
As a reminder, the Reynolds number is discussed in Chapter 9. Dimensionless Number.
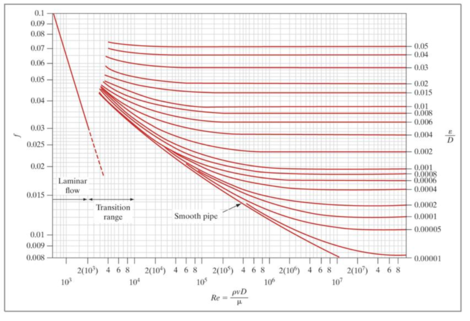
When discussing the flow of a fluid through a piping system, we say that friction occurs between the fluid and the pipe wall due to viscous drag. The loss of energy due to the friction against the pipe wall is described by the friction factor. The Darcy friction factor (f) was developed by Henry Darcy (1803–1858), a French scientist who made several important contributions to the field of hydraulics. The friction factor depends on several other factors, including flow regime, Reynolds number, and pipe roughness. The friction factor can be determined in several ways, including from the Moody diagram (show below).
Olive oil having a specific gravity of 0.914 and viscosity of 100.8 centipoise is draining by gravity from the bottom of a tank. The drain line from the tank is a 4-diameter pipe made of commercial steel (pipe roughness, ε=0.045 millimeters). The velocity is 11 meters per second. Determine the friction factor for this system, using the following process.
Step 1: Determine the Reynolds number:
Step 2: Determine flow regima.
- If the flow is laminar (Re £ 2000), continue with step 3.
- If the flow is turbulent or transitional (Re > 2000), continue with step 3.
Step 3: Determine the relative roughness ratio: (ε/D).
Step 4: Determine the Darcy friction factor (f) from the diagram.
ICA 13-23
Repeat ICA 13-22 with the following conditions:
Lactic acid, with a specific gravity of 1.249 and dynamic viscosity of 40.33 centipoise, is flowing in a
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Concepts Of Programming Languages
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
Computer Science: An Overview (13th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
- Can someone explain please with conversionsarrow_forwardCorrect Answer is written below. Detailed and complete fbd only please. I will upvote, thank you. 1: The assembly shown is composed of a rigid plank ABC, supported by hinge at A, spring at B and cable at C.The cable is attached to a frictionless pulley at D and rigidly supported at E. The cable is made of steel with E = 200,000MPa and cross-sectional area of 500 mm2. The details of pulley at D is shown. The pulley is supported by a pin, passingthough the pulley and attached to both cheeks. Note that E is directly above B.Given: H = 3 m; L1 = 2 m; L2 = 4 m; w = 12 kN/m; x:y = 3:4Spring Parameters:Wire diameter = 30 mmMean Radius = 90 mmNumber of turns = 12Modulus of Rigidity = 80 GPaAllowable stresses:Allowable shear stress of Pin at D = 85 MPaAllowable normal stress of cheek at D = 90MPaAllowable bearing stress of cheek at D = 110MPa1. Calculate the reaction of spring Band tension in cable at C.2. Calculate the vertical displacementat C and the required diameter ofpin at D.3.…arrow_forwardCorrect answer and complete fbd only. I will upvote. The compound shaft, composed of steel,aluminum, and bronze segments, carries the two torquesshown in the figure. If TC = 250 lb-ft, determine the maximumshear stress developed in each material (in ksi). The moduliof rigidity for steel, aluminum, and bronze are 12 x 106 psi, 4x 106 psi, and 6 x 106 psi, respectivelyarrow_forward
- Can you explain the algebra steps that aren't shown but stated to be there, on how to get this equationarrow_forwardCorrect answer and complete fbd only. I will upvote. A flanged bolt coupling consists of two concentric rows of bolts. The inner row has 6 nos. of 16mm diameterbolts spaced evenly in a circle of 250mm in diameter. The outer row of has 10 nos. of 25 mm diameter bolts spaced evenly in a circle of 500mm in diameter. If the allowable shear stress on one bolt is 60 MPa, determine the torque capacity of the coupling. The Poisson’s ratio of the inner row of bolts is 0.2 while that of the outer row is 0.25 and the bolts are steel, E =200 GPa.arrow_forwardCorrect answer and complete fbd only. I will upvote. 10: The constant wall thickness of a steel tube with the cross sectionshown is 2 mm. If a 600-N-m torque is applied to the tube. Use G = 80 GPa forsteel.1. Find the shear stress (MPa) in the wall of the tube.2. Find the angle of twist, in degrees per meter of length.arrow_forward
- CORRECT ANSWER WITH COMPLETE FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE. A torque wrench is used to tighten the pipe shown.Dimensions: S1 = 400 mm; S2 = 250 mm; S3 = 100 mmModulus of Rigidity G = 78 GPa1. The diameter of the solid pipe is 20 mm. How much is themaximum force P (N) that can be applied based on theallowable shear stress of 60 MPa?2. For a hollow pipe with 50 mm outside diameter and is 6 mmthick, compute for the maximum force P (kN) that can beapplied such that the angle of twist at A does not exceed 5degrees.3. The torque applied to tighten the hollow pipe is 200 N-m.Given: Pipe outside diameter = 50 mm Pipe thickness = 6 mmSolve for the resulting maximum shear stress (MPa) in the pipe.arrow_forwardCorrect answer and complete fbd only. I will upvote. 6: The shaft carries a total torque T0 that is uniformly distributedover its length L. Determine the angle of twist (degrees) of the shaft in termsif T0 = 1.2 kN-m, L = 2 m, G = 80 GPa, and diameter = 120 mm.arrow_forward2. Calculate the force in all members of the trusses shown using the method of joints. A 5525 lb C 3500 lb BY 14'-0" D 10'- 0" 6250 lb 10'- 0" Earrow_forward
- Correct answer and complete fbd only. I will upvote. 8: The steel rod fits loosely inside the aluminum sleeve. Both components are attached to a rigid wall at A andjoined together by a pin at B. Because of a slight misalignmentof the pre-drilled holes, the torque T0 = 750 N-m was appliedto the steel rod before the pin could be inserted into theholes. Determine the torque (N-m) in each component afterT0 was removed. Use G = 80 GPa for steel and G = 28 GPa foraluminumarrow_forwardCorrect answer and complete fbd only. I will upvote. 9: The two steel shafts, each with one end builtinto a rigid support, have flanges attached to their freeends. The flanges are to be bolted together. However,initially there is a 6⁰ mismatch in the location of the boltholes as shown in the figure. Determine the maximumshear stress(ksi) in each shaft after the flanges have beenbolted together. The shear modulus of elasticity for steelis 12 x 106 psi. Neglect deformations of the bolts and theflanges.arrow_forwardCorrect answer and complete fbd only. I will upvote. The tapered, wrought iron shaft carriesthe torque T = 2000 lb-in at its free end. Determine theangle of twist (degrees) of the shaft. Use G = 10 x 106psi for wrought ironarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





