
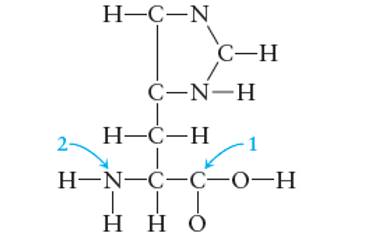
Interpretation: The complete Lewis structure for histidine in which all the bonded atoms must have zero formal charge needs to be determined and bond angle of C1-N2 in the given figure needs to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs that existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure.
Formal charge on each atom can be determined with the help of number of valence shell electrons, number of lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons. The formula for the formal charge can be written as:
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 13 Solutions
Chemical Principles
- Use the provided information to calculate Kc for the following reaction at 550 °C: H2(g) + CO2(g) ⇌ CO(g) + H2O(g) Kc = ?CoO(s) + CO(g) ⇌ Co(s) + CO2(g) Kc1 = 490CoO(s) + H2(g) ⇌ Co(s) + H2O(g) Kc2 = 67arrow_forwardCalculate Kc for the reaction: I2 (g) ⇋ 2 I (g) Kp = 6.26 x 10-22 at 298Karrow_forwardFor each scenario below, select the color of the solution using the indicator thymol blue during the titration. When you first add indicator to your Na2CO3solution, the solution is basic (pH ~10), and the color is ["", "", "", "", ""] . At the equivalence point for the titration, the moles of added HCl are equal to the moles of Na2CO3. One drop (or less!) past this is called the endpoint. The added HCl begins to titrate the thymol blue indicator itself. At the endpoint, the indicator color is ["", "", "", "", ""] . When you weren't paying attention and added too much HCl (~12 mL extra), the color is ["", "", "", "", ""] . When you really weren't paying attention and reached the second equivalence point of Na2CO3, the color isarrow_forward
- To convert cyclopentane-CH2-CHO to cyclopentane-CH2-CH3, compound A is added, followed by (CH3)3CO-K+, DMS at 100oC. Indicate which compound A is.arrow_forwardIndicate how to obtain the compound 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol.arrow_forwardIndicate the reagent needed to go from cyclopentane-CH2-CHO to cyclopentane-CH2-CH=CH-C6H5.arrow_forward
- esc Write the systematic name of each organic molecule: structure CH3 CH3-C=CH2 CH3-CH2-C-CH2-CH3 CH-CH3 CH3 ☐ ☐ ☐ CI-CH-CH=CH2 Explanation Check F1 F2 name 80 F3 F4 F5 F6 A 7 ! 2 # 3 4 % 5 6 & 7 Q W E R Y FT 2025 Mcarrow_forwardTwo reactants X and Z are required to convert the compound CH3-CH2-CH2Br to the compound CH3-CH2-CH=P(C6H5)3. State reactants X and Z.arrow_forward2. Write a reasonable mechanism that converts the reactants into the products. Avoid issues A-U from the previous page. You can use any number of steps (it does not have to be a one-step mechanism). Do not use any other chemicals (solvents, acids, bases, etc.) in your mechanism. 2 2 H ΗΘarrow_forward
- For the following reaction, the partial pressures were determined for the reaction components as shownbelow. Is the reaction at equilibrium? If not, in which direction will it proceed?I2 (g) + Cl2 (g) ⇋ 2 ICl (g) Kp = 81.9 partial pressures: I2 = 0.114 atm; Cl2 = 0.102 atm; ICl = 0.355 atmarrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H3O+ + Oarrow_forwardWrite the law of mass action for the following quilibrium 2N2O5(g) --> 4 NO2(g) + O2(g).arrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning





