
(a)
Interpretation:
Condensed structural formula has to be written for the given alcohols and IUPAC name has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
The structural representation of organic compound can be done in 2D and 3D. In two-dimensional representation, there are four types of representation in which an organic compound can be drawn. They are,
- Expanded structural formula
- Condensed structural formula
- Skeletal structural formula
- Line-angle structural formula
Structural formula which shows all the atoms in a molecule along with all the bonds that is connecting the atoms present in the molecule is known as Expanded structural formula.
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Structural formula that shows the bonding between carbon atoms alone in the molecule ignoring the hydrogen atoms being shown explicitly is known as Skeletal structural formula.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula.
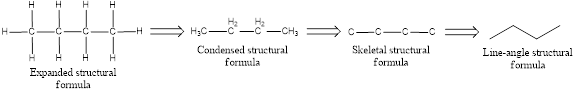
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain single hydroxyl group:
- Longest carbon chain has to be identified that contains hydroxyl group also. The chain name is obtained by replacing the letter “-e” in
alkane with “-ol”. - The numbering has to be given so that the hydroxyl group gets the least numbering.
- Name and location of any other substituent present in the chain has to be identified.
- If in a ring the hydroxyl group is present, then that carbon is numbered 1 and the numbering then proceeds counterclockwise or clockwise in a way that substituents present if any gets the least numbering.
- Hydroxyl group as a substituent in a molecule is named as hydroxy group rather than hydroxyl group.
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain more than one hydroxyl group:
- The same rules said above is followed but the prefix di-, tri-, tetra etc is added corresponding to the number of hydroxyl groups that is present.
(a)
Answer to Problem 14.13EP
The condensed structural formula is,
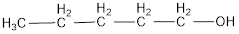
The IUPAC name of the given alcohol is 1-pentanol.
Explanation of Solution
Given name of alcohol is pentyl alcohol.
From the name it is identified that the alkyl group is pentyl and the hydroxyl group is attached to the first carbon atom. The structure can be drawn as,
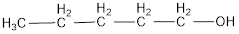
The condensed structural formula for the given alcohol is drawn as shown above.
IUPAC name can be identified by finding the longest continuous carbon chain with the hydroxyl group. In this case it is found to be a five carbon chain and hence the parent is pentane. As the structure has a hydroxyl group in it, the suffix “-ol” has to be added instead of “-e” in the parent alkane. The numbering has to be given in a way that the hydroxyl group gets the least numbering. This gives the IUPAC name of the alcohol as 1-pentanol as hydroxyl is in the first carbon atom.
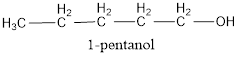
The condensed structural formula for the given alcohol is drawn and IUPAC name is assigned.
(b)
Interpretation:
Condensed structural formula has to be written for the given alcohols and IUPAC name has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
The structural representation of organic compound can be done in 2D and 3D. In two-dimensional representation, there are four types of representation in which an organic compound can be drawn. They are,
- Expanded structural formula
- Condensed structural formula
- Skeletal structural formula
- Line-angle structural formula
Structural formula which shows all the atoms in a molecule along with all the bonds that is connecting the atoms present in the molecule is known as Expanded structural formula.
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Structural formula that shows the bonding between carbon atoms alone in the molecule ignoring the hydrogen atoms being shown explicitly is known as Skeletal structural formula.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula.
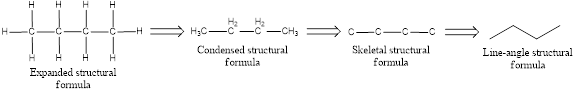
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain single hydroxyl group:
- Longest carbon chain has to be identified that contains hydroxyl group also. The chain name is obtained by replacing the letter “-e” in alkane with “-ol”.
- The numbering has to be given so that the hydroxyl group gets the least numbering.
- Name and location of any other substituent present in the chain has to be identified.
- If in a ring the hydroxyl group is present, then that carbon is numbered 1 and the numbering then proceeds counterclockwise or clockwise in a way that substituents present if any gets the least numbering.
- Hydroxyl group as a substituent in a molecule is named as hydroxy group rather than hydroxyl group.
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain more than one hydroxyl group:
- The same rules said above is followed but the prefix di-, tri-, tetra etc is added corresponding to the number of hydroxyl groups that is present.
(b)
Answer to Problem 14.13EP
The condensed structural formula is,
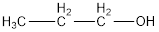
The IUPAC name of the given alcohol is 1-propanol.
Explanation of Solution
Given name of alcohol is propyl alcohol.
From the name it is identified that the alkyl group is propyl and the hydroxyl group is attached to the first carbon atom. The structure can be drawn as,
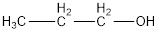
The condensed structural formula for the given alcohol is drawn as shown above.
IUPAC name can be identified by finding the longest continuous carbon chain with the hydroxyl group. In this case it is found to be a three carbon chain and hence the parent is propane. As the structure has a hydroxyl group in it, the suffix “-ol” has to be added instead of “-e” in the parent alkane. The numbering has to be given in a way that the hydroxyl group gets the least numbering. This gives the IUPAC name of the alcohol as 1-propanol as hydroxyl is in the first carbon atom.
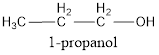
The condensed structural formula for the given alcohol is drawn and IUPAC name is assigned.
(c)
Interpretation:
Condensed structural formula has to be written for the given alcohols and IUPAC name has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
The structural representation of organic compound can be done in 2D and 3D. In two-dimensional representation, there are four types of representation in which an organic compound can be drawn. They are,
- Expanded structural formula
- Condensed structural formula
- Skeletal structural formula
- Line-angle structural formula
Structural formula which shows all the atoms in a molecule along with all the bonds that is connecting the atoms present in the molecule is known as Expanded structural formula.
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Structural formula that shows the bonding between carbon atoms alone in the molecule ignoring the hydrogen atoms being shown explicitly is known as Skeletal structural formula.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula.
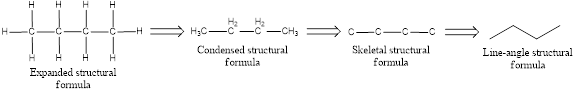
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain single hydroxyl group:
- Longest carbon chain has to be identified that contains hydroxyl group also. The chain name is obtained by replacing the letter “-e” in alkane with “-ol”.
- The numbering has to be given so that the hydroxyl group gets the least numbering.
- Name and location of any other substituent present in the chain has to be identified.
- If in a ring the hydroxyl group is present, then that carbon is numbered 1 and the numbering then proceeds counterclockwise or clockwise in a way that substituents present if any gets the least numbering.
- Hydroxyl group as a substituent in a molecule is named as hydroxy group rather than hydroxyl group.
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain more than one hydroxyl group:
- The same rules said above is followed but the prefix di-, tri-, tetra etc is added corresponding to the number of hydroxyl groups that is present.
(c)
Answer to Problem 14.13EP
The condensed structural formula is,
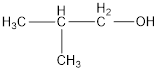
The IUPAC name of the given alcohol is 2-methyl-1-propanol.
Explanation of Solution
Given name of alcohol is isobutyl alcohol.
From the name it is identified that the alkyl group is isobutyl and the hydroxyl group is attached present. The structure can be drawn as,
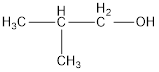
The condensed structural formula for the given alcohol is drawn as shown above.
IUPAC name can be identified by finding the longest continuous carbon chain with the hydroxyl group. In this case it is found to be a three carbon chain and hence the parent is propane. As the structure has a hydroxyl group in it, the suffix “-ol” has to be added instead of “-e” in the parent alkane. The numbering has to be given in a way that the hydroxyl group gets the least numbering. Looking for the substituents, a methyl group is present in the second carbon atom. This gives the IUPAC name of the alcohol as 2-methyl-1-propanol as hydroxyl is in the first carbon atom.
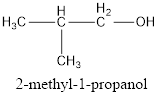
The condensed structural formula for the given alcohol is drawn and IUPAC name is assigned.
(d)
Interpretation:
Condensed structural formula has to be written for the given alcohols and IUPAC name has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
The structural representation of organic compound can be done in 2D and 3D. In two-dimensional representation, there are four types of representation in which an organic compound can be drawn. They are,
- Expanded structural formula
- Condensed structural formula
- Skeletal structural formula
- Line-angle structural formula
Structural formula which shows all the atoms in a molecule along with all the bonds that is connecting the atoms present in the molecule is known as Expanded structural formula.
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Structural formula that shows the bonding between carbon atoms alone in the molecule ignoring the hydrogen atoms being shown explicitly is known as Skeletal structural formula.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula.
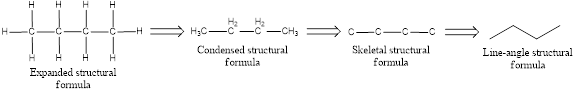
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain single hydroxyl group:
- Longest carbon chain has to be identified that contains hydroxyl group also. The chain name is obtained by replacing the letter “-e” in alkane with “-ol”.
- The numbering has to be given so that the hydroxyl group gets the least numbering.
- Name and location of any other substituent present in the chain has to be identified.
- If in a ring the hydroxyl group is present, then that carbon is numbered 1 and the numbering then proceeds counterclockwise or clockwise in a way that substituents present if any gets the least numbering.
- Hydroxyl group as a substituent in a molecule is named as hydroxy group rather than hydroxyl group.
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain more than one hydroxyl group:
- The same rules said above is followed but the prefix di-, tri-, tetra etc is added corresponding to the number of hydroxyl groups that is present.
(d)
Answer to Problem 14.13EP
The condensed structural formula is,
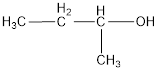
The IUPAC name of the given alcohol is 2-butanol.
Explanation of Solution
Given name of alcohol is sec-butyl alcohol.
From the name it is identified that the alkyl group is sec-butyl and the hydroxyl group is attached to the second carbon atom. The structure can be drawn as,
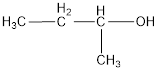
The condensed structural formula for the given alcohol is drawn as shown above.
IUPAC name can be identified by finding the longest continuous carbon chain with the hydroxyl group. In this case it is found to be a four carbon chain and hence the parent is butane. As the structure has a hydroxyl group in it, the suffix “-ol” has to be added instead of “-e” in the parent alkane. The numbering has to be given in a way that the hydroxyl group gets the least numbering. This gives the IUPAC name of the alcohol as 2-butanol as hydroxyl is in the second carbon atom.
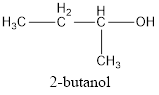
The condensed structural formula for the given alcohol is drawn and IUPAC name is assigned.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry Seventh Edition
- The quantum yield of the photochemical decay of HI is 2. Calculating the moles of HI per kJ of radiant energy can be decayed knowing that the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 490 kJ.arrow_forwardThe quantum yield of the photochemical decay of HI is 2. Calculate the number of Einsteins absorbed per mole knowing that the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 490 kJ.arrow_forwardThe quantum yield of the photochemical decay of HI is 2. How many moles of HI per kJ of radiant energy can be decayed knowing that the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 490 kJ.arrow_forward
- If the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 450 kJ, the number of Einsteins absorbed per 1 mole.arrow_forwardWhen propionic aldehyde in vapor form at 200 mmHg and 30°C is irradiated with radiation of wavelength 302 nm, the quantum yield with respect to the formation of CO is 0.54. If the intensity of the incident radiation is 1.5x10-3 W, find the rate of formation of CO.arrow_forwardDraw mechanismarrow_forward
- Does Avogadro's number have units?arrow_forwardExplain why the total E in an Einstein depends on the frequency or wavelength of the light.arrow_forwardIf the dissociation energy of one mole of O2 is 5.17 eV, determine the wavelength that must be used to dissociate it with electromagnetic radiation. Indicate how many Einstein's of this radiation are needed to dissociate 1 liter of O2 at 25°C and 1 atm of pressure.Data: 1 eV = 96485 kJ mol-1; R = 0.082 atm L K-1; c = 2.998x108 m s-1; h = 6.626x10-34 J s; NA = 6.022x 1023 mol-1arrow_forward
- Indicate the number of Einsteins that are equivalent to 550 kJ mol⁻¹ of absorbed energy (wavelength 475 nm).arrow_forwardIndicate the number of einsteins that are equivalent to 550 kJ mol⁻¹ of absorbed energy?arrow_forwardA unit used in photochemistry is the einstein. If 400 kJ mol-1 of energy has been absorbed, how many einsteins is this equivalent to?arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning





