
Concept explainers
The following table lists the concentrations of the principal ions in seawater:
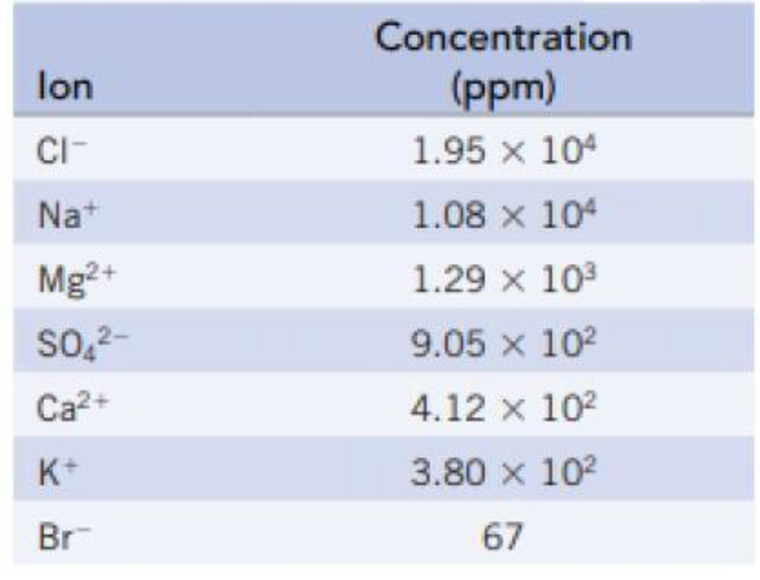
- (a) Calculate the freezing point of seawater.
- (b) Calculate the osmotic pressure of seawater at 25 °C. What is the minimum pressure needed to purify seawater by reverse osmosis?
(a)
Interpretation: The freezing point of seawater has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Colligative properties: Properties of solutions which having influence on the concentration of the solute in it. Colligative properties are,
- Decrease in the vapor pressure
- Increase in the boiling point
- Decline in the freezing point
- Osmotic pressure
Freezing point depression: The freezing point of the solution varies with the solute concentration.
The number of moles of any substance can be determined using the equation
Answer to Problem 79GQ
Freezing point of seawater is
Explanation of Solution
Given,
Molal freezing point depression constant of water is
The value
Hence, the concentration given in ppm can be taken as the mass of each of the ions on
The number of moles of any substance can be determined using the equation
Number of moles of
Number of moles of
Number of moles of
Number of moles of
Number of moles of
Number of moles of
Number of moles of
So the total moles of principle ions in
Molality of seawater is,
Depression in freezing point is,
Therefore,
Freezing point of seawater is,
Freezing point of seawater is
(b)
Interpretation: The osmotic pressure of seawater at
Concept introduction:
Colligative properties: Properties of solutions which having influence on the concentration of the solute in it. Colligative properties are,
- Decrease in the vapor pressure
- Increase in the boiling point
- Decline in the freezing point
- Osmotic pressure
Osmotic pressure: The pressure created by the column of solution for the system at equilibrium is a measure of the osmotic pressure and is calculated by using the equation,
where,
c is the molar concentration
The number of moles of any substance can be determined using the equation
Answer to Problem 79GQ
The osmotic pressure of seawater at
Explanation of Solution
Given,
The molarity of the solute is
The osmotic pressure of seawater is,
The osmotic pressure of seawater at
To purify the seawater using reverse osmosis method, there should be a minimum pressure of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections (2nd Edition)
Physical Science
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Organic Chemistry
- er your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward5.arrow_forward6.arrow_forward
- 0/5 alekscgi/x/sl.exe/1o_u-IgNglkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBaHhvlTCeeBZbufuBYTi0Hz7m7D3ZcSLEFovsXaorzoFtUs | AbtAURtkqzol 1HRAS286, O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 3 pressure (atm) + 0- 0 5+ 200 temperature (K) 400 Explanation Check X 0+ F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 S 2025 McGraw Hill LLC All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Accessibility Q Search LUCR + F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 * % & ( 5 6 7 8 9 Y'S Dele Insert PrtSc + Backsarrow_forward5.arrow_forward9arrow_forward
- alekscgi/x/lsl.exe/1o_u-IgNslkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBanHhvlTCeeBZbufu BYTI0Hz7m7D3ZS18w-nDB10538ZsAtmorZoFusYj2Xu9b78gZo- O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 3- 200 temperature (K) Explanation Chick Q Sowncharrow_forward0+ aleksog/x/lsl.exe/1ou-lgNgkr7j8P3H-IQs pBaHhviTCeeBZbufuBYTOHz7m7D3ZStEPTBSB3u9bsp3Da pl19qomOXLhvWbH9wmXW5zm O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 Gab The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 0.75 atm and -229. °C is increased until the sample sublimes. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.50 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. F3 pressure (atm) 0- 0 200 Explanation temperature (K) Check F4 F5 ☀+ Q Search Chill Will an 9 ENG F6 F7 F8 F9 8 Delete F10 F11 F12 Insert PrtSc 114 d Ararrow_forwardx + LEKS: Using a phase diagram a X n/alekscgi/x/lsl.exe/10_u-IgNsikr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBan HhvlTCeeBZbufu BYTI0Hz7m7D3ZcHYUt80XL-5alyVpw ○ States of Matter Using a phase diagram to find a phase transition temperature or pressure Use the phase diagram of Substance X below to find the melting point of X when the pressure above the solid is 1.1 atm. pressure (atm) 16 08- solid liquid- 0 200 400 gas 600 temperature (K) Note: your answer must be within 25 °C of the exact answer to be graded correct. × 5arrow_forward
- S: Using a phase diagram leksogi/x/sl.exe/1ou-IgNs kr 7j8P3jH-IQs_pBan HhvTCeeBZbufuBYTI0Hz7m7D3ZdHYU+80XL-5alyVp O States of Matter Using a phase diagram to find a phase transition temperature or pressure se the phase diagram of Substance X below to find the boiling point of X when the pressure on the liquid is 1.6 atm. pressure (atm) 32- 16- solid liquid 0. gas 100 200 temperature (K) 300 Note: your answer must be within 12.5 °C of the exact answer to be graded correct. 10 Explanation Check § Q Search J 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Researrow_forward151.2 254.8 85.9 199.6 241.4 87.6 242.5 186.4 155.8 257.1 242.9 253.3 256.0 216.6 108.7 239.0 149.7 236.4 152.1 222.7 148.7 278.2 268.7 234.4 262.7 283.2 143.6 QUESTION: Using this group of data on salt reduced tomato sauce concentration readings answer the following questions: 1. 95% Cl Confidence Interval (mmol/L) 2. [Na+] (mg/100 mL) 3. 95% Na+ Confidence Interval (mg/100 mL)arrow_forwardResults Search Results Best Free Coursehero Unloc xb Success Confirmation of Q x O Google Pas alekscgi/x/lsl.exe/1o_u-IgNslkr 7j8P3jH-IQs_pBanHhvlTCeeBZbufu BYTI0Hz7m7D3ZcHYUt80XL-5alyVpwDXM TEZayFYCavJ17dZtpxbFD0Qggd1J O States of Matter Using a phase diagram to find a phase transition temperature or pressure Gabr 3/5 he pressure above a pure sample of solid Substance X at 101. °C is lowered. At what pressure will the sample sublime? Use the phase diagram of X below to nd your answer. pressure (atm) 24- 12 solid liquid gas 200 400 temperature (K) 600 ote: your answer must be within 0.15 atm of the exact answer to be graded correct. atm Thanation Check © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center I Q Search L³ ملةarrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning





