
Concept explainers
To determine:
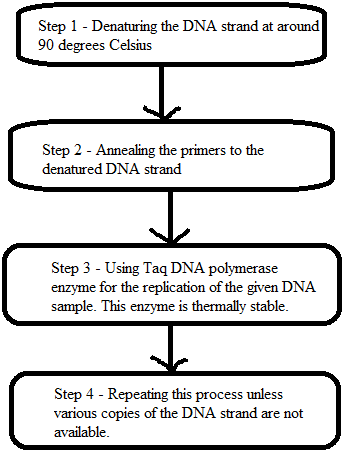
The flowchart for PCR technique.
Introduction:
PCR is polymerase chain reaction. This method is used to make millions copies of the required DNA fragment. In this process, only a small quantity of sample DNA is required, and this small quantity is much enough to study the process in detail.
Explanation of Solution
Steps of PCR are as follows:
Step 1 − Denaturation − More than 90 degrees Celsius of temperature is required to denature the given DNA double stranded strand. The hydrogen bonds in DNA are broken down at such higher temperature.
Step 2 − Annealing − Primers are used in PCR technique. These primers are small and synthetic single strand
Step 3 − Extension − This process takes place at 72 degrees Celsius. Here Taq DNA polymerase enzyme is used for the replication of DNA strands. This DNA polymerase is thermally stable. This DNA pol uses dNTPs present in the experiment solution.
Step 4 − End of first PCR cycle − When two identical copies of the sample DNA are formed, then their 5’ ends are defined by the primer, but their 3’ ends are still not defined.
The flowchart for the above PCR process is as below:
Chapter 13 Solutions
EP BIOLOGY 2012-STUDENTWORKS ONLINE
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
- Can I get a handwritten answer please. I'm having a hard time understanding this process. Thanksarrow_forwardSay you get AATTGGCAATTGGCAATTGGCAATTGGCAATTGGCAATTGGCAATTGGC 3ʹ and it is cleaved with Mspl restriction enzyme - how do I find how many fragments?arrow_forwardWhat is amplification bias?arrow_forward
- What would happen if transcriptome analysis were done on liver and muscle cells?arrow_forwardBiology How many grams of sucrose would you add to 100mL of water to make a 100 mL of 5% (w/v) sucrosesolution?arrow_forwardWhich marker does this DNA 5ʹ AATTGGCAATTGGCAATTGGCAATTGGCAATTGGCAATTGGCAATTGGC 3ʹ show?arrow_forward
- The Z value of LOD for two genes is 4, what does it mean for linkage and inheritance?arrow_forwardBiology How will you make a 50-ul reaction mixture with 2uM primer DNA using 10 uM primer DNA stocksolution and water?arrow_forwardBiology You’re going to make 1% (w/v) agarose gel in 0.5XTBE buffer 100 ml. How much agarose are you goingto add to 100 ml of buffer? The volume of agaroseis negligible.arrow_forward
- Biology How will you make a 50-ul reaction mixture with0.2 mM dNTP using 2-mM dNTP stock solution andwater?arrow_forwardBiology What is 200 pmole/uL in Molar concentration?arrow_forwardBiology How will you make a 50-ul reaction mixture with 1Xreaction buffer in it using water and 5X buffer stocksolution?arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





