
Concept explainers
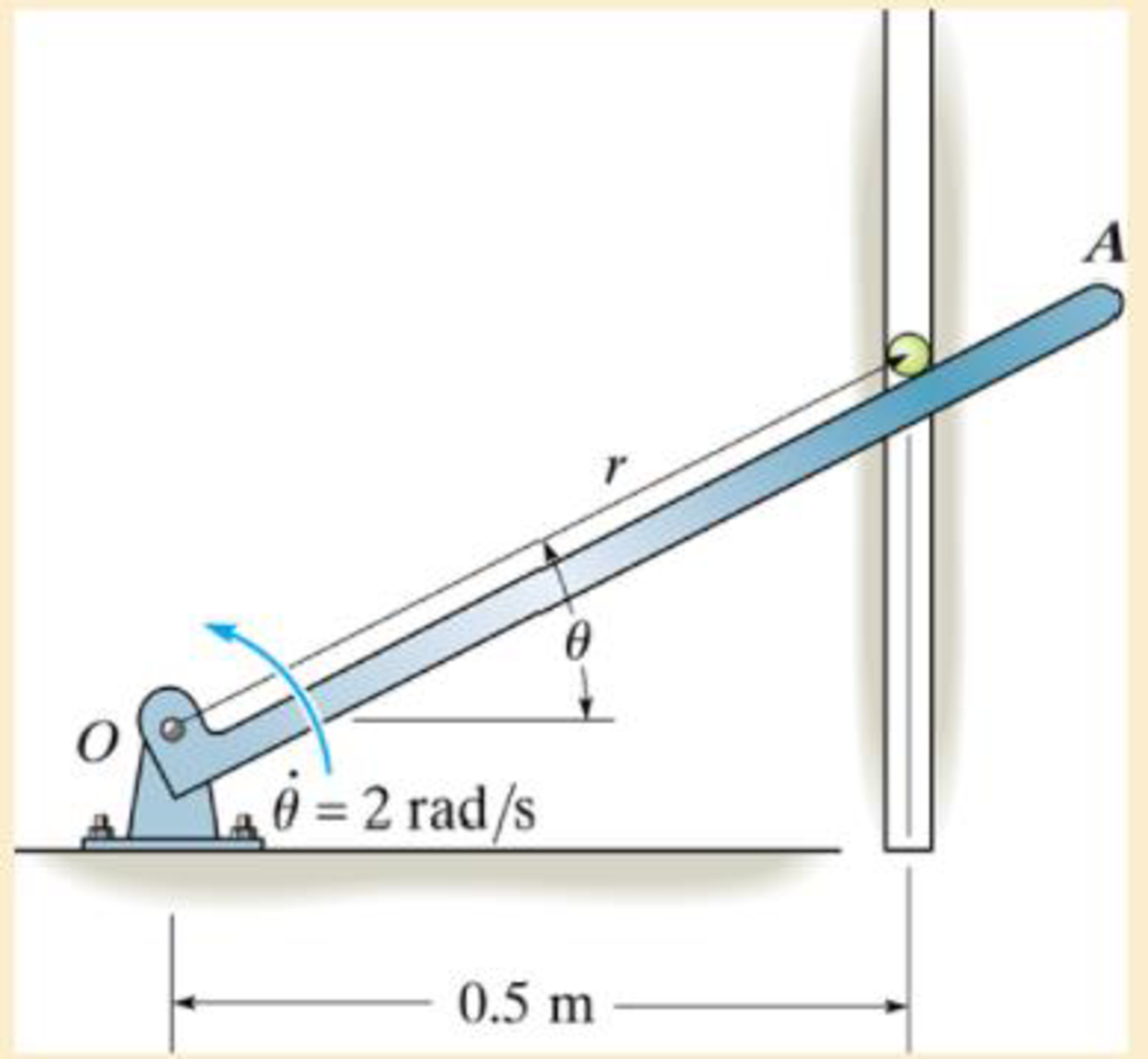
The particle has a mass of 0.5 kg and is confined to move along the smooth vertical slot due to the rotation of the arm OA. Determine the force of the rod on the particle and the normal force of the slot on the particle when θ = 30°. The rod is rotating with a constant angular velocity
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 13 Solutions
EP ENGR.MECH.:DYNAMICS-REV.MOD.MAS.ACC.
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Statics & Dynamics (14th Edition)
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, and Service (5th Edition)
Statics and Mechanics of Materials (5th Edition)
Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Applied Fluid Mechanics (7th Edition)
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (3rd Edition)
- The smooth particle has a mass of 80g. It is attached to an elastic cord extending from O to P and due to the slotted arm guide moves along the horizonta! circular path r = (0.8 sin 8)m. If the cord has a stiffness k = 30(N/m) and an un-stretched length of 0.25m, determine the angular velocity required so the force of the guide on the particle is 7.67N when 0 = 60°. 0.4 marrow_forwardThe 0.5-lb particle is guided along the circular path using the slotted arm guide. If the arm has an angular velocity ?̇ = 8 rad/s and an angular acceleration ?̈ = 4 rad/s2 at the instant ? = 30°, determine the force of the guide on the particle. Motion occurs in the horizontal plane. Show every single step of the solution pleasearrow_forwardThe spring is not stretched or compressed when “s=0.8m" and the 11 kg block which is subjected to a force of 105 N has a speed of 5.5 m/s down the smooth plane. Using "THE PRINCIPLE OF WORK AND ENERGY", find the distance "s" when the block STOPS. k = 200 N/m 5 m/s F = 100 N 30°arrow_forward
- The particle of mass m = 2.5 kg is attached to the light rigid rod of length L = 1.27 m, and the assembly rotates about a horizontal axis through O with a constant angular velocity = w = 3.2 rad/s. Determine the force T in the rod when 0 = 36°. The force Tis positive if in tension, negative if in compression. L Ꮎ marrow_forwardRod OA rotates counterclockwise at a constant angular rate θ˙ = 4 rad/s. The double collar B is pin-connected together such that one collar slides over the rotating rod and the other collar slides over the circular rod described by the equation r=(1.6cosθ)m. Both collars have a mass of 0.55 kg . Motion is in the horizontal plane. Determine the magnitude of the force which the circular rod exerts on one of the collars at the instant θ = 45∘ Determine the magnitude of the force that OA exerts on the other collar at the instant θ = 45∘arrow_forwardThe smooth particle has a mass of 80 g. It is attached to an elastic cord extending from O to P and due to the slotted arm guide moves along the horizontal circular path r=(0.8sinθ)m. If the cord has a stiffness k= 24 N/m and an unstretched length of 0.25 m, determine the force of the guide on the particle when θ=60. The guide has a constant angular velocity θ˙=5rad/sarrow_forward
- The 1.334-Mg car is traveling along the curved road described by r = (50e28) m, where 0 is in radians. If a camera is located at A and it rotates with an angular velocity of Ó = 0.083 rad/s and an angular acceleration of ö = 0.304 rad/s? at the instant 0 = 0.879 rad, .determine the resultant friction force developed between the tires and the road at this instant %3D r= (50")marrow_forwardThe 4-lb collar is compressed against a spring a distance of 6 inches and then releasedfrom rest. The spring can be considered elastic and has a constant of k = 10 lb/in. Thespring is not adhered to the collar, and can be considered massless, so it will notextend into tension. Plot the acceleration of the collar as a function of x for x = 0 to 7 inches.What is the velocity as the collar leaves the spring?arrow_forwardThe box with a weight of 6 lb slides down the smooth surface that has a circular portion AB. If the speed of the box is 8 ft/sec at A, calculate the magnitude of the normal force acting on the box at C. Present your answer in lb using 3 significant figures. The following relations may be useful: sin(A + B)=sin A c ·cos B±cos A-sin B cos(A + B) = cos A cos B sin A-sin B 45° B 0=30° 20 ft 8 ft/s A 45°arrow_forward
- Solve it correctly please. Iarrow_forwardvery quick reply thank you in advancearrow_forwardRod OA rotates counterclockwise at a constant angular rate 0 = 4 rad/s. The double collar Bis pin-connected together such that Determine the magnitude of the force which the circular rod exerts on one of the collars at the instant 0 = 45°. one collar slides over the rotating rod and the other collar slides over the circular rod described by the equation r = (1.6 cos 0) m Both collars have a mass of 0.65 kg. Motion is in the vertical plane. (Figure 1) Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. HA ? F = - 11.766 Figure 1 of 1 Submit Previous Answers Request Answer X Incorrect; Try Again; 3 attempts remaining r = 1.6 cos 0 0 = 4 rad/s B Part B Determine the magnitude of the force that OA exerts on the other collar at the instant 0 = 45°. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. 0.8 m HẢ ? FOA = 11.766arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





