
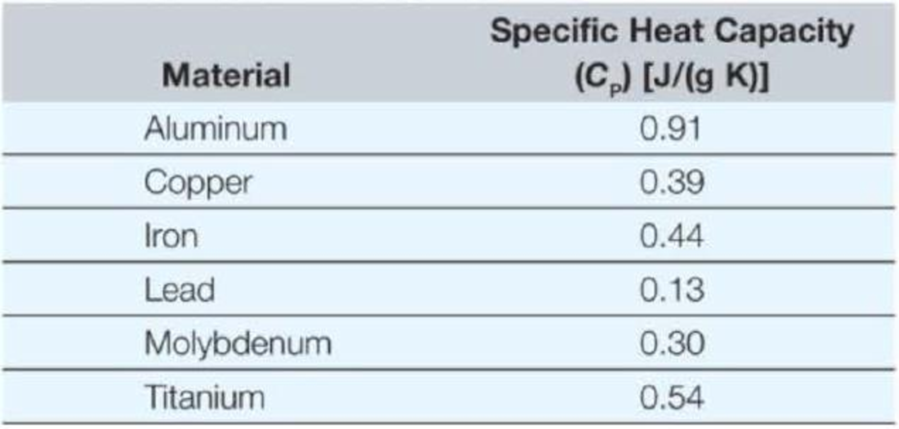
If an object is heated, the temperature of the object will increase. The thermal energy (Q) associated with a change in temperature (ΔT) is a function of the mass of the object (m) and the specific heat (C2). Specific heat is a material property, and values are available in literature. In an experiment, heat is applied to the end of an object, and the temperature change at the other end of the object recorded. An unknown material is tested in the lab, yielding the following results.

- a. Show the resulting data and trendline, with equation and R2 value, on the appropriate graph type (xy scatter, semilog, or log–log) to make the data appear linear.
- b. If the material was titanium, what mass of sample was tested?
- c. If a 4-gram sample was used which of the following materials was tested?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
Modern Database Management
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
- Qu 3 Nickel (Ni) single crystal turbine blades burn less fuel at higher temperatures because blades are grown on [110] closed packed direction. Nickel (Ni) at 20°C is FCC, and has an atomic radius, R, of 0.125 nm. Draw a reduced-sphere unit cell for this crystal and draw and label the vector [I 10], starting from the origin (0, 0, 0). a) Calculate the length of the vector [| 10] in nanometers. Express your answer in nanometers to one significant figure. b) Calculate the linear density of Nickel in the [| 1 0] direction in [atom/nm]. Express your answer in atoms/nm to one significant figure. show all work problemsarrow_forwardhandwritten-solutions, please!arrow_forwardhandwritten-solutions, please!arrow_forward
- Required information An eccentric force P is applied as shown to a steel bar of 25 × 90-mm cross section. The strains at A and B have been measured and found to be εΑ = +490 μ εB=-70 μ Know that E = 200 GPa. 25 mm 30 mm 90 mm 45 mm B Determine the distance d. The distance dis 15 mm mm.arrow_forwardhandwritten-solutions, please!arrow_forwardhandwritten-solutions, please!arrow_forward
- ! Required information Assume that the couple shown acts in a vertical plane. Take M = 25 kip.in. r = 0.75 in. A B 4.8 in. M 1.2 in. [1.2 in. Determine the stress at point B. The stress at point B is ksi.arrow_forwardhandwritten-solutions, please!arrow_forwardhandwritten-solutions, please!arrow_forward
- No use chatgptarrow_forwardProblem 6 (Optional, extra 6 points) 150 mm 150 mm 120 mm 80 mm 60 mm PROBLEM 18.103 A 2.5 kg homogeneous disk of radius 80 mm rotates with an angular velocity ₁ with respect to arm ABC, which is welded to a shaft DCE rotating as shown at the constant rate w212 rad/s. Friction in the bearing at A causes ₁ to decrease at the rate of 15 rad/s². Determine the dynamic reactions at D and E at a time when ₁ has decreased to 50 rad/s. Answer: 5=-22.01 +26.8} N E=-21.2-5.20Ĵ Narrow_forwardProblem 1. Two uniform rods AB and CE, each of weight 3 lb and length 2 ft, are welded to each other at their midpoints. Knowing that this assembly has an angular velocity of constant magnitude c = 12 rad/s, determine: (1). the magnitude and direction of the angular momentum HD of the assembly about D. (2). the dynamic reactions (ignore mg) at the bearings at A and B. 9 in. 3 in. 03 9 in. 3 in. Answers: HD = 0.162 i +0.184 j slug-ft²/s HG = 2.21 k Ay =-1.1 lb; Az = 0; By = 1.1 lb; B₂ = 0.arrow_forward
 Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
