
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The missing reagents for each step in Your Turn 13.6 are to be supplied.
Concept introduction:
In order to identify the missing reagents in the given reaction sequence, it is important to identify if the reaction involves a
Under basic conditions, the nucleophile attacks the
Answer to Problem 13.1P
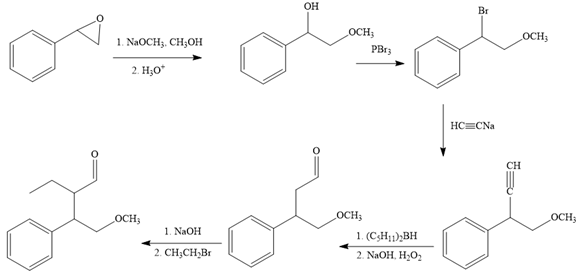
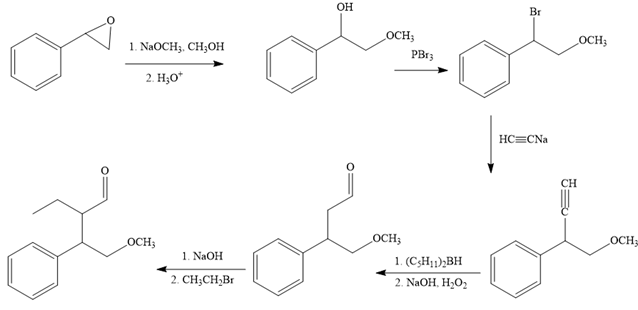
The missing reagents for each step in the given reaction sequence are given below:
Explanation of Solution
The reaction sequence given in Your Turn 13.6 is:
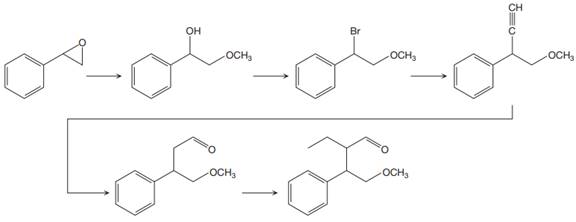
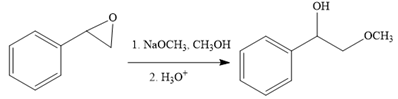
The first reaction is the conversion of an epoxide to alcohol. Thus, it is a functional group transformation reaction in which the nucleophile,
The first reaction and the missing reagents for it are shown below:
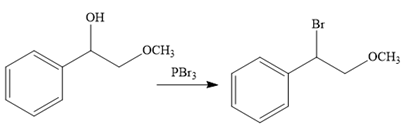
The second reaction also involves functional group transformation. The alcoholic (
In the third reaction, the bromine atom is replaced by an acetylene group (
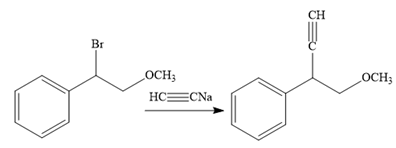
The fourth reaction in the given reaction sequence is a reaction involving a functional group transformation. Terminal alkynes undergo a hydroboration-oxidation reaction which leads to the formation of an aldehyde. The reagents used in the hydroboration-oxidation reaction are disiamylborane [
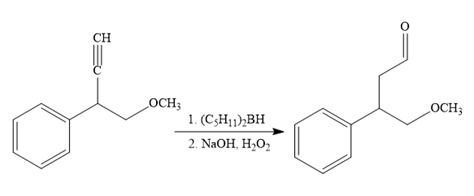
The fifth reaction involves the alteration of the carbon skeleton. The alpha hydrogen attached to an alpha carbon in aldehydes is weakly acidic. A strong base abstracts this alpha hydrogen to form an enolate ion. This enolate serves as a nucleophile and reacts with an alkyl halide via
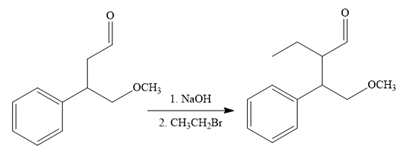
The complete reaction sequence with appropriate reagents for each are given below:
In order to identify the missing reagents in the given reaction sequence, it is important to identify if the reaction involves a functional group transformation or it is a reaction that alters the carbon skeleton.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- What is the approximate bond angle around the nitrogen atom? HNH H Harrow_forwardOH 1. NaOCH2CH3 Q 2. CH3CH2Br (1 equiv) H3O+ Select to Draw 1. NaOCH2 CH3 2. CH3Br (1 equiv) heat Select to Edit Select to Drawarrow_forwardComplete and balance the following half-reaction in acidic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. S₂O₃²⁻(aq) → S₄O₆²⁻(aq)arrow_forward
- Q Select to Edit NH3 (CH3)2CHCI (1 equiv) AICI 3 Select to Draw cat. H2SO4 SO3 (1 equiv) HO SOCl2 pyridine Select to Edit >arrow_forwardComplete and balance the following half-reaction in basic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. Zn(s) → Zn(OH)₄²⁻(aq)arrow_forwardb. ὋΗ CH3CH2OH H2SO4arrow_forward
- For the reaction A (g) → 3 B (g), Kp = 0.379 at 298 K. What is the value of ∆G for this reaction at 298 K when the partial pressures of A and B are 5.70 atm and 0.250 atm?arrow_forward14. Calculate the concentrations of Ag+, Ag(S2O3), and Ag(S2O3)23- in a solution prepared by mixing 150.0 mL of 1.00×10-3 M AgNO3 with 200.0 mL of 5.00 M Na2S2O3 Ag+ + S20 Ag(S203)¯ K₁ = 7.4 × 108 Ag(S203)¯ + S20¯ = Ag(S203) K₂ = 3.9 x 104arrow_forwardΗΝ, cyclohexanone pH 4-5 Draw Enamine I I CH3CH2Br THF, reflux H3O+ I Drawing Draw Iminium Ionarrow_forward
- :0: :0: Select to Add Arrows :0: (CH3)2NH :0: ■ Select to Add Arrows :0: :0: (CH3)2NH ■ Select to Add Arrowsarrow_forwardDraw the product of the following H action sequence. Ignore any inorganic byproducts formed. 1. (CH3CH2)2CuLi, THF 2. CH3Br Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings H Charges ㅁarrow_forwardPlease help me with this the problem is so confusingarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
