
(a)
Interpretation:
Structural formula for the simplest secondary alcohol with an acyclic R group has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary depending upon the number of carbon atoms that is bonded to the carbon atom bearing hydroxyl group.
Primary alcohol is the one in which the carbon atom bearing the hydroxyl group is bonded to only one other carbon atom.
Secondary alcohol is the one in which the carbon atom bearing the hydroxyl group is bonded to two other carbon atoms.
Tertiary alcohol is the one in which the carbon atom bearing the hydroxyl group is bonded to three other carbon atoms.
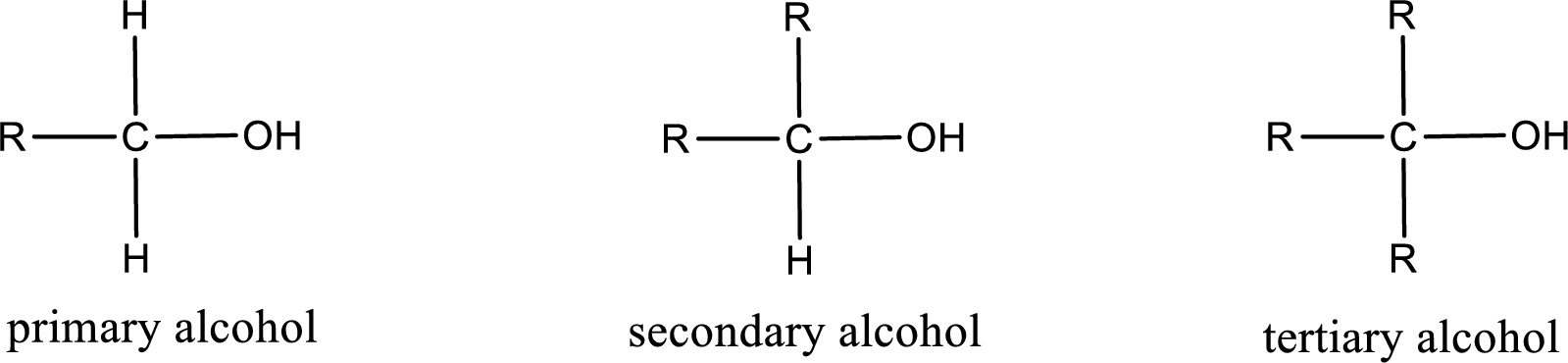
Primary is denoted as
(b)
Interpretation:
Structural formula for the simplest tertiary alcohol with a cyclic R group has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Alcohols are classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary depending upon the number of carbon atoms that is bonded to the carbon atom bearing hydroxyl group.
Primary alcohol is the one in which the carbon atom bearing the hydroxyl group is bonded to only one other carbon atom.
Secondary alcohol is the one in which the carbon atom bearing the hydroxyl group is bonded to two other carbon atoms.
Tertiary alcohol is the one in which the carbon atom bearing the hydroxyl group is bonded to three other carbon atoms.
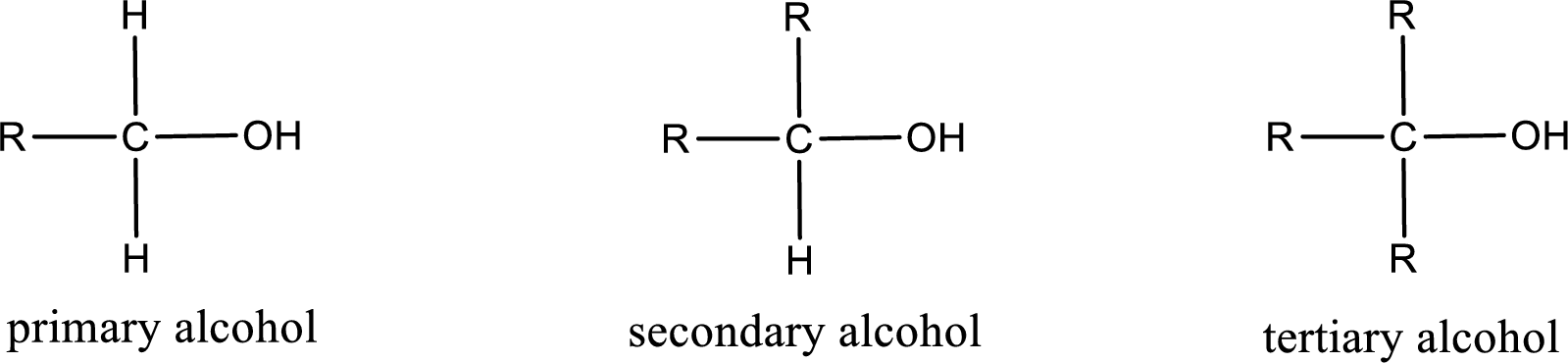
Primary is denoted as
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 14 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry Seventh Edition
- 8:16 PM Sun Mar 30 K Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Proble 1. CH3MgBr 2. H3O+ F Drawingarrow_forwardо но оarrow_forwardName the major organic product of the following action of 4-chloro-4-methyl-1-pentanol in neutral pollution 10+ Now the product. The product has a molecular formula f b. In a singly hain, the starting, material again converts into a secule with the molecular kormula CIO. but with comply Draw the major organic structure inhalationarrow_forward
- Macmillan Learning Alcohols can be oxidized by chromic acid derivatives. One such reagent is pyridinium chlorochromate, (C,H,NH*)(CICTO3), commonly known as PCC. Draw the proposed (neutral) intermediate and the organic product in the oxidation of 1-butanol by PCC when carried out in an anhydrous solvent such as CH₂C₁₂. PCC Intermediate OH CH2Cl2 Draw the intermediate. Select Draw Templates More с H Cr о Product Draw the product. Erase Select Draw Templates More H о Erasearrow_forwardIf I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound A, I have to add NaOH and another compound. Indicate which compound that would be. A C6H5 CH3arrow_forwardProvide the reagents for the following reactions.arrow_forward
- If I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound Z, I have to add two compounds A1 and A2. Indicate which compounds are needed. P(C6H5)3arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Assume that the water side product is continuously removed to drive the reaction toward products. O CH3CH2NH2, TSOH Select to Draw >arrow_forwardPredict the major organic product(s) for the following reaction.arrow_forward
- Predict the major organic product(s) for the following reactions.arrow_forwardProvide the complete mechanism for the reactions below. You must include appropriate arrows,intermediates, and formal charges.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by reacting fluorobenzene with a sulfonitric mixture.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





