
To sequence:
The basic steps in scientific methods by completing the given flowchart
Introduction:
Science is a body of knowledge based on study of nature. Biologists follow specific steps to do research and answer queries. These are called scientific methods. They conduct experiments, collect data, make hypothesis and gather evidences. There are no fixed steps to follow yet scientific investigations involve making observations and collecting information.
Answer to Problem 4MI
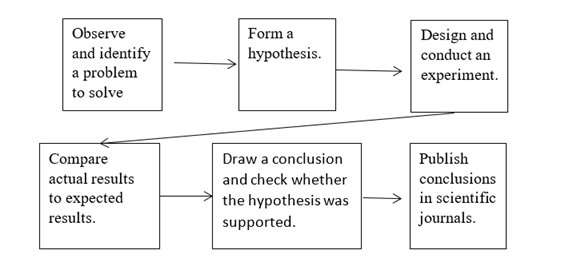
Explanation of Solution
Biologists follow the same basic steps to do research and answer queries. These are called scientific methods. No matter where the biologists work, they use similar methods to gather information and answer questions. These include making observations, collecting data, forming hypothesis, conducting experiments, recording data, drawing inferences, comparing results with other experiments etc.
- Make observations− This is the first step towards any scientific discovery which occurs when a scientist notices something new which no one else has seen before. First a scientist observes something new which catches his/ her attention. This is called observation. Scientists look for minute details if they see something interesting. For example after the discovery of cell by Robert Hooke, many scientists observed cells in a variety of organisms.
- Form a hypothesis − A testable explanation of a situation is called a hypothesis. When the hypothesis is supported by data from additional investigations, usually it is considered valid and is accepted by scientific community. If not, the hypothesis is revised, and more investigations are conducted.
- Conduct experiments − A test or investigation designed to evaluate a hypothesis or a theory in a controlled setting is called an experiment. In scientific methods, experiments play an important role. While some experiments are done in laboratories, others are done outside in natural setting. Controlled experiments involve a control group and an experimental group. Experimental group includes a group that is exposed to the factor being tested. Control group includes a group that is used for comparison without the factor. By comparing the results of the control and experimental groups the biologists draw conclusions about the effect of the variable.
- Compare data- As scientists test their hypothesis; they gather data which can be quantitative or qualitative. They compare the actual results of their experiment with expected results and conduct other kinds of scientific inquiry.
- Draw conclusions- After analyzing data from investigations; a biologist draws conclusions about whether his or her hypothesis has been supported by the data. If the hypothesis is not supported, they repeat the experiment or test an alternative hypothesis.
- Publish the conclusions- Biologists report their findings in science journals. Before publishing the work, it is also sent for peer reviewing where the reviewers examine the paper for originality, accuracy and competence of scientific method used. If the reviewers do not find any fault, the paper is published for use by other scientists.
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
- 22. Which of the following mutant proteins is expected to have a dominant negative effect when over- expressed in normal cells? a. mutant PI3-kinase that lacks the SH2 domain but retains the kinase function b. mutant Grb2 protein that cannot bind to RTK c. mutant RTK that lacks the extracellular domain d. mutant PDK that has the PH domain but lost the kinase function e. all of the abovearrow_forwardWhat is the label ?arrow_forwardCan you described the image? Can you explain the question as well their answer and how to get to an answer to an problem like this?arrow_forward
- Describe the principle of homeostasis.arrow_forwardExplain how the hormones of the glands listed below travel around the body to target organs and tissues : Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forwardWhat are the functions of the hormones produced in the glands listed below: Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





