
Concept explainers
When Mendel did crosses of true-breeding purple- and white-flowered pea plants, the white-flowered trait disappeared from the F1. generation but reappeared in the F2 generation. Use genetic terms to explain why that happened.
To explain: Why the white color trait disappeared in the F1 generation and was again observed in the F2 generation in Mendel’s cross between purple- and white- flowered pea plants.
Introduction: Genes have alternate forms known as alleles, which are transmitted to offspring. If the two alleles are different, then there is a hybrid in the F1 generation. The dominant allele out of the two expresses itself and determines the phenotype. In F1 individuals, two different alleles segregate into gametes. During self-pollination, the gametes unite randomly, thereby giving a chance to recessive alleles to be expressed in a homozygous state at the F2 generation.
Explanation of Solution
The cross between the individuals that are true breeding homozygous for one allele gives different traits in F1 progeny. This is called as monohybrid cross. Several traits of pea plants were studied in which Mendel used the purple- and white-colored flower traits to perform monohybrid experiment. When Mendel crossed these plants, the F1 hybrids or first true breeding generation received was both dominant and recessive alleles equally but showed a purple pigment. This is because the purple-colored trait was dominant over white. That is, white-colored trait is and was not expressed recessive in the F1 generation. However, the white trait was expressed in F2 generation of the experiment. This was because it is only possible for a white allele to exist in a homozygous state, which causes the white trait to be expressed in F2 generation.
Pictorial representation: Fig.1 shows Mendel’s cross between purple- and white-flowered pea plants.
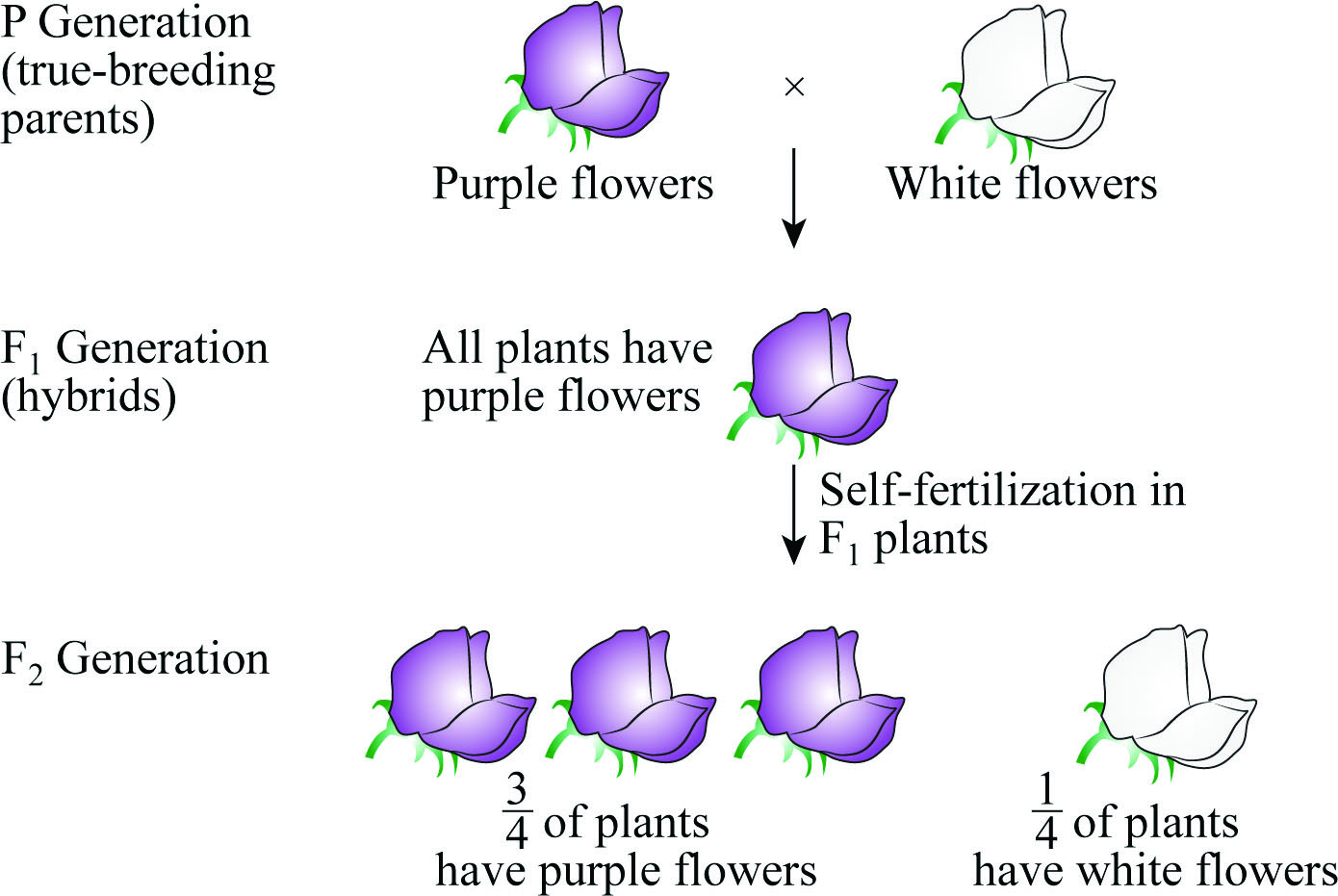
Fig.1: Mendel’s cross between purple- and white-flowered pea plants
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Campbell Biology (10th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
- In one paragraph show how atoms and they're structure are related to the structure of dna and proteins. Talk about what atoms are. what they're made of, why chemical bonding is important to DNA?arrow_forwardWhat are the structure and properties of atoms and chemical bonds (especially how they relate to DNA and proteins).arrow_forwardThe Sentinel Cell: Nature’s Answer to Cancer?arrow_forward
- Molecular Biology Question You are working to characterize a novel protein in mice. Analysis shows that high levels of the primary transcript that codes for this protein are found in tissue from the brain, muscle, liver, and pancreas. However, an antibody that recognizes the C-terminal portion of the protein indicates that the protein is present in brain, muscle, and liver, but not in the pancreas. What is the most likely explanation for this result?arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Explain/discuss how “slow stop” and “quick/fast stop” mutants wereused to identify different protein involved in DNA replication in E. coli.arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Question A gene that codes for a protein was removed from a eukaryotic cell and inserted into a prokaryotic cell. Although the gene was successfully transcribed and translated, it produced a different protein than it produced in the eukaryotic cell. What is the most likely explanation?arrow_forward
- Molecular Biology LIST three characteristics of origins of replicationarrow_forwardMolecular Biology Question Please help. Thank you For E coli DNA polymerase III, give the structure and function of the b-clamp sub-complex. Describe how the structure of this sub-complex is important for it’s function.arrow_forwardMolecular Biology LIST three characteristics of DNA Polymerasesarrow_forward
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning





