
Classify the carbon atoms in each compound as 1°, 2°, 3°, or 4°.
a.
b.
(a)
Interpretation:
The carbon in the following compound should be classified as
Concept Introduction:
Compounds consist of carbon and hydrogen is known as hydrocarbons. Hydrocarbons are classified as saturated hydrocarbon and unsaturated hydrocarbon. Saturated hydrocarbons are those hydrocarbons in which carbon-carbon single bond is present as carbon is linked with four atoms. Unsaturated hydrocarbons are those hydrocarbons in which carbon-carbon multiple bonds are present that is double and triple bond.
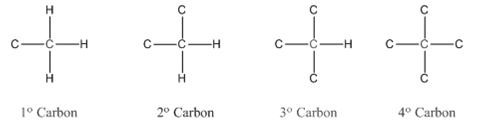
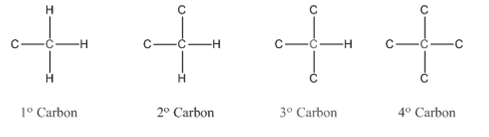
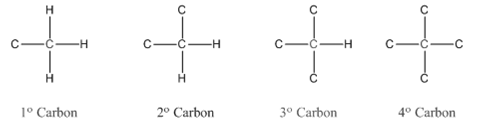
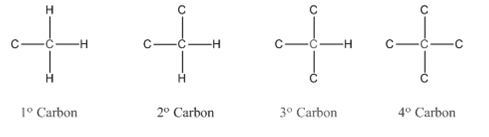
In organic chemistry, carbons are classified as primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary carbons.
Primary carbon (
Secondary carbon (
Tertiary carbon (
Quaternary carbon (
Answer to Problem 12.3PP
Explanation of Solution
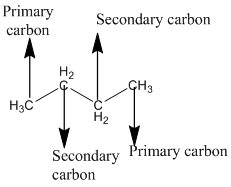
The given compound is
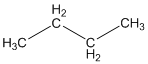
According to the above structure of compound, the terminal carbons present on both sides of the chain is classified as primary carbon as they are linked with one other carbon atom whereas carbon atoms which are present in between the terminal carbonsof the chain are linked with two other carbon atoms thus, classified as secondary carbon.
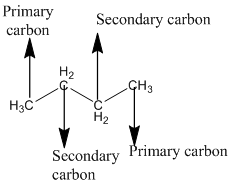
Thus, two primary and two secondary carbons are present in the structure.
(b)
Interpretation:
The carbon in the following compound should be classified as
Concept Introduction:
Compounds consist of carbon and hydrogen is known as hydrocarbons. Hydrocarbons are classified as saturated hydrocarbon and unsaturated hydrocarbon. Saturated hydrocarbons are those hydrocarbons in which carbon-carbon single bond is present as carbon is linked with four atoms. Unsaturated hydrocarbons are those hydrocarbons in which carbon-carbon multiple bonds are present that is double and triple bond.
In organic chemistry, carbons are classified as primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary carbons.
Primary carbon (
Secondary carbon (
Tertiary carbon (
Quaternary carbon (
Answer to Problem 12.3PP
Explanation of Solution
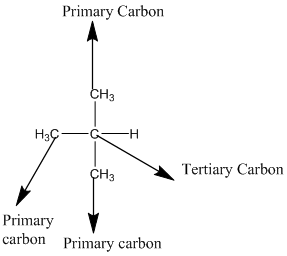
The given compound is
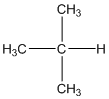
According to the above structure of compound, the terminal carbons (3 carbons) present is classified as primary carbon as they are linked with one other carbon atom whereas carbon atom which is present in the middle linked with three other carbon atoms thus, classified as tertiary carbon.
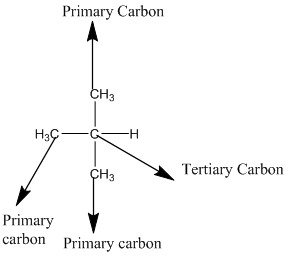
Thus, three primary carbons and onetertiary carbon atom are present in the structure.
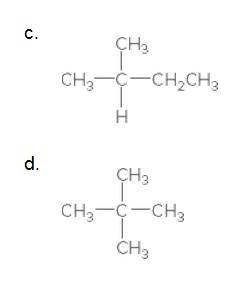
(c)
Interpretation:
The carbon in the following compound should be classified as
Concept Introduction:
Compounds consist of carbon and hydrogen is known as hydrocarbons. Hydrocarbons are classified as saturated hydrocarbon and unsaturated hydrocarbon. Saturated hydrocarbons are those hydrocarbons in which carbon-carbon single bond is present as carbon is linked with four atoms. Unsaturated hydrocarbons are those hydrocarbons in which carbon-carbon multiple bonds are present that is double and triple bond.
In organic chemistry, carbons are classified as primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary carbons.
Primary carbon (
Secondary carbon (
Tertiary carbon (
Quaternary carbon (
Answer to Problem 12.3PP
Explanation of Solution
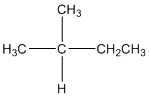
The given compound is
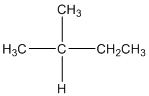
According to the above structure of compound, the terminal carbons (3 carbons) present is classified as primary carbon as they are linked with one other carbon atom whereas the carbon which is linked with two other carbon atoms is classified as secondary carbon and the carbon which is linked with three other carbon atoms is classified as tertiary carbon.
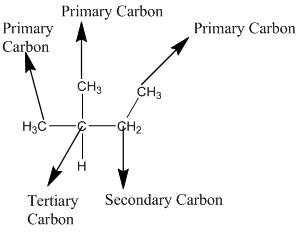
Thus, three primary carbons, one secondary carbon atom and one tertiary carbon atom are present in the structure.
(d)
Interpretation:
The carbon in the following compound should be classified as
Concept Introduction:
Compounds consist of carbon and hydrogen is known as hydrocarbons. Hydrocarbons are classified as saturated hydrocarbon and unsaturated hydrocarbon. Saturated hydrocarbons are those hydrocarbons in which carbon-carbon single bond is present as carbon is linked with four atoms. Unsaturated hydrocarbons are those hydrocarbons in which carbon-carbon multiple bonds are present that is double and triple bond.
In organic chemistry, carbons are classified as primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary carbons.
Primary carbon (
Secondary carbon (
Tertiary carbon (
Quaternary carbon (
Answer to Problem 12.3PP
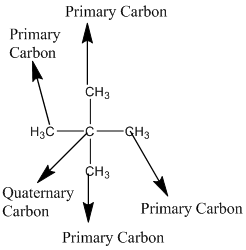
Explanation of Solution
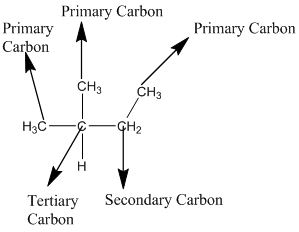
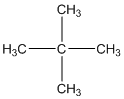
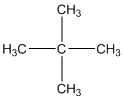
The given compound is
According to the above structure of compound, the terminal carbons (four carbons) present is classified as primary carbon as they are linked with one other carbon atom whereas the carbon which is linked with four other carbon atoms is classified as quaternary carbon.
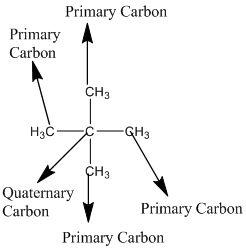
Thus, four primary carbons and one quaternary carbon atom are present in the structure.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Loose Leaf for General, Organic and Biological Chemistry with Connect 2 Year Access Card
- Don't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardDetermine whether the following reaction is an example of a nucleophilic substitution reaction: Br OH HO 2 -- Molecule A Molecule B + Br 义 ollo 18 Is this a nucleophilic substitution reaction? If this is a nucleophilic substitution reaction, answer the remaining questions in this table. Which of the reactants is referred to as the nucleophile in this reaction? Which of the reactants is referred to as the organic substrate in this reaction? Use a ŏ + symbol to label the electrophilic carbon that is attacked during the substitution. Highlight the leaving group on the appropriate reactant. ◇ Yes O No O Molecule A Molecule B Molecule A Molecule B टेarrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forward
- Show work..don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forwardPheromone G of the maize stalk borer, chilo partelus, can be synthesized based on the partial scheme shown below. Complete the scheme by identifying the structures of the intermediate compounds A, B, C, D, E, F and pheromone G. Indicate stereochemistry where relevantarrow_forwardQ8: Draw the resonance structures for the following molecule. Show the curved arrows (how you derive each resonance structure). Circle the major resonance contributor. одarrow_forward
- Q9: Explain why compound I is protonated on O while compound II is protonated on N. NH2 DD I II NH2arrow_forwardComplete the following reaction by identifying the principle organic product of the reactionarrow_forwardDenote the dipole for the indicated bonds in the following molecules. ✓ H3C CH3 B F-CCl3 Br-Cl H3C —Si(CH3)3 CH3 OH HO HO H HO OH vitamin Carrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





