
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the given structure has to be written.
Concept introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts, namely Prefix, suffix and root word.
Prefix- Represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix- Denotes the presence of
Root word - Represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
(a)
Answer to Problem 14.21UKC
The name of the compound is 5-Methyl-3-hexanol.
Explanation of Solution
The name of the alcohol is given below,
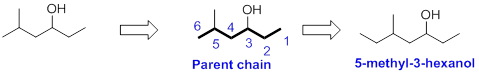
The number of carbon in parent chain is six, hence it is called as hexane. The functional group of the given molecule is alcohol therefore the suffix “ane” is replaced with “ol” indicating the presence of alcohol. In the given structure the third carbon is bonded with alcohol
(b)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the given structure has to be written.
Concept introduction:
Naming
- (1) Substituted benzenes are named using ‘-benzene’ as the parent.
- (2) When benzene has more than one substituent, the position of those substituents is indicated by numbers or by ortho(o-), meta(m-) or para(p-).
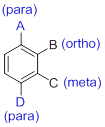
(b)
Answer to Problem 14.21UKC
The name of the compound is 1-Methoxy-3-methylbenzene.
Explanation of Solution
The name of the compound is given below,
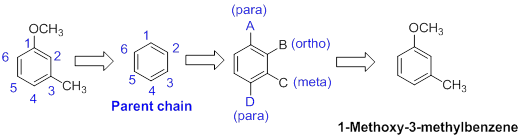
The parent ring is benzene. The functional group of the given molecule is methoxy and methyl group. The location of methoxy is in the first carbon and methyl group is third carbon of the benzene ring. Therefore the name of the molecule is 1-Methoxy-3-methylbenzene.
(c)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the given structure has to be written.
Concept introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts, namely Prefix, suffix and root word.
Prefix- Represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix- Denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc. To add suffix to name a compound, the suffix “-ane” in the parent alkane is replaced by the respective suffix, which corresponds to the functional group present in the given compound. For carboxylic acid, suffix “-oic” will be added, for alcohol, suffix “-ol” will be added and so on
Root word - Represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
(c)
Answer to Problem 14.21UKC
The name of the compound is 3-Methylcyclohexanol.
Explanation of Solution
The name of the compound is given below,
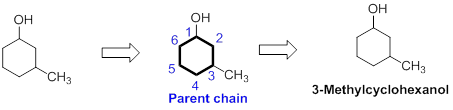
The number of carbon in parent chain is six and it is in the form of cycle, hence it is called as cyclohexane. The functional group of the given molecule is alcohol therefore the suffix “ane” is replaced with “ol” indicating the presence of alcohol. In the given structure, the first carbon is bonded with alcohol and third carbon is bonded with methyl
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
FUND.OF GEN CHEM CHAP 1-13 W/ACCESS
- Which type of enzyme catalyses the following reaction? oxidoreductase, transferase, hydrolase, lyase, isomerase, or ligase.arrow_forward+NH+ CO₂ +P H₂N + ATP H₂N NH₂ +ADParrow_forwardWhich type of enzyme catalyses the following reaction? oxidoreductase, transferase, hydrolase, lyase, isomerase, or ligase.arrow_forward
- Which features of the curves in Figure 30-2 indicates that the enzyme is not consumed in the overall reaction? ES is lower in energy that E + S and EP is lower in energy than E + P. What does this tell you about the stability of ES versus E + S and EP versus E + P.arrow_forwardLooking at the figure 30-5 what intermolecular forces are present between the substrate and the enzyme and the substrate and cofactors.arrow_forwardprovide short answers to the followings Urgent!arrow_forward
- Pyruvate is accepted into the TCA cycle by a “feeder” reaction using the pyruvatedehydrogenase complex, resulting in acetyl-CoA and CO2. Provide a full mechanismfor this reaction utilizing the TPP cofactor. Include the roles of all cofactors.arrow_forwardB- Vitamins are converted readily into important metabolic cofactors. Deficiency inany one of them has serious side effects. a. The disease beriberi results from a vitamin B 1 (Thiamine) deficiency and ischaracterized by cardiac and neurological symptoms. One key diagnostic forthis disease is an increased level of pyruvate and α-ketoglutarate in thebloodstream. How does this vitamin deficiency lead to increased serumlevels of these factors? b. What would you expect the effect on the TCA intermediates for a patientsuffering from vitamin B 5 deficiency? c. What would you expect the effect on the TCA intermediates for a patientsuffering from vitamin B 2 /B 3 deficiency?arrow_forwardDraw the Krebs Cycle and show the entry points for the amino acids Alanine,Glutamic Acid, Asparagine, and Valine into the Krebs Cycle - (Draw the Mechanism). How many rounds of Krebs will be required to waste all Carbons of Glutamic Acidas CO2?arrow_forward
 Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning- Essentials of Pharmacology for Health ProfessionsNursingISBN:9781305441620Author:WOODROWPublisher:Cengage
 Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College





