
EP ENGR.MECH.:DYNAMICS-REV.MOD.MAS.ACC.
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133976588
Author: HIBBELER
Publisher: PEARSON CO
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 13.5, Problem 80P
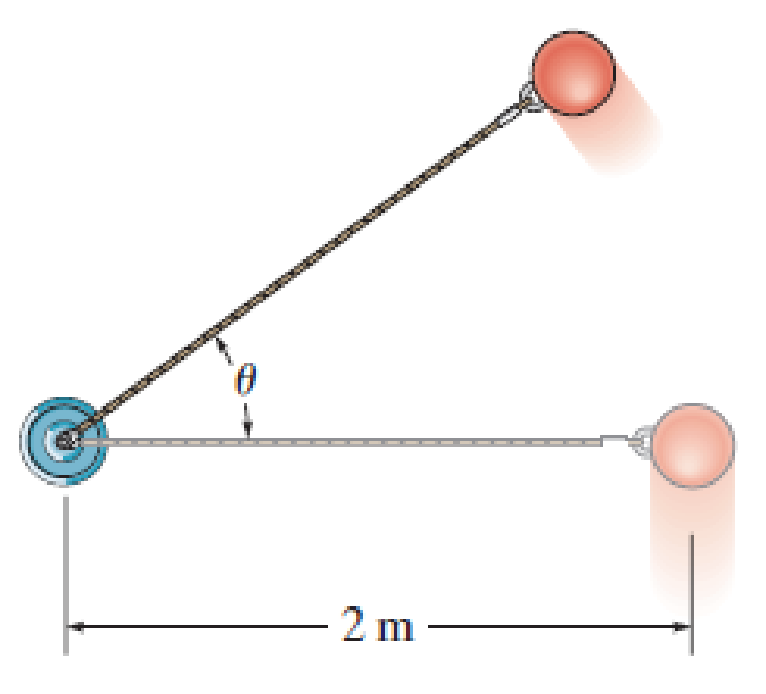
The 2-kg pendulum bob moves in the vertical plane with a velocity of 8 m/s when θ = 0°. Determine the initial tension in the cord and also at the instant the bob reaches θ = 30°. Neglect the size of the bob.
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule08:17
Students have asked these similar questions
۳/۱
العنوان
O
не
شكا
+91x PU + 96852
A heavy car plunges into a lake during an accident and lands at the bottom of the lake
on its wheels as shown in figure. The door is 1.2 m high and I m wide, and the top edge of
Deine the hadrostatic force on the
Plot the displacement diagram for a cam with roller follower of diameter 10 mm. The required
motion is as follows;
1- Rising 60 mm in 135° with uniform acceleration and retardation motion.
2- Dwell 90°
3- Falling 60 mm for 135° with Uniform acceleration-retardation motion.
Then design the cam profile to give the above displacement diagram if the minimum circle
diameter of the cam is 50 mm.
=
-20125
750 x2.01
Plot the displacement diagram for a cam with roller follower of diameter 10 mm. The required
motion is as follows;
1- Rising 60 mm in 135° with uniform acceleration and retardation motion.
2- Dwell 90°
3- Falling 60 mm for 135° with Uniform acceleration-retardation motion.
Then design the cam profile to give the above displacement diagram if the minimum circle
diameter of the cam is 50 mm.
Q1/ A vertical, circular gate with water on one side as shown. Determine
the total resultant force acting on the gate and the location of the center of
pressure, use water specific weight 9.81 kN/m³
1 m
4 m
Chapter 13 Solutions
EP ENGR.MECH.:DYNAMICS-REV.MOD.MAS.ACC.
Ch. 13.4 - In each case, determine its velocity when t = 2 s...Ch. 13.4 - In each case, determine its velocity at s = 8 m if...Ch. 13.4 - Determine the initial acceleration of the 10-kg...Ch. 13.4 - Write the equations of motion in the x and y...Ch. 13.4 - The motor winds n the cable with a constant...Ch. 13.4 - If motor M exerts a force of F = (10t2 + 100) N on...Ch. 13.4 - A spring of stiffness k = 500 N/m is mounted...Ch. 13.4 - The spring has a stiffness k = 200 N/m and is...Ch. 13.4 - Block B rests upon a smooth surface. If the...Ch. 13.4 - The 6-lb particle is subjected to the action of...
Ch. 13.4 - The two boxcars A and B have a weight of 20 000 lb...Ch. 13.4 - If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the...Ch. 13.4 - If the 50-kg crate starts from rest and achieves a...Ch. 13.4 - If blocks A and B of mass 10 kg and 6 kg...Ch. 13.4 - The 10-lb block has a speed of 4 ft/s when the...Ch. 13.4 - The 10-lb block has a speed of 4 ft/s when the...Ch. 13.4 - The speed of the 3500-lb sports car is plotted...Ch. 13.4 - The conveyor belt is moving at 4 m/s. If the...Ch. 13.4 - The conveyor belt is designed to transport...Ch. 13.4 - Determine the time needed to pull the cord at B...Ch. 13.4 - Cylinder B has a mass m and is hoisted using the...Ch. 13.4 - Block A has a weight of 8 lb and block B has a...Ch. 13.4 - The 2-Mg truck is traveling at 15 m/s when the...Ch. 13.4 - The motor lifts the 50-kg crate with an...Ch. 13.4 - The 75-kg man pushes on the 150-kg crate with a...Ch. 13.4 - The coefficient of kinetic friction is k, and the...Ch. 13.4 - A 40-lb suitcase slides from rest 20 ft down the...Ch. 13.4 - Solve Prob. 13-18 if the suitcase has an initial...Ch. 13.4 - If the coefficient of kinetic friction between...Ch. 13.4 - The conveyor belt delivers each 12-kg crate to the...Ch. 13.4 - The 50-kg block A is released from rest. Determine...Ch. 13.4 - If the supplied force F = 150 N, determine the...Ch. 13.4 - A 60-kg suitcase slides from rest 5 m down the...Ch. 13.4 - Solve Prob. 13-24 if the suitcase has an initial...Ch. 13.4 - The 1.5 Mg sports car has a tractive force of F =...Ch. 13.4 - The conveyor belt is moving downward at 4 m/s. If...Ch. 13.4 - At the instant shown the 100-lb block A is moving...Ch. 13.4 - Determine the velocity of the 200-lb crate when t...Ch. 13.4 - Determine the velocity of the 400-kg crate A when...Ch. 13.4 - The tractor is used to lift the 150-kg load B with...Ch. 13.4 - If the tractor travels to the right with an...Ch. 13.4 - Block A and B each have a mass m. Determine the...Ch. 13.4 - The 4-kg smooth cylinder is supported by the...Ch. 13.4 - The coefficient of static friction between the...Ch. 13.4 - If the spring is unstretched when s = 0 and the...Ch. 13.4 - Neglecting the mass of the rope and pulley, and...Ch. 13.4 - Determine the force in the cable when t = 5 s, if...Ch. 13.4 - An electron of mass m is discharged with an...Ch. 13.4 - The 400-lb cylinder at A is hoisted using the...Ch. 13.4 - What is their velocity at this instant?Ch. 13.4 - Block A has a mass mA and is attached to a spring...Ch. 13.4 - A parachutist having a mass m opens his parachute...Ch. 13.4 - Neglect the mass of the motor and pulleys.Ch. 13.4 - If the force exerted on cable AB by the motor is F...Ch. 13.4 - Blocks A and B each have a mass m. Determine the...Ch. 13.4 - Blocks A and Beach have a mass m. Determine the...Ch. 13.4 - If the board AC pushes on the block at an angle ...Ch. 13.4 - If a horizontal force P = 12lb is applied to block...Ch. 13.4 - A freight elevator, including its load, has a mass...Ch. 13.4 - The block A has a mass mA and rests on the pan B,...Ch. 13.5 - P13-5.Set up the n, t axes and write the equations...Ch. 13.5 - P13-6.Set up the n, b, t axes and write the...Ch. 13.5 - The block rests at a distance of 2 m from the...Ch. 13.5 - Prob. 8FPCh. 13.5 - A pilot weighs 150 lb and is traveling at a...Ch. 13.5 - The sports car is traveling along a 30 banked road...Ch. 13.5 - If the 10-kg ball has a velocity of 3m/ s when it...Ch. 13.5 - The motorcycle has a mass of 0.5 Mg and a...Ch. 13.5 - Prob. 52PCh. 13.5 - Prob. 53PCh. 13.5 - The 2-kg block B and 15-kg cylinder A are...Ch. 13.5 - Determine the maximum constant speed at which the...Ch. 13.5 - Cartons having a mass of 5 kg are required to move...Ch. 13.5 - Prob. 57PCh. 13.5 - Prob. 58PCh. 13.5 - Prob. 59PCh. 13.5 - Prob. 60PCh. 13.5 - At the instant B = 60, the boys center of mass G...Ch. 13.5 - A girl having a mass of 25 kg sits at the edge of...Ch. 13.5 - The pendulum bob B has a weight of 5 lb and is...Ch. 13.5 - The pendulum bob B has a mass m and is released...Ch. 13.5 - Determine the constant speed of the passengers on...Ch. 13.5 - A motorcyclist in a circus rides his motorcycle...Ch. 13.5 - The vehicle is designed to combine the feel of a...Ch. 13.5 - The 0.8-Mg car travels over the hill having the...Ch. 13.5 - The 0.8-Mg car travels over the hill having the...Ch. 13.5 - When it reaches the curved portion AB, it is...Ch. 13.5 - Determine the resultant normal and frictional...Ch. 13.5 - If he rotates about the z axis with a constant...Ch. 13.5 - Determine the maximum speed at which the car with...Ch. 13.5 - Determine the maximum constant speed at which the...Ch. 13.5 - The box has a mass m and slides down the smooth...Ch. 13.5 - Prove that if the block is released from rest at...Ch. 13.5 - The cylindrical plug has a weight of 2 lb and it...Ch. 13.5 - When crossing an intersection, a motorcyclist...Ch. 13.5 - The airplane, traveling at a constant speed of 50...Ch. 13.5 - The 2-kg pendulum bob moves in the vertical plane...Ch. 13.5 - The 2-kg pendulum bob moves in the vertical plane...Ch. 13.5 - If it has a speed of 1.5 m/s when y = 0.2 m,...Ch. 13.5 - The ball has a mass m and is attached to the cord...Ch. 13.6 - If the attached spring has a stiffness k = 2...Ch. 13.6 - Determine the constant angular velocity of the...Ch. 13.6 - If = ( t2) rad, where t is in seconds, determine...Ch. 13.6 - The 2-Mg car is traveling along the curved road...Ch. 13.6 - The 0.2-kg pin P is constrained to move in the...Ch. 13.6 - If the cam is rotating at a constant rate of 6...Ch. 13.6 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force...Ch. 13.6 - Determine the magnitude of the unbalanced force...Ch. 13.6 - Rod OA rotates counterclockwise with a constant...Ch. 13.6 - The boy of mass 40 kg is sliding down the spiral...Ch. 13.6 - Using a forked rod, a 0.5-kg smooth peg P is...Ch. 13.6 - The arm is rotating at a rate of = 4 rad/s when ...Ch. 13.6 - If arm OA rotates with a constant clockwise...Ch. 13.6 - Determine the normal and frictional driving forces...Ch. 13.6 - A smooth can C, having a mass of 3 kg, is lifted...Ch. 13.6 - Prob. 96PCh. 13.6 - Prob. 97PCh. 13.6 - The particle has a mass of 0.5 kg and is confined...Ch. 13.6 - A car of a roller coaster travels along a track...Ch. 13.6 - The 0.5-lb ball is guided along the vertical...Ch. 13.6 - The ball of mass misguided along the vertical...Ch. 13.6 - Using a forked rod, a smooth cylinder P, having a...Ch. 13.6 - The pilot of the airplane executes a vertical loop...Ch. 13.6 - The collar has a mass of 2 kg and travels along...Ch. 13.6 - The particle has a mass of 0.5 kg and is confined...Ch. 13.6 - Solve Prob. 13-105 If the arm has an angular...Ch. 13.6 - The forked rod is used to move the smooth 2-lb...Ch. 13.6 - Prob. 108PCh. 13.6 - Rod OA rotates counterclockwise at a constant...Ch. 13.6 - Solve Prob. 13-109 if motion is in the vertical...Ch. 13.7 - If his speed is a constant vP = 80 ft/s, determine...Ch. 13.7 - The earth has an orbit with eccentricity 0.0167...Ch. 13.7 - Prob. 114PCh. 13.7 - Determine the speed of a satellite launched...Ch. 13.7 - Prob. 116PCh. 13.7 - Prove Keplers third law of motion. Hint: Use Eqs....Ch. 13.7 - Prob. 118PCh. 13.7 - Prob. 119PCh. 13.7 - Determine the constant speed of satellite S so...Ch. 13.7 - Prob. 121PCh. 13.7 - Prob. 122PCh. 13.7 - Prob. 123PCh. 13.7 - Prob. 124PCh. 13.7 - The rocket is traveling around the earth in free...Ch. 13.7 - Prob. 127PCh. 13.7 - Prob. 128PCh. 13.7 - Prob. 129PCh. 13.7 - Prob. 130PCh. 13.7 - The rocket is traveling around the earth in free...Ch. 13.7 - Prob. 132PCh. 13.7 - Prob. 3CPCh. 13.7 - If the trailer has a mass of 250 kg and coasts 45...Ch. 13.7 - The coefficient of kinetic friction between the...Ch. 13.7 - Block B rests on a smooth surface. If the...Ch. 13.7 - If the motor draws in the cable at a rate of v =...Ch. 13.7 - The ball has a mass of 30 kg and a speed v = 4 m/s...Ch. 13.7 - If the coefficient of static friction between the...Ch. 13.7 - If at the instant it reaches point A it has a...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
102* The sum of seven interior angles ofa closed-polygon traverse each read to the nearest
3 ” is
$99 a 59 '39...
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
In the text, JUMP instructions were expressed by identifying the destination explicitly by stating the name (or...
Computer Science: An Overview (13th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Test Average and Grade Write a program that asks the user to enter five test scores. The program should display...
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Determine the force in members HG, HE and DE of the truss, and state if the members are in tension or compressi...
INTERNATIONAL EDITION---Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 14th edition (SI unit)
Are you required to have a return statement in a void function definition?
Problem Solving with C++ (10th Edition)
Consider the following skeletal C program: void fun1(void); / prototype / void fun2(void); / prototype / void f...
Concepts Of Programming Languages
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- I need handwritten solution with sketches for eacharrow_forwardGiven answers to be: i) 14.65 kN; 6.16 kN; 8.46 kN ii) 8.63 kN; 9.88 kN iii) Bearing 6315 for B1 & B2, or Bearing 6215 for B1arrow_forward(b) A steel 'hot rolled structural hollow section' column of length 5.75 m, has the cross-section shown in Figure Q.5(b) and supports a load of 750 kN. During service, it is subjected to axial compression loading where one end of the column is effectively restrained in position and direction (fixed) and the other is effectively held in position but not in direction (pinned). i) Given that the steel has a design strength of 275 MN/m², determine the load factor for the structural member based upon the BS5950 design approach using Datasheet Q.5(b). [11] ii) Determine the axial load that can be supported by the column using the Rankine-Gordon formula, given that the yield strength of the material is 280 MN/m² and the constant *a* is 1/30000. [6] 300 600 2-300 mm wide x 5 mm thick plates. Figure Q.5(b) L=5.75m Pinned Fixedarrow_forward
- Q1: For the following force system, find the moments with respect to axes x, y, and zarrow_forwardQ10) Body A weighs 600 lb contact with smooth surfaces at D and E. Determine the tension in the cord and the forces acting on C on member BD, also calculate the reaction at B and F. Cable 6' 3' wwwarrow_forwardHelp ارجو مساعدتي في حل هذا السؤالarrow_forward
- Q3: Find the resultant of the force system.arrow_forwardQuestion 1 A three-blade propeller of a diameter of 2 m has an activity factor AF of 200 and its ratio of static thrust coefficient to static torque coefficient is 10. The propeller's integrated lift coefficient is 0.3.arrow_forward(L=6847 mm, q = 5331 N/mm, M = 1408549 N.mm, and El = 8.6 x 1014 N. mm²) X A ΕΙ B L Y Marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Introduction to Undamped Free Vibration of SDOF (1/2) - Structural Dynamics; Author: structurefree;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BkgzEdDlU78;License: Standard Youtube License