (Fig. P15.25) has a period of oscillation of 0.250 s. The wheel is constructed so that its mass of 20.0 g is concentrated around a rim of radius 0.500 cm. What are (a) the wheels moment of inertia and (b) the torsion constant of the attached spring? Figure P15.23arrow_forwardIn an engine, a piston oscillates with simple harmonic motion so that its position varies according to the expression x=5.00cos(2t+6) where x is in centimeters and t is in seconds. At t = 0, find (a) the position of the piston, (b) its velocity, and (c) its acceleration. Find (d) the period and (e) the amplitude of the motion.arrow_forward
- Consider the simplified single-piston engine in Figure CQ15.13. Assuming the wheel rotates with constant angular speed, explain why the piston rod oscillates in simple harmonic motion.arrow_forwardA spherical bob of mass m and radius R is suspended from a fixed point by a rigid rod of negligible mass whose length from the point of support to the center of the bob is L (Fig. P16.75). Find the period of small oscillation. N The frequency of a physical pendulum comprising a nonuniform rod of mass 1.25 kg pivoted at one end is observed to be 0.667 Hz. The center of mass of the rod is 40.0 cm below the pivot point. What is the rotational inertia of the pendulum around its pivot point?arrow_forwardAn object of mass m1 = 9.00 kg is in equilibrium when connected to a light spring of constant k = 100 N/m that is fastened to a wall as shown in Figure P12.67a. A second object, m2 = 7.00 kg, is slowly pushed up against m1, compressing the spring by the amount A = 0.200 m (see Fig. P12.67b). The system is then released, and both objects start moving to the right on the frictionless surface. (a) When m1 reaches the equilibrium point, m2 loses contact with m1 (see Fig. P12.67c) and moves to the right with speed v. Determine the value of v. (b) How far apart are the objects when the spring is fully stretched for the first time (the distance D in Fig. P12.67d)? Figure P12.67arrow_forward
- A lightweight spring with spring constant k = 225 N/m is attached to a block of mass m1 = 4.50 kg on a frictionless, horizontal table. The blockspring system is initially in the equilibrium configuration. A second block of mass m2 = 3.00 kg is then pushed against the first block, compressing the spring by x = 15.0 cm as in Figure P16.77A. When the force on the second block is removed, the spring pushes both blocks to the right. The block m2 loses contact with the springblock 1 system when the blocks reach the equilibrium configuration of the spring (Fig. P16.77B). a. What is the subsequent speed of block 2? b. Compare the speed of block 1 when it again passes through the equilibrium position with the speed of block 2 found in part (a). 77. (a) The energy of the system initially is entirely potential energy. E0=U0=12kymax2=12(225N/m)(0.150m)2=2.53J At the equilibrium position, the total energy is the total kinetic energy of both blocks: 12(m1+m2)v2=12(4.50kg+3.00kg)v2=(3.75kg)v2=2.53J Therefore, the speed of each block is v=2.53J3.75kg=0.822m/s (b) Once the second block loses contact, the first block is moving at the speed found in part (a) at the equilibrium position. The energy 01 this spring-block 1 system is conserved, so when it returns to the equilibrium position, it will be traveling at the same speed in the opposite direction, or v=0.822m/s. FIGURE P16.77arrow_forwardWhich of the following statements is not true regarding a massspring system that moves with simple harmonic motion in the absence of friction? (a) The total energy of the system remains constant. (b) The energy of the system is continually transformed between kinetic and potential energy. (c) The total energy of the system is proportional to the square of the amplitude. (d) The potential energy stored in the system is greatest when the mass passes through the equilibrium position. (e) The velocity of the oscillating mass has its maximum value when the mass passes through the equilibrium position.arrow_forwardA block of unknown mass is attached to a spring with a spring constant of 6.50 N/m and undergoes simple harmonic motion with an amplitude of 10.0 cm. When the block is halfway between its equilibrium position and the end point, its speed is measured to be 30.0 cm/s. Calculate (a) the mass of the block, (b) the period of the motion, and (c) the maximum acceleration of the block.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION (Physics Animation); Author: EarthPen;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XjkUcJkGd3Y;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY