
Concept explainers
The equilibrium constant for the conjugate acid-base pair
(a) calculate the absorbance at 430 nmand 600 nm for the following indicator concentrations:
3.00 × 10-4M,2.00 × 10-4M, 1.00 × 10-4M, 0.500 × 10-4 M, and 0.250 × 10-4M.
(b) plot absorbance as a function of indicator concentration.
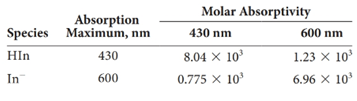
(a)
Interpretation:
Absorbance values of the conjugate acid-base pair solutions of different concentrations at
Concept introduction:
The absorbance can be calculated using the following formula:
For the given conjugate acid-base pair, equilibrium can be written as,
Answer to Problem 13.11QAP
Explanation of Solution
Let’s use the equilibrium equation to find the concentrations of HIn and In-(denoted as [HIn] and [In-]) at a situation in which the total concentration (cHIn) is
Now, the absorbance values of this solution at 430 and 600 nm can be calculated as follows,
The cell length (b) is not given in the question, therefore taken as 1.00cm.
Similarly, other absorbance values can be calculated for solutions with different concentrations.
(b)
Interpretation:
Absorbance as a function of indicator concentration should be plotted.
Explanation of Solution
The data obtained is as follows:
From the data, the graph between absorbance and concentration can be plotted as follows:
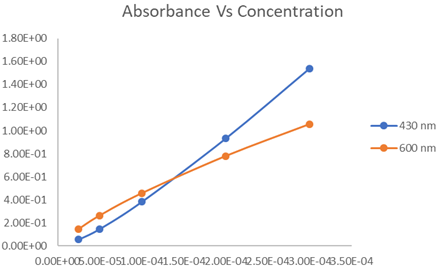
Here, blue curve indicates the plot at 430 nm and orange curve indicates the same at 600 nm.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Principles of Instrumental Analysis
- At an electrified interface according to the Gouy-Chapman model, what types of interactions do NOT occur between the ions and the solvent according to this theory?arrow_forwardPlease predict the products for each of the following reactions. Clearly show the regiochemistry (Markovnikov vs anti-Markovnikov) and stereochemistry (syn- vs anti- or both). If a mixture of enantiomers is formed, please draw all the enantiomers. Hint: In this case you must choose the best answer to demonstrate the stereochemistry of H2 addition. 1.03 2. (CH3)2S BIZ CH₂OH 2. DMS KMnO4, NaOH ΖΗ Pd or Pt (catalyst) HBr 20 1 HBr ROOR (peroxide) HO H-SO HC 12 11 10 BH, THE 2. H2O2, NaOH Brz cold HI 19 18 17 16 MCPBA 15 14 13 A Br H₂O BH3⚫THF Brz EtOH Pd or Ni (catalyst) D₂ (deuterium) 1. Os04 2. H2O2 CH3CO3H (peroxyacid) 1. MCPBA 2. H₂O* H B + H H H "H C H H Darrow_forwardExplain how Beer’s Law can be used to determine the concentration in a selected food sample. Provide examples.arrow_forward
- Explain the importance of having a sampling plan with respect to food analysis. Explain the importance of having a sampling plan with respect to food analysis. Provide examples.arrow_forwardPlease predict the products for each of the following reactions. Clearly show the regiochemistry (Markovnikov vs anti-Markovnikov) and stereochemistry (syn- vs anti- or both). If a mixture of enantiomers is formed, please draw all the enantiomers. cold KMnO4, NaOH 2. DMS 1. 03 CH3OH Br2 1. 03 2. (CH3)2S H₂ Pd or Pt (catalyst) HBr 18 19 20 1 HBr ROOR (peroxide) H₂O H₂SO4 HCI HI 17 16 6 15 MCPBA 1. BH3 THF 2. H₂O2, NaOH 1. OsO4 2. H₂O₂ 110 CH3CO₂H (peroxyacid) 1. MCPBA 2. H₂O* Br2 H₂O BH3 THF B12 EtOH Pd or Ni (catalyst) D₂ (deuterium) Bra A B C D H OH H OH OH H OH α α α OH H OH OH фон d H "Harrow_forwardBriefly indicate the models that describe the structure of the interface: Helmholtz-Perrin, Gouy-Chapman, Stern and Grahame models.arrow_forward
 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning


