
Concept explainers
The equilibrium constant for the reaction
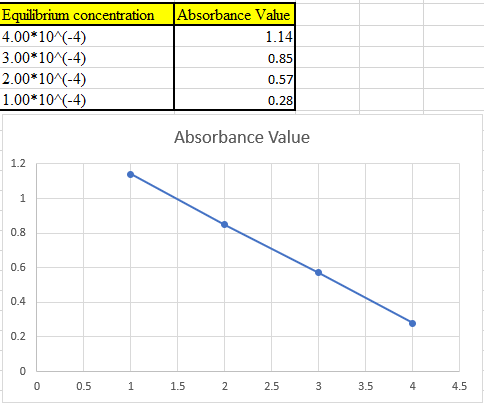
Four solutions were preparedby dissolving 4.00 × 10-4, 3.00 × 10-4, 2.00 × 10-4,and 1.00 × 10-4 moles of K2 Cr2 O7 in water and diluting to 1.00 L with a pH 5.60 buffer. Derive theoretical absorbance values (1.00-cm cells) for each solution and plot the data for (a) 345 nm, (b) 370 nm, and (c) 400 nm.
(a)
Interpretation:
The theoretical absorbance value for 345 nm should be derived and the data should be plotted.
Concept introduction:
The relationship between absorbance and concentration of absorbance is linear. If the incident light
In the case of no absorbing sample, all the light gets passed and the value of
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The equilibrium constant is
The given reaction is
The equilibrium constant for the given reaction is
The formula to determine pH is:
Therefore
For the given reaction the expression for the equilibrium constant can be written as
The equilibrium concentration of dichromate is
The theoretical absorbance value of the first solution can be calculated as below
For the second solution, everything will remain the same, just the equilibrium concentration of dichromate will change to
So, the new required concentration will be as
The theoretical absorbance value of the first solution can be calculated as below
For the third solution, everything will remain the same, just the equilibrium concentration of dichromate will change to
So, the new required concentration will be as
The theoretical absorbance value of the first solution can be calculated as below
For the fourth solution, everything will remain the same, just the equilibrium concentration of dichromate will change to
So, the new required concentration will be as
The theoretical absorbance value of the first solution can be calculated as below:
Now take the values in excel and plot to get the graph:
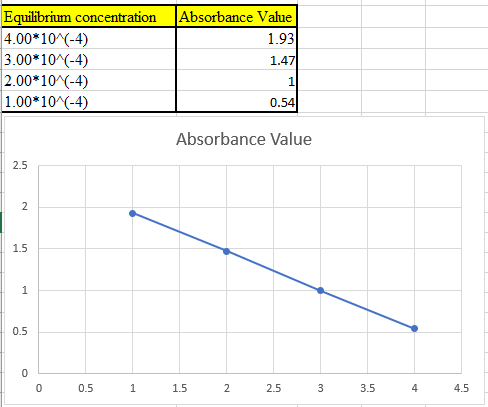
(b)
Interpretation:
The theoretical absorbance value for 370 nm should be derived and the data should be plotted.
Concept introduction:
The relationship between absorbance and concentration of absorbance is linear. If the incident light
In the case of no absorbing sample, all the light gets passed and the value of
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The equilibrium constant is
The given reaction is
The equilibrium constant for the given reaction is
The formula to determine pH is:
Therefore
For the given reaction the expression for the equilibrium constant can be written as
The equilibrium concentration of dichromate is
The theoretical absorbance value of the first solution can be calculated as below
For the second solution, everything will remain the same, just the equilibrium concentration of dichromate will change to
So, the new required concentration will be as
The theoretical absorbance value of the first solution can be calculated as below
For the third solution, everything will remain the same, just the equilibrium concentration of dichromate will change to
So, the new required concentration will be as
The theoretical absorbance value of the first solution can be calculated as below
For the fourth solution, everything will remain the same, just the equilibrium concentration of dichromate will change to
So, the new required concentration will be as
The theoretical absorbance value of the first solution can be calculated as below
Now take the values in excel and plot to get the graph:
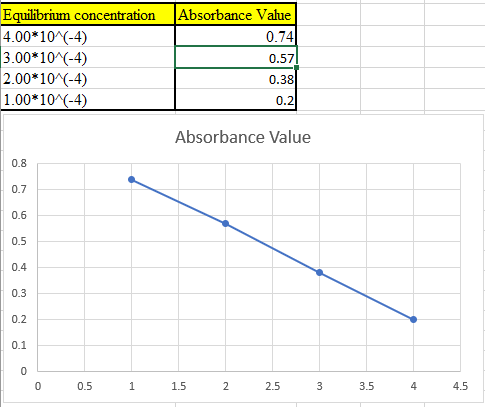
(c)
Interpretation:
The theoretical absorbance value for 400 nm should be derived and the data should be plotted.
Concept introduction:
The relationship between absorbance and concentration of absorbance is linear. If the incident light
In the case of no absorbing sample, all the light gets passed and the value of
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The equilibrium constant is
The given reaction is
The equilibrium constant for the given reaction is
The formula to determine pH is:
Therefore
For the given reaction the expression for the equilibrium constant can be written as
The equilibrium concentration of dichromate is
The theoretical absorbance value of the first solution can be calculated as below
For the second solution, everything will remain the same, just the equilibrium concentration of dichromate will change to
So, the new required concentration will be as
The theoretical absorbance value of the first solution can be calculated as below
For the third solution, everything will remain the same, just the equilibrium concentration of dichromate will change to
So, the new required concentration will be as
The theoretical absorbance value of the first solution can be calculated as below
For the fourth solution, everything will remain the same, just the equilibrium concentration of dichromate will change to
So, the new required concentration will be as
Theoretical absorbance value of first solution can be calculated as below
Now take the values in excel and plot to get the graph:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Principles of Instrumental Analysis
- ASP please....arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardConsider the structure of 1-bromo-2-fluoroethane. Part 1 of 2 Draw the Newman projection for the anti conformation of 1-bromo-2-fluoroethane, viewed down the C1-C2 bond. ✡ ぬ Part 2 of 2 H H F Br H H ☑ Draw the Newman projection for the gauche conformation of 1-bromo-2-fluoroethane, viewed down the C1-C2 bond. H F Br H Harrow_forward
- Please help me answer this question. I don't understand how or where the different reagents will attach and it's mostly due to the wedge bond because I haven't seen a problem like this before. Please provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how it can happen and what the final product will look like.arrow_forwardWhich of the following compounds is the most acidic in the gas phase? Group of answer choices H2O SiH4 HBr H2Sarrow_forwardWhich of the following is the most acidic transition metal cation? Group of answer choices Fe3+ Sc3+ Mn4+ Zn2+arrow_forward
- Based on the thermodynamics of acetic acid dissociation discussed in Lecture 2-5, what can you conclude about the standard enthalpy change (ΔHo) of acid dissociation for HCl? Group of answer choices You cannot arrive at any of the other three conclusions It is a positive value It is more negative than −0.4 kJ/mol It equals −0.4 kJ/molarrow_forwardPLEASE HELP URGENT!arrow_forwardDraw the skeletal structure corresponding to the following IUPAC name: 7-isopropyl-3-methyldecanearrow_forward
 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning





