
Interpretation:
Matter
(Physical substance in general which occupies space and possesses rest mass)
| Solid | Liquid | Gas |
| (1) A solid is a sample of matter that retains its shape and density when not confined. (2) Strong molecular force of attraction exist between atoms ions molecules. |
(1) A liquid is a sample of matter that conforms to shape of container in which it is held and which acquires a defined surface in the presence of gravity. (2) Weak molecular force of attraction exists between atoms/ions/molecule. |
(1) A gas is a sample of matter that conforms to the shape of container in which it is placed and acquire whole volume of container. (2) Negligible force of attraction exists between atoms/ion/molecules. |
Concept Introduction:
Physical change: physical change occurs when a substance alters its state , but does not change its chemical composition.
State of matter depends upon temperature and pressure. As temperature or pressure or both change then state of matter may also change.
Phase change: transition of a substance from one state to another state
Phase: it is defined as a homogenous portion of a system that has uniform physical and chemical characteristic.
Draw initial temperature and pressure on phase diagram identify the initial phase similarly draw final temperature and pressure on phase diagram identify the final phase. After that you can decide which phase transition occurs.
To determine:
A sample of the substance in this phase diagram is initially at and . Which phase transition occurs when the pressure is decreased to at constant temperature?
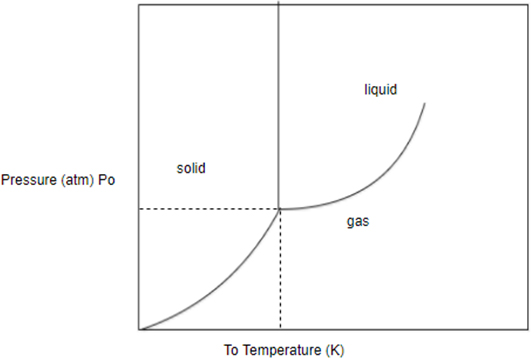
Solid to liquid.
Liquid to gas.
Solid to gas.
Liquid to solid.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
Chemistry: Structure and Properties
- How many chiral centers are there in the following molecule? HO 0 1 ○ 2 ♡ 4 'N'arrow_forwardThe following chemical structure represents a molecule of what molecular formula?arrow_forwardWhich region(s) of the following phospholipid is/are hydrophobic? RO I hydro-water phobic-dislikes = Hydrophobic dislikes water ○ I only Il only I and III only II and IV only O II, III, and IV only III || IVarrow_forward
- Given the following data, determine the order of the reaction with respect to H2. H2(g) + 21Cl(g) → I2(g) + 2HCl(g) Experiment [H2] (torr) [ICI] (torr) Rate (M/s) 1 250 325 0.266 2 250 81 0.0665 3 50 325 0.266arrow_forwardWhich one of the following molecules is chiral? H- NH₂ H3C དང་།་ OH H HO H₂N HO- -H CHO -OH H HO- OH H- -H CH₂OH OHarrow_forwardThe structure of an unsaturated phospholipid is shown below. Which region of the molecule is most hydrophilic ? H₂N-CH₂ H₂C IV CH3 CH3 hydro-water philic-likes = Hydrophilic likes water ○ IV All regions are equally hydrophilic. IIIarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning





