
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
From the condensed structures for 2,3-dimethyl-2-pentene whether cis-trans isomers exist or not has to be given. And if it exists, both the isomers has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Condensed structures: A condensed structures only shows the total number of atoms but not bonds exist between the atoms. The vertical and horizontal line which represents bonding all should be omitted.
Line structure: In organic compounds, the series of atoms in the compound are bonded together which shown by drawing a line between them. End of line segment represents carbon
Predicting cis-trans isomers:
In general, the
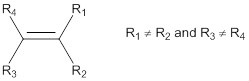
Cis-isomer: In cis-configuration, the two bulkier substituents of the double bond are on the same side.
Trans-isomer: In trans-configuration, the two bulkier substituents of the double bond are on the opposite side.
(b)
Interpretation:
From the both condensed and line structures for 2-Methyl-2-hexene whether cis-trans isomers exist or not has to be given. And if it exists, both the isomers has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Condensed structures: A condensed structures only shows the total number of atoms but not bonds exist between the atoms. The vertical and horizontal line which represents bonding all should be omitted.
Line structure: In organic compounds, the series of atoms in the compound are bonded together which shown by drawing a line between them. End of line segment represents carbon
Cis-isomer: In cis-configuration, the two bulkier substituents of the double bond are on the same side.
Trans-isomer: In trans-configuration, the two bulkier substituents of the double bond are on the opposite side.
(c)
Interpretation:
From the line structures for 2-hexene whether cis-trans isomers exist or not has to be given. And if it exists, both the isomers has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Condensed structures: A condensed structures only shows the total number of atoms but not bonds exist between the atoms. The vertical and horizontal line which represents bonding all should be omitted.
Line structure: In organic compounds, the series of atoms in the compound are bonded together which shown by drawing a line between them. End of line segment represents carbon
Cis-isomer: In cis-configuration, the two bulkier substituents of the double bond are on the same side.
Trans-isomer: In trans-configuration, the two bulkier substituents of the double bond are on the opposite side.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
FUND.OF GEN CHEM CHAP 1-13 W/ACCESS
- Draw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H H ⚫OH HO- -H H- -OH H- -OH CH2OH Ag*, NH4OH, H2O Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H₂O -OH H ⚫OH HO H HO- CH2OH Cu2+ Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H、 H -OH H ⚫OH H -OH CH2OH Fehlings' solution ⑤ Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forward
- Draw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. HO C=0 H ⚫OH H ⚫OH HO- H HO H CH2OH Tollens' solution Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H-C=O HO H HO H H- ⚫OH HO H CH2OH HNO3, H2O Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. HO HO- HO H HO ∙H HO CH2OH NaBH4, CH3OH Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forward
- Draw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Но сво HO H HO H H OH H -OH CH2OH H2 Pd Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forwardDraw the Haworth projection for Gulose-ẞ-1,6-sorbose and answer the following questions. (Gulose will be in the pyranose form and Sorbose will be in the furanose form) a. Label the reducing and nonreducing ends of the disaccharide b. Label the glycosidic bond c. Circle the anomeric carbons and label them as hemiacetals or acetals. d. Can this disaccharide undergo mutarotation?arrow_forwardDraw the product of the reaction below. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H OH HO HO HO ·H H OH H OH excess CH3CH2I KOHarrow_forward
- Draw the Haworth structures for the following: a. α-D-Gulopyranose b. ẞ-D-Sorbofuranose c. The two possible isomers of a-D-altrose (furanose and pyranose forms)arrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. HO H ⚫OH HO- ∙H H- -OH H ⚫OH CH2OH HNO3, H2Oarrow_forwardDraw the product of the reaction below. Ignore inorganic byproducts. HO CH2OH OH OH OH excess CHзI Ag2Oarrow_forward
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College





