
Concept explainers
Dwayne Cole, owner of a Florida firm that manufactures display cabinets, develops an 8-month aggregate plan. Demand and capacity (in units) are
The cost of producing each unit is $1,000 on regular time, $1,300 on overtime, and $1,800 on a subcontract. Inventory carrying cost is $200 per unit per month. There is no beginning or ending inventory in stock, and no backorders are permitted from period to period.
Let the production (workforce) vary by using regular time first, then overtime, and then subcontracting.
a) Set up a production plan that minimizes cost by producing exactly what the demand is each month. This plan allows no backorders or inventory. What is this plan’s cost?
b) Through better planning, regular time production can be set at exactly the same amount, 275 units, per month. If demand cannot be met there is no cost assigned to shortages and they will not be filled. Does this alter the solution?
c) If overtime costs per unit rise from $1,300 to $1,400, will your answer to (a) change? What if overtime costs then fall to $1,200?
a)
To determine: The total cost of the plan.
Introduction: The aggregate plan is the output of sales and operations planning. The major concern of aggregate planning is the production time and quantity for the intermediate future. Aggregate planning would encompass a time prospect of approximately 3 to 18 months.
Answer to Problem 19P
The total cost of the plan is $2,608,300.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Regular time cost per unit is given as $1,000, overtime cost is $1,300, and subcontract cost is $1,800 per unit. The capacity and demand are given as follows:
| Month | Demand | Regular time capacity | Overtime capacity | Subcontract capacity |
| Initial | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| January | 255 | 235 | 20 | 12 |
| February | 294 | 255 | 24 | 16 |
| March | 321 | 290 | 26 | 15 |
| April | 301 | 300 | 24 | 17 |
| May | 330 | 300 | 30 | 17 |
| June | 320 | 290 | 28 | 19 |
| July | 345 | 300 | 30 | 19 |
| August | 340 | 290 | 30 | 20 |
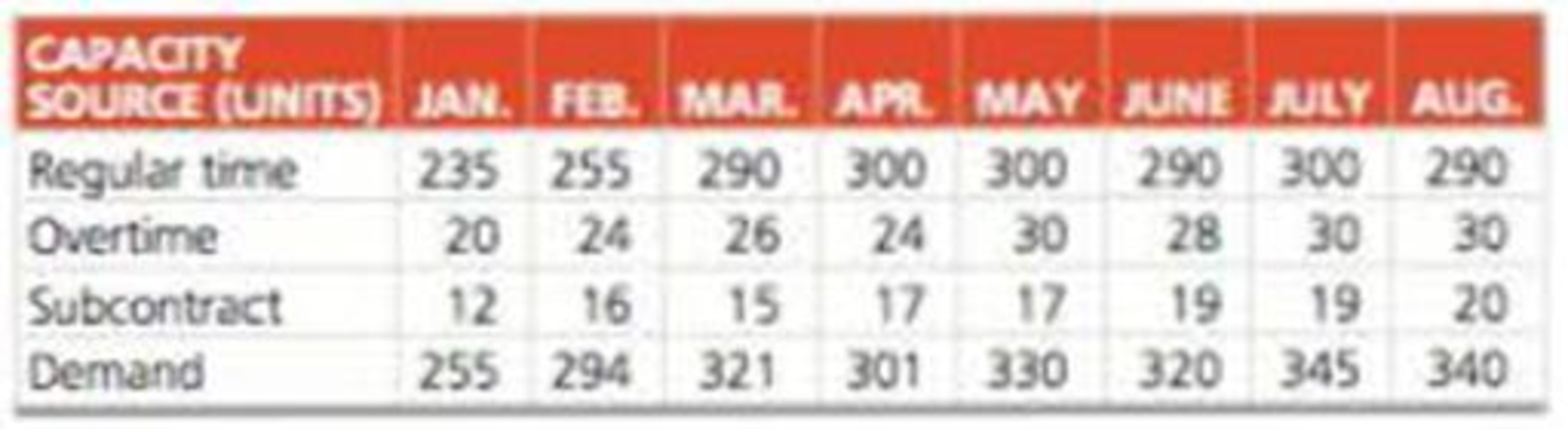
Calculate the total cost:
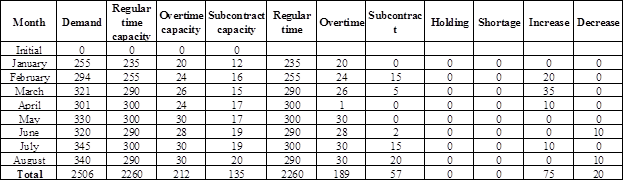
Table 1
Working note:
Demand, regular time capacity, overtime capacity, and subcontract capacity are given.
Determine regular time, overtime, and subcontract units for the month of January:
It is given that the demand for the month of January is 255 units. 235 units would be produced in the regular time (as the regular time capacity is 235). Remaining 20 units would be produced in the overtime (as the overtime capacity is 20). Hence, regular time unit is 235 units and overtime unit is 20 units.
Determine regular time, overtime, and subcontract units for the month of February:
It is given that the demand for the month of February is 294 units. 255 units would be produced in the regular time (as the regular time capacity is 255). From the remaining 39 units, 24 units would be produced in the overtime (as the overtime capacity is 24) and 15 units would be produced using subcontract (as the subcontract capacity is 16). Hence, regular time unit is 255 units, overtime unit is 24 units, and subcontract unit is 15 units.
Determine regular time, overtime, and subcontract units for the month of March:
It is given that the demand for the month of March is 321 units. 290 units would be produced in the regular time (as the regular time capacity is 290). From the remaining 31 units, 26 units would be produced in the overtime (as the overtime capacity is 26) and 5 units would be produced using subcontract (as the subcontract capacity is 15). Hence, regular time unit is 290 units, overtime unit is 26 units, and subcontract unit is 5 units.
Note: The procedure continues for all months.
Increase or decrease for the month of January:
There would be no increase or decrease for the month of January as there is no period compare.
Increase or decrease for the month of February:
Production in the month of January is 235 units and production in the month of February is 255 units. There is an increase of 20 units. Hence, there would be 20 units increase in February.
Increase or decrease for the month of March:
Production in the month of February is 255 units and production in the month of March is 290 units. There is an increase of 35 units. Hence, there would be 35 units increase in March.
Increase or decrease for the month of April:
Production in the month of March is 290 units and production in the month of April is 300 units. There is an increase of 10 units. Hence, there would be 10 units increase in April.
Increase or decrease for the month of May:
Production in the month of April is 300 units and production in the month of May is 300 units. As there is no change in the production units, there would not be any increase or decrease.
Increase or decrease for the month of June:
Production in the month of May is 300 units and production in the month of June is 290 units. There is a decrease of 10 units. Hence, there would be 10 units decrease in June.
Increase or decrease for the month of July:
Production in the month of June is 290 units and production in the month of July is 300 units. There is an increase of 10 units. Hence, there would be 10 units increase in July.
Increase or decrease for the month of August:
Production in the month of July is 300 units and production in the month of August is 290 units. There is a decrease of 10 units. Hence, there would be 10 units decrease in August.
Summary of the table:
| Type | Units | Cost |
| Regular time | 2,260 | $2,260,000 |
| Overtime | 189 | $245,700 |
| Subcontract | 57 | $102,600 |
| Holding | 0 | 0 |
| Shortage | 0 | 0 |
| Increase | 75 | 0 |
| Decrease | 20 | 0 |
| $2,608,300 |
Table 2
Working note:
Total units of regular time, overtime, subcontract, shortage, holding, increase, and decrease were calculated in theTable 1.
Calculate the regular time cost:
Regular time cost is calculated by multiplying regular time unit and the given regular time cost per unit. Hence, the regular time cost is $2,260,000.
Calculate the overtime cost:
Overtime cost is calculated by multiplying overtime unit and the given overtime cost per unit. Hence, the overtime cost is $245,700.
Calculate the subcontract cost:
Subcontract cost is calculated by multiplying subcontract unit and the given subcontract cost per unit. Hence, the subcontract cost is $102,600.
Calculate the increase and decrease cost:
As there is no increase or decrease cost per unit, it would remain 0.
Calculate the total cost:
Total cost is calculated by adding regular time cost, overtime cost, subcontract cost, holding cost, shortage cost, increase cost, and decrease cost.
Hence, the total cost of the plan is $2,608,300.
b)
To determine: The total cost of the plan.
Introduction: The aggregate plan is the output of sales and operations planning. The major concern of aggregate planning is the production time and quantity for the intermediate future. Aggregate planning would encompass a time prospect of approximately 3 to 18 months.
Answer to Problem 19P
The total cost of the plan is $2,585,100.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Regular time cost per unit is given as $1,000, overtime cost is $1,300, and subcontract cost is $1,800 per unit. The capacity and demand are given as follows:
| Month | Demand | Regular time capacity | Overtime capacity | Subcontract capacity |
| Initial | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| January | 255 | 275 | 20 | 12 |
| February | 294 | 275 | 24 | 16 |
| March | 321 | 275 | 26 | 15 |
| April | 301 | 275 | 24 | 17 |
| May | 330 | 275 | 30 | 17 |
| June | 320 | 275 | 28 | 19 |
| July | 345 | 275 | 30 | 19 |
| August | 340 | 275 | 30 | 20 |
Calculate the total cost:
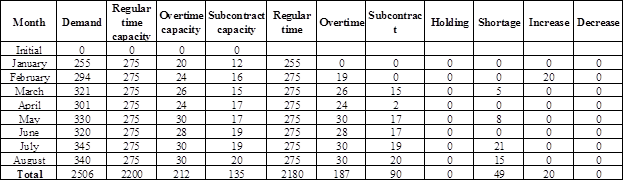
Table 3
Working note:
Demand, regular time capacity, overtime capacity, and subcontract capacity are given.
Determine regular time, overtime, and subcontract units for the month of January:
It is given that the demand for the month of January is 255 units. Whole 255 units would be produced in the regular time (as the regular time capacity is 275). Hence, regular time unit is 255 units.
Determine regular time, overtime, and subcontract units for the month of February:
It is given that the demand for the month of February is 294 units. 275 units would be produced in the regular time (as the regular time capacity is 275). Remaining 19 units would be produced in the overtime (as the overtime capacity is 24). Hence, regular time unit is 275 units and overtime unit is 19 units.
Determine regular time, overtime, and subcontract units for the month of March:
It is given that the demand for the month of March is 321 units. 275 units would be produced in the regular time (as the regular time capacity is 290). From the remaining 46 units, 26 units would be produced in the overtime (as the overtime capacity is 26) and 15 units would be produced using subcontract (as the subcontract capacity is 15). Hence, regular time unit is 275 units, overtime unit is 26 units, and subcontract unit is 15 units. Remaining 5 units is a shortage.
Note: The procedure continues for all months.
Increase or decrease for the month of January:
There would be no increase or decrease for the month of January as there is no period compare.
Increase or decrease for the month of February:
Production in the month of January is 255 units and production in the month of February is 275 units. There is an increase of 20 units. Hence, there would be 20 units increase in February.
Increase or decrease from the month of March to August:
As the production for regular time remains the same, there would be no increase or decrease from the month of March to August.
Summary of the table:
| Type | Units | Cost |
| Regular time | 2,180 | $2,180,000 |
| Overtime | 187 | $243,100 |
| Subcontract | 90 | $162,000 |
| Holding | 0 | 0 |
| Shortage | 49 | 0 |
| Increase | 20 | 0 |
| Decrease | 0 | |
| $2,585,100 |
Table 4
Working note:
Total units of regular time, overtime, subcontract, shortage, holding, increase, and decrease were calculated in theTable 3.
Calculate the regular time cost:
Regular time cost is calculated by multiplying regular time unit and the given regular time cost per unit. Hence, the regular time cost is $2,180,000.
Calculate the overtime cost:
Overtime cost is calculated by multiplying overtime unit and the given overtime cost per unit. Hence, the overtime cost is $243,100.
Calculate the subcontract cost:
Subcontract cost is calculated by multiplying subcontract unit and the given subcontract cost per unit. Hence, the subcontract cost is $162,000.
Calculate the increase and decrease cost:
As there is no increase or decrease cost per unit, it would remain 0.
Calculate the total cost:
Total cost is calculated by adding regular time cost, overtime cost, subcontract cost, holding cost, shortage cost, increase cost, and decrease cost.
Hence, the total cost of the plan is $2,585,100.
c)
To determine: The total cost of the plan, if the overtime increased to $1,400.
Introduction: The aggregate plan is the output of sales and operations planning. The major concern of aggregate planning is the production time and quantity for the intermediate future. Aggregate planning would encompass a time prospect of approximately 3 to 18 months.
Answer to Problem 19P
The total cost of the plan is $2,627,200.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Regular time cost per unit is given as $1,000, overtime cost is $1,400, and subcontract cost is $1,800 per unit. The capacity and demand are given as follows:
| Month | Demand | Regular time capacity | Overtime capacity | Subcontract capacity |
| Initial | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| January | 255 | 235 | 20 | 12 |
| February | 294 | 255 | 24 | 16 |
| March | 321 | 290 | 26 | 15 |
| April | 301 | 300 | 24 | 17 |
| May | 330 | 300 | 30 | 17 |
| June | 320 | 290 | 28 | 19 |
| July | 345 | 300 | 30 | 19 |
| August | 340 | 290 | 30 | 20 |
Calculate the total cost:
Table 5
Working note:
Demand, regular time capacity, overtime capacity, and subcontract capacity are given.
Determine regular time, overtime, and subcontract units for the month of January:
It is given that the demand for the month of January is 255 units. 235 units would be produced in the regular time (as the regular time capacity is 235). Remaining 20 units would be produced in the overtime (as the overtime capacity is 20). Hence, regular time unit is 235 units and overtime unit is 20 units.
Determine regular time, overtime, and subcontract units for the month of February:
It is given that the demand for the month of February is 294 units. 255 units would be produced in the regular time (as the regular time capacity is 255). From the remaining 39 units, 24 units would be produced in the overtime (as the overtime capacity is 24) and 15 units would be produced using subcontract (as the subcontract capacity is 16). Hence, regular time unit is 255 units, overtime unit is 24 units, and subcontract unit is 15 units.
Determine regular time, overtime, and subcontract units for the month of March:
It is given that the demand for the month of March is 321 units. 290 units would be produced in the regular time (as the regular time capacity is 290). From the remaining 31 units, 26 units would be produced in the overtime (as the overtime capacity is 26) and 5 units would be produced using subcontract (as the subcontract capacity is 15). Hence, regular time unit is 290 units, overtime unit is 26 units, and subcontract unit is 5 units.
Note: The procedure continues for all months.
Increase or decrease for the month of January:
There would be no increase or decrease for the month of January as there is no period compare.
Increase or decrease for the month of February:
Production in the month of January is 235 units and production in the month of February is 255 units. There is an increase of 20 units. Hence, there would be 20 units increase in February.
Increase or decrease for the month of March:
Production in the month of February is 255 units and production in the month of March is 290 units. There is an increase of 35 units. Hence, there would be 35 units increase in March.
Increase or decrease for the month of April:
Production in the month of March is 290 units and production in the month of April is 300 units. There is an increase of 10 units. Hence, there would be 10 units increase in April.
Increase or decrease for the month of May:
Production in the month of April is 300 units and production in the month of May is 300 units. As there is no change in the production units, there would not be any increase or decrease.
Increase or decrease for the month of June:
Production in the month of May is 300 units and production in the month of June is 290 units. There is a decrease of 10 units. Hence, there would be 10 units decrease in June.
Increase or decrease for the month of July:
Production in the month of June is 290 units and production in the month of July is 300 units. There is an increase of 10 units. Hence, there would be 10 units increase in July.
Increase or decrease for the month of August:
Production in the month of July is 300 units and production in the month of August is 290 units. There is a decrease of 10 units. Hence, there would be 10 units decrease in August.
Calculate the total cost if the overtime cost per unit increased to $1,400:
| Type | Units | Cost |
| Regular time | 2,260 | $2,260,000 |
| Overtime | 189 | $264,600 |
| Subcontract | 57 | $102,600 |
| Holding | 0 | 0 |
| Shortage | 0 | 0 |
| Increase | 75 | 0 |
| Decrease | 20 | 0 |
| $2,627,200 |
Table 6
Working note:
Total units of regular time, overtime, subcontract, shortage, holding, increase, and decrease were calculated in theTable 5.
Calculate the regular time cost:
Regular time cost is calculated by multiplying regular time unit and the given regular time cost per unit. Hence, the regular time cost is $2,260,000.
Calculate the overtime cost:
Overtime cost is calculated by multiplying overtime unit and the given overtime cost per unit. Hence, the overtime cost is $264,600.
Calculate the subcontract cost:
Subcontract cost is calculated by multiplying subcontract unit and the given subcontract cost per unit. Hence, the subcontract cost is $102,600.
Calculate the increase and decrease cost:
As there is no increase or decrease cost per unit, it would remain 0.
Calculate the total cost:
Total cost is calculated by adding regular time cost, overtime cost, subcontract cost, holding cost, shortage cost, increase cost, and decrease cost.
Hence, the total cost of the plan is $2,627,200.
Calculate the total cost if the overtime cost per unit increased to $1,200:
| Type | Units | Cost |
| Regular time | 2,260 | $2,260,000 |
| Overtime | 189 | $226,800 |
| Subcontract | 57 | $102,600 |
| Holding | 0 | 0 |
| Shortage | 0 | 0 |
| Increase | 75 | 0 |
| Decrease | 20 | 0 |
| $2,589,400 |
Table 7
Working note:
Total units of regular time, overtime, subcontract, shortage, holding, increase, and decrease were calculated in theTable 6.
Calculate the regular time cost:
Regular time cost is calculated by multiplying regular time unit and the given regular time cost per unit. Hence, the regular time cost is $2,260,000.
Calculate the overtime cost:
Overtime cost is calculated by multiplying overtime unit and the given overtime cost per unit. Hence, the overtime cost is $264,600.
Calculate the subcontract cost:
Subcontract cost is calculated by multiplying subcontract unit and the given subcontract cost per unit. Hence, the subcontract cost is $102,600.
Calculate the increase and decrease cost:
As there is no increase or decrease cost per unit, it would remain 0.
Calculate the total cost:
Total cost is calculated by adding regular time cost, overtime cost, subcontract cost, holding cost, shortage cost, increase cost, and decrease cost.
Hence, the total cost of the plan is $2,589,400.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Pearson eText Principles of Operations Management: Sustainability and Supply Chain Management -- Instant Access (Pearson+)
- Please show all units, work, and steps needed to solve this problem I need answer typing clear urjent no chatgpt used pls i will give 5 Upvotes.arrow_forwardIM.82 A distributor of industrial equipment purchases specialized compressors for use in air conditioners. The regular price is $50, however, the manufacturer of this compressor offers quantity discounts per the following discount schedule: Option Plan Quantity Discount A 1 - 299 0% B 300 - 1,199 0.50% C 1,200+ 1.50% The distributor pays $56 each time it places an order with the manufacturer. Holding costs are negligible (none) but they do earn 10% annual interest on all cash balances (meaning there will be a financial opportunity cost when they put cash into inventory). Annual demand is expected to be 10,750 units. When there is no quantity discount (Option Plan A, the first row of the schedule listed above), what is the adjusted order quantity? (Display your answer to the nearest whole number.) 491 Based on your answer to the previous question, and based on the annual demand as stated above, what will be the annual ordering costs? (Display your answer to the…arrow_forwardExcel Please. The workload of many areas of banking operations varies considerably based on time of day. A variable capacity can be achieved effectively by employing part-time personnel. Because part-timers are not entitled to all the fringe benefits, they are often more economical than full-time employees. Other considerations, however, may limit the extent to which part-time people can be hired in a given department. The problem is to find an optimal workforce schedule that would meet personnel requirements at any given time and also be economical. Some of the factors affecting personnel assignments are listed here: The bank is open from 9:00am to 7:00pm. Full-time employees work for 8 hours (1 hour for lunch included) per day. They do not necessarily have to start their shift when the bank opens. Part-time employees work for at least 4 hours per day, but less than 8 hours per day and do not get a lunch break. By corporate policy, total part-time personnel hours is limited…arrow_forward
- IM.84 An outdoor equipment manufacturer sells a rugged water bottle to complement its product line. They sell this item to a variety of sporting goods stores and other retailers. The manufacturer offers quantity discounts per the following discount schedule: Option Plan Quantity Price A 1 - 2,399 $5.50 B 2,400 - 3,999 $5.20 C 4,000+ $4.50 A large big-box retailer expects to sell 9,700 units this year. This retailer estimates that it incurs an internal administrative cost of $225 each time it places an order with the manufacturer. Holding cost for the retailer is $55 per case per year. (There are 40 units or water bottles per case.) Based on this information, and not taking into account any quantity discount offers, what is the calculated EOQ (in units)? (Display your answer to the nearest whole number.) Number Based on this information, sort each quantity discount plan from left to right by dragging the MOST preferred option plan to the left, and the LEAST preferred…arrow_forwardIn less than 150 words, what is an example of what your reflection of core values means to you and your work: Commitment, Perseverance, Community, Service, Pride?arrow_forwardPrepare a report on the following: Part 1: Discuss the role of the corporate secretary in facilitating effective governance in a limited liability company. Include the relationships with directors, shareholders, and other officers. Part 2: Compare and contrast two characteristics of different business entities (sole trader, partnership, and limited liability company). Use examples to recommend the most appropriate type of business entity for the scenario below: Scenario Background Alex, Taylor, and Jordan plan to collaborate to launch a tech startup focused on developing and selling innovative software solutions. Each individual brings unique skills and resources to the venture: Alex: A skilled software developer with technical expertise and a vision for the product. Taylor: A marketing professional with extensive connections in the technology industry, aiming to drive sales and build the brand. Jordan: An investor willing to contribute significant financial resources but…arrow_forward
- Problem 1 (20 Points) Davison Electronics manufactures three LED television monitors, identified as Model A, Model B, and Model C. Davison Electronics four manufacturing plants. Each model has its lowest possible production cost when produced at Plant 1. However, Plant 1 does not have the capacity to handle the total production of all three models. As a result, at least some of the production must be routed to the other manufacturing plants. The following table shows the minimum production requirements for next month, the plant capacities in units per month, and the production cost per unit at each plant: Model Production Cost per Unit Minimum Production Requirements Plant 1 Plant 2 Plant 3 Plant 4 A $25 $28 $37 $34 48,000 B $26 $35 $36 $41 75,000 C $20 $31 $26 $23 60,000 Production Capacity 65,000 50,000 32,000 43,000 Davison’s objective is to determine the cost-minimizing production plan. Without…arrow_forwardSECTION B: TOPIC STRUCTURE CAPSTONE PROJECT TOPIC SUBMISSION TEMPLATE SECTION A: STUDENT DETAILS Student number Title (Mr/Miss/Ms/Mrs) Surname First name/s Title of research Date and year of registration Work Home Contact details Cell Region Date submitted Email 1.1 Title Insert title of the research. Choose a title that captures the essence of your proposed project. 1.2 Background to the Problem This section will be used to create the readers' interest. It can include a specific description of the topic that is to be investigated. A brief preview of the topic and the foundation of the problem should also be given. The researcher can achieve this through building up a detailed background of circumstances that lead to the problem being examined. Therefore, the background helps the reader understand the specific problem addressed by the researcher. This section should not include the background/history of the organisation. The background to the problem should not be more than ½ a page.…arrow_forwardDoes Nike Corporation's emphasis on lean operations help the Vietnamese workforce that still earns $150.00 minimum wage a month since 2014?arrow_forward
- Information Security Innovation within a Contemporary Business Environment All organisations using computers need to consider the security of information they keep. Many organisations utilise Websites for their core business functions and this results in monetary transactions being carried out on the Websites.arrow_forwardPlease help with a complete research report on the topic below: "Information Security Innovation within a Contemporary Business Environment " The format of the report should follow this below.arrow_forward7. Wireless Infrastructure in the Cloud Wireless devices have changed the way organisations and their customers interact. Wireless enabled devices have driven the mindset that wireless networks must be ubiquitous, fast, and constantly available. These are demands that have traditionally put organisations and their user communities in direct conflict with their IT departments, as constructing and maintaining wireless infrastructures are typically time-consuming, complex, and costly endeavours.arrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage LearningMarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage LearningMarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing




