
(a)
To find: the surface area of the cube.
(a)
Answer to Problem 15PPS
The surface area of the cube is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
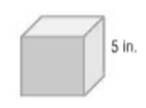
Formula used:
The surface area S of a square pyramid is S = L + 2B
Calculation:
The objective is to find the surface area of the cube.
The lateral area L of a square pyramid is given by the formula
L = Ph
Where P is the perimeter of the base and h is the height the square pyramid.
The surface area S of a square pyramid is given by the formula
S = L + 2B
Where L is the lateral surface area and B is the area of the base.
On combining the last two formulas, the surface area is given by
Find the surface area of the square box
Put side = 5 in the surface area formula to find the surface area of the cube.
Therefore, the surface area of the cube is
Conclusion:
Therefore, the surface area of the cube is
(b)
To complete: the given table.
(b)
Answer to Problem 15PPS
| Scale Factor of Dilation | Original | ||
| Length of Side | 5 | ||
| Surface Area |
Explanation of Solution
Given:
| Scale Factor of Dilation | Original | ||
| Length of Side | ■ | ■ | ■ |
| Surface Area | ■ | ■ | ■ |
Calculation:
Consider the table
| Scale Factor of Dilation | Original | ||
| Length of Side | 5 | ||
| Surface Area |
The objective is to complete the table.
Put side = 10 in the volume formula to find the surface area of the cube.
Therefore, the surface area of the cube is
Put side = 15 in the volume formula to find the surface area of the cube.
Therefore, the surface area of the cube is
Therefore, the complete table is
| Scale Factor of Dilation | Original | ||
| Length of Side | 5 | ||
| Surface Area |
Conclusion:
Therefore, the given table is completed.
(c)
To compare: the original surface area to the surface area after dilation.
(c)
Answer to Problem 15PPS
The new surface area is 4 times the original surface area when the scale factor is 2
The new surface area is 9 times the original surface area when the scale factor is 3
Explanation of Solution
The objective is to compare the original surface area to the surface are after dilation.
When the side of the cube is dilation by a scale factor 2 the new surface area is 4 times the original surface area.
When the side of the cube is dilation by a scale factor 3 the new surface area is 9 times the original surface area.
(d)
To explain:whether the same relationship exists with rectangular prism or not
(d)
Answer to Problem 15PPS
The same relation exist with the surface are of a rectangular prism
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The same relation exist with the surface are of a rectangular prism too because a cube is form of rectangle prism whose sides are equal.
The new surface area is the square of the scale factor of the side multiplied to the original surface area.
The original formula for surface area is
When length and width are double the new surface area becomes
Conclusion:
Therefore, the same relation exist with the surface are of a rectangular prism
Chapter 12 Solutions
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Introductory Statistics
Intro Stats, Books a la Carte Edition (5th Edition)
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Elementary Statistics
- 10 6 9. 8 -7- 6. 5. 4- 3. 2 1- -1 0 -1 2 3 4 ·10 5 6 7 00 8 6 10arrow_forwardWeek 3: Mortgages and Amortiza X + rses/167748/assignments/5379530?module_item_id=23896312 11:59pm Points 10 Submitting an external tool Gider the following monthly amortization schedule: Payment # Payment Interest Debt Payment Balance 1 1,167.34 540.54 626.80 259,873.20 2 1,167.34 539.24 628.10 259,245.10 3 1,167.34 With the exception of column one, all amounts are in dollars. Calculate the annual interest rate on this loa Round your answer to the nearest hundredth of a percent. Do NOT round until you calculate the final answer. * Previous a Earrow_forwardCafé Michigan's manager, Gary Stark, suspects that demand for mocha latte coffees depends on the price being charged. Based on historical observations, Gary has gathered the following data, which show the numbers of these coffees sold over six different price values: Price Number Sold $2.70 765 $3.50 515 $2.00 990 $4.30 240 $3.10 325 $4.00 475 Using simple linear regression and given that the price per cup is $1.85, the forecasted demand for mocha latte coffees will be cups (enter your response rounded to one decimal place).arrow_forward
- Given the correlation coefficient (r-value), determine the strength of the relationship. Defend your answersarrow_forward??!!arrow_forwardrections: For problem rough 3, read each question carefully and be sure to show all work. 1. Determine if 9(4a²-4ab+b²) = (6a-3b)² is a polynomial identity. 2. Is (2x-y) (8x3+ y³) equivalent to 16x4-y4? 3. Find an expression that is equivalent to (a - b)³. Directions: For problems 4 and 5, algebraically prove that the following equations are polynomial identities. Show all of your work and explain each step. 4. (2x+5)² = 4x(x+5)+25 5. (4x+6y)(x-2y)=2(2x²-xy-6y²)arrow_forward
- Name: Mussels & bem A section of a river currently has a population of 20 zebra mussels. The population of zebra mussels increases 60 % each month. What will be the population of zebra mussels after 2 years? 9 10 # of months # of mussels 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 o Graph your data. Remember to title your graph. What scale should be used on the y-axis? What scale should be used on the x-axis? Exponential Growth Equation y = a(1+r)*arrow_forwardIn a national park, the current population of an endangered species of bear is 80. Each year, the population decreases by 10%. How can you model the population of bears in the park? # of years # of bears 9 10 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 ° 1 Graph your data. Remember to title your graph. What scale should be used on the y-axis? What scale should be used on the x-axis? SMOKY 19 OUNTAINS NATIONAL Exponential Decay Equation y = a(1-r)* PARKarrow_forwardOn Feb. 8, this year, at 6am in the morning all UiB meteorology professors met to discuss a highly unfortunate and top-urgent crisis: Their most precious instrument, responsible for measuring the air temperature hour-by- hour, had failed - what if the Bergen public would find out? How would they plan their weekend without up-to-date air temperature readings? Silent devastation - and maybe a hint of panic, also - hung in the room. Apprentice Taylor, who - as always - was late to the meeting, sensed that this was his chance to shine! Could they fake the data? At least for some hours (until the measurements would work again)? He used to spend a lot of time online and thus knew the value of fake data, especially when it spread fast! He reminded the crying professors of a prehistoric project with the title "Love your derivatives as you love yourself!" - back then, they had installed top-modern technology that not only measured the air temperature itself, but also its 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, and…arrow_forward
- Consider a forest where the population of a particular plant species grows exponentially. In a real-world scenario, we often deal with systems where the analytical function describing the phenomenon is not available. In such cases, numerical methods come in handy. For the sake of this task, however, you are provided with an analytical function so that you can compare the results of the numerical methods to some ground truth. The population P(t) of the plants at time t (in years) is given by the equation: P(t) = 200 0.03 t You are tasked with estimating the rate of change of the plant population at t = 5 years using numerical differentiation methods. First, compute the value of P'(t) at t = 5 analytically. Then, estimate P'(t) at t = 5 years using the following numerical differentiation methods: ⚫ forward difference method (2nd-order accurate) 3 ⚫ backward difference method (2nd-order accurate) ⚫ central difference method (2nd-order accurate) Use h = 0.5 as the step size and round all…arrow_forwardNicole organized a new corporation. The corporation began business on April 1 of year 1. She made the following expenditures associated with getting the corporation started: Expense Date Amount Attorney fees for articles of incorporation February 10 $ 40,500 March 1-March 30 wages March 30 6,550 March 1-March 30 rent Stock issuance costs March 30 2,850 April 1-May 30 wages Note: Leave no answer blank. Enter zero if applicable. April 1 May 30 24,000 16,375 c. What amount can the corporation deduct as amortization expense for the organizational expenditures and for the start-up costs for year 1 [not including the amount determined in part (b)]? Note: Round intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places and final answer to the nearest whole dollar amount. Start-up costs amortized Organizational expenditures amortizedarrow_forwardLast Chance Mine (LCM) purchased a coal deposit for $2,918,300. It estimated it would extract 18,950 tons of coal from the deposit. LCM mined the coal and sold it, reporting gross receipts of $1.24 million, $13 million, and $11 million for years 1 through 3, respectively. During years 1-3, LCM reported net income (loss) from the coal deposit activity in the amount of ($11,400), $550,000, and $502,500, respectively. In years 1-3, LCM extracted 19,950 tons of coal as follows: (1) Tons of Coal 18,950 Depletion (2) Basis (2)(1) Rate $2,918,300 $154.00 Tons Extracted per Year Year 1 4,500 Year 2 8,850 Year 3 6,600 Note: Leave no answer blank. Enter zero if applicable. Enter your answers in dollars and not in millions of dollars. a. What is LCM's cost depletion for years 1, 2, and 3? Cost Depletion Year 1 Year 2 Year 3arrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





