
Chemistry: Structure and Properties
1st Edition
ISBN: 9780321834683
Author: Nivaldo J. Tro
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 13, Problem 66E
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
You have to find out which is at lower temperature triple point or normal melting point. If d and triple point is below
Concept introduction:
If the solid phase is less dense than the liquid phase, then the line separates solid and liquids bends left.
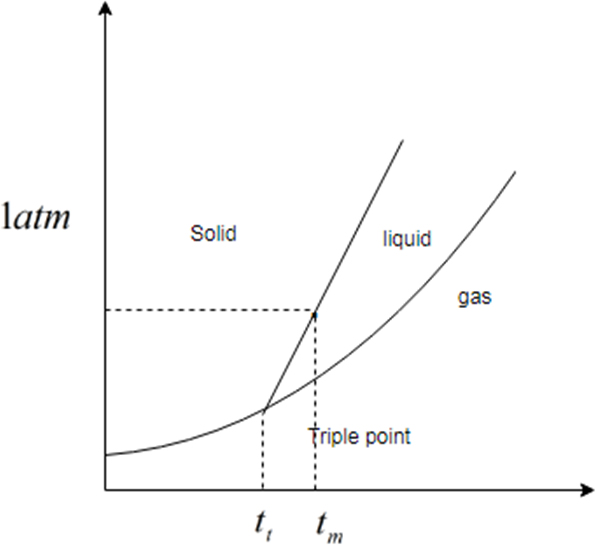
Melting curve is inclined to the solid phase is denser than the liquid phase. The line that separates solid and liquid bends right.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
What are is the organic molecule X and product Y of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.
At 300 K, in the decomposition reaction
of a reactant R into products, several
measurements of the concentration of R
over time have been made (see table).
Without using graphs, calculate the
order of the reaction.
t/s
[R]/(mol L-1)
0
0,5
171
0,16
720
0,05
1400
0,027
Predict the organic products that form in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic products. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.
Chapter 13 Solutions
Chemistry: Structure and Properties
Ch. 13 - Determine what state this substance is in at 1 atm...Ch. 13 - Prob. 2SAQCh. 13 - Prob. 3SAQCh. 13 - Prob. 4SAQCh. 13 - Prob. 5SAQCh. 13 - Prob. 6SAQCh. 13 - Prob. 7SAQCh. 13 - Prob. 8SAQCh. 13 - Prob. 9SAQCh. 13 - Prob. 10SAQ
Ch. 13 - What is a phase diagram?Ch. 13 - Draw a generic phase diagram and label its...Ch. 13 - What is the significance of crossing a line in a...Ch. 13 - What is graphene? Why is graphene unique?Ch. 13 - Prob. 5ECh. 13 - What is a crystalline lattice? How is the lattice...Ch. 13 - Prob. 7ECh. 13 - Prob. 8ECh. 13 - What is the difference between hexagonal closest...Ch. 13 - What are the three basic types of solids and the...Ch. 13 - Prob. 11ECh. 13 - What kinds of forces hold each of the three basic...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13ECh. 13 - Prob. 14ECh. 13 - Prob. 15ECh. 13 - Prob. 16ECh. 13 - Prob. 17ECh. 13 - Prob. 18ECh. 13 - Prob. 19ECh. 13 - Consider the phase diagram for iodine shown here....Ch. 13 - Prob. 21ECh. 13 - Prob. 22ECh. 13 - Prob. 23ECh. 13 - Prob. 24ECh. 13 - Prob. 25ECh. 13 - An X-ray beam of unknown wavelength is diffracted...Ch. 13 - Prob. 27ECh. 13 - Determine the coordination number for each...Ch. 13 - Prob. 29ECh. 13 - Molybdenum crystallizes with the body-centred unit...Ch. 13 - Prob. 31ECh. 13 - An atom has a radius of 142 pm and crystallizes in...Ch. 13 - Rhodium has a density of 12.41 g / cm3 and...Ch. 13 - Barium has a density of 3.59 g/cm3 and...Ch. 13 - Prob. 35ECh. 13 - Palladium crystallizes with a face-centered cubic...Ch. 13 - Prob. 37ECh. 13 - Identify each solid as molecular, ionic, or...Ch. 13 - Which solid has the highest melting point? Why?...Ch. 13 - Which solid has the highest melting point? Why?...Ch. 13 - Which solid in each pair has the higher melting...Ch. 13 - Which solid in each pair has the higher melting...Ch. 13 - Prob. 43ECh. 13 - Prob. 44ECh. 13 - Prob. 45ECh. 13 - Prob. 46ECh. 13 - The unit cells for cesium chloride and barium(ll)...Ch. 13 - Prob. 48ECh. 13 - Prob. 49ECh. 13 - Prob. 50ECh. 13 - Prob. 51ECh. 13 - Prob. 52ECh. 13 - Prob. 53ECh. 13 - Prob. 54ECh. 13 - Prob. 55ECh. 13 - Prob. 56ECh. 13 - Prob. 57ECh. 13 - The density of an unknown metal is 12.3 g/cm3 and...Ch. 13 - Prob. 59ECh. 13 - Consider a planet where the pressure of the...Ch. 13 - An unknown metal is found to have a density of...Ch. 13 - Prob. 62ECh. 13 - Potassium chloride crystallizes in the rock salt...Ch. 13 - Calculate the fraction of empty space in cubic...Ch. 13 - Prob. 65ECh. 13 - Prob. 66ECh. 13 - Prob. 67E
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- What are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forwardWhat are the products of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forwardWhat would happen if you added the HCI to the Grignard reagent before adding benzophenone? Draw a reaction mechanism to support your answer.arrow_forward
- At 300 K, in the decomposition reaction of a reactant R into products, several measurements of the concentration of R over time have been made (see table). Calculate the order of the reaction. t/s [R]/ (mol L-1) 0 0,5 171 0,16 720 0,05 1400 0,027arrow_forwardWrite the correct IUPAC names of the molecules in the picturearrow_forwardHow many grams of solid NaCN have to be added to 1.5L of water to dissolve 0.18 mol of Fe(OH)3 in the form Fe(CN)63 - ? ( For simplicity, ignore the reaction of CN - ion with water) Ksp for Fe(OH)3 is 2.8E -39, and Kform for Fe(CN)63 - is 1.0E31arrow_forward
- Draw the most stable chair conformation of 1-ethyl-1-methylcyclohexane, clearly showing the axial and equatorial substituents. [4] Draw structures corresponding to the following IUPAC name for each of the following compounds; [5] i) 4-Isopropyl-2,4,5-trimethylheptane ii) trans-1-tert-butyl-4-ethylcyclohexane iii) Cyclobutylcycloheptane iv) cis-1,4-di-isopropylcyclohexane (chair conformation) v) 3-Ethyl-5-isobutylnonanearrow_forwardDraw and name molecules that meet the following descriptions; [4] a) An organic molecule containing 2 sp2 hybridised carbon and 1 sp-hybridised carbon atom. b) A cycloalkene, C7H12, with a tetrasubstituted double bond. Also answer question 2 from the imagearrow_forwardH 14. Draw the line angle form of the following molecule make sure you use the proper notation to indicate spatial positioning of atoms. F F H 15. Convert the following condensed form to line angle form: (CH3)3CCH2COCH2CON(CH2CH3)2arrow_forward
- In a reaction between two reactants A and B, the half-life is the same for both only if(A) the stoichiometry A:B is 1:1.(B) the stoichiometry A:B is 1:2 or 2:1.arrow_forwardIn a reaction between two reactants A and B, the half-life is the same for both.(1) Only if the stoichiometry A:B is 1:1.(2) If the initial quantities of A and B are in their stoichiometric ratios.arrow_forwardThere are 48 pairs of students in the following table. Each pair has quantitatively determined the mass of taurine in a 250 mL can of the popular energy drink marketed as “Munster” using High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). The class results are presented below: QUESTION: Calculate the measurement of uncertainty and provide the data in a spreadsheet table. Mass of Taurine (mg) Mass of Taurine (mg) (Table continued) 152.01 152.23 151.87 151.45 154.11 152.64 152.98 153.24 152.88 151.45 153.49 152.48 150.68 152.33 151.52 153.63 152.48 151.68 153.17 153.40 153.77 153.67 152.34 153.16 152.57 153.02 152.86 151.50 151.23 152.57 152.72 151.54 146.47 152.38 152.44 152.54 152.53 152.54 151.32 152.87 151.24 153.26 152.02 152.90 152.87 151.49 152.46 152.58arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Cengage Learning

EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC L
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305446021
Author:Lampman
Publisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079113
Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Cengage Learning