
VEC MECH 180-DAT EBOOK ACCESS(STAT+DYNA)
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781260916942
Author: BEER
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 12.1, Problem 12.6P
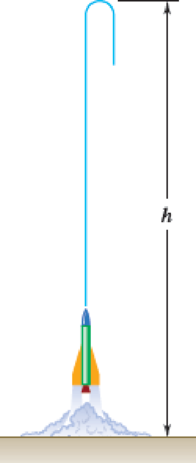
A 0.5-oz model rocket is launched vertically from rest at time t = 0 with a constant thrust of 0.9 lb for 0.3 s and no thrust for t > 0.3 s. Neglecting air resistance and the decrease in mass of the rocket, determine (a) the maximum height h reached by the rocket, (b) the time required to reach this maximum height.
Fig. P12.6
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
(a) What kind of equation is it?(b) Is it linear or non-linear?(c) Is it a coupled system or uncoupled?
What kind of system is presented in Figure 2? Open loop or closed loop?
What are the control hardware shown in the Figure?
Chapter 12 Solutions
VEC MECH 180-DAT EBOOK ACCESS(STAT+DYNA)
Ch. 12.1 - A 1000-lb boulder B is resting on a 200-lb...Ch. 12.1 - Marble A is placed in a hollow tube, and the tube...Ch. 12.1 - The two systems shown start from rest. On the...Ch. 12.1 - Blocks A and B are released from rest in the...Ch. 12.1 - People sit on a Ferris wheel at points A, B, C,...Ch. 12.1 - Crate A is gently placed with zero initial...Ch. 12.1 - Two blocks weighing WA and WB are at rest on a...Ch. 12.1 - Objects A, B, and C have masses mA, mB, and mC,...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.4FBPCh. 12.1 - Blocks A and B have masses mA and mB,...
Ch. 12.1 - A pilot of mass m flies a jet in a half-vertical...Ch. 12.1 - Wires AC and BC are attached to a sphere that...Ch. 12.1 - A collar of mass m is attached to a spring and...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.9FBPCh. 12.1 - At the instant shown, the length of the boom AB is...Ch. 12.1 - Disk A rotates in a horizontal plane about a...Ch. 12.1 - Pin B has a mass m and slides along the slot in...Ch. 12.1 - The acceleration due to gravity on Mars is 3.75...Ch. 12.1 - The value of g at any latitude may be obtained...Ch. 12.1 - A Global Positioning System (GPS) satellite is in...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.4PCh. 12.1 - A loading car is at rest on a track forming an...Ch. 12.1 - A 0.5-oz model rocket is launched vertically from...Ch. 12.1 - Determine the maximum theoretical speed that may...Ch. 12.1 - A tugboat pulls a small barge through a harbor....Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.9PCh. 12.1 - A 4-kg package is released from rest at point A...Ch. 12.1 - The coefficients of friction between the load and...Ch. 12.1 - A light train made up of two cars is traveling at...Ch. 12.1 - The two blocks shown are originally at rest....Ch. 12.1 - The two blocks shown are originally at rest....Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.15PCh. 12.1 - Prob. 12.16PCh. 12.1 - A 5000-lb truck is being used to lift a 1000-lb...Ch. 12.1 - Block A has a mass of 40 kg, and block B has a...Ch. 12.1 - Block A has a mass of 40 kg, and block B has a...Ch. 12.1 - The flat-bed trailer carries two 1500-kg beams...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.21PCh. 12.1 - To unload a bound stack of plywood from a truck,...Ch. 12.1 - To transport a series of bundles of shingles A to...Ch. 12.1 - An airplane has a mass of 25 Mg and its engines...Ch. 12.1 - Determine the maximum theoretical speed that a...Ch. 12.1 - A constant force P is applied to a piston and rod...Ch. 12.1 - A spring AB of constant k is attached to a support...Ch. 12.1 - Block A has a mass of 10 kg, and blocks B and C...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.29PCh. 12.1 - Prob. 12.30PCh. 12.1 - A 10-lb block B rests as shown on a 20-lb bracket...Ch. 12.1 - Knowing that k = 0.30, determine the acceleration...Ch. 12.1 - Knowing that k = 0.30, determine the acceleration...Ch. 12.1 - The 30-lb block B is supported by the 55-lb block...Ch. 12.1 - Block B of mass 10 kg rests as shown on the upper...Ch. 12.1 - Knowing that the swings of an amusement park ride...Ch. 12.1 - During a hammer throwers practice swings, the...Ch. 12.1 - Human centrifuges are often used to simulate...Ch. 12.1 - A single wire ACB passes through a ring at C...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.41PCh. 12.1 - The 0.5-kg flyballs of a centrifugal governor...Ch. 12.1 - As part of an outdoor display, a 5-kg model C of...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.44PCh. 12.1 - During a high-speed chase, a 2400-lb sports car...Ch. 12.1 - An airline pilot climbs to a new flight level...Ch. 12.1 - The roller-coaster track shown is contained in a...Ch. 12.1 - A spherical-cap governor is fixed to a vertical...Ch. 12.1 - A series of small packages, each with a mass of...Ch. 12.1 - A 55-kg pilot flies a jet trainer in a half...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.51PCh. 12.1 - A curve in a speed track has a radius of 1000 ft...Ch. 12.1 - Tilting trains, such as the Acela Express that...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.54PCh. 12.1 - A 3-kg block is at rest relative to a parabolic...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.56PCh. 12.1 - A turntable A is built into a stage for use in a...Ch. 12.1 - The carnival ride from Prob. 12.51 is modified so...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.59PCh. 12.1 - A small 8-oz collar D can slide on portion AB of a...Ch. 12.1 - A small block B fits inside a slot cut in arm OA...Ch. 12.1 - The parallel-link mechanism ABCD is used to...Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 12.63PCh. 12.1 - A small 250-g collar C can slide on a semicircular...Ch. 12.1 - A small 250-g collar C can slide on a semicircular...Ch. 12.1 - An advanced spatial disorientation trainer is...Ch. 12.1 - The 3-kg collar B slides on the frictionless arm...Ch. 12.1 - A 0.5-kg block B slides without friction inside a...Ch. 12.1 - Pin B weighs 4 oz and is free to slide in a...Ch. 12.1 - The parasailing system shown uses a winch to let...Ch. 12.1 - A 700-kg horse A lifts a 50-kg hay bale B as...Ch. 12.2 - A particle of mass m is projected from point A...Ch. 12.2 - A particle of mass m is projected from point A...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the mass of the earth knowing that the...Ch. 12.2 - Show that the radius r of the moons orbit can be...Ch. 12.2 - Communication satellites are placed in a...Ch. 12.2 - Prob. 12.81PCh. 12.2 - The orbit of the planet Venus is nearly circular...Ch. 12.2 - A satellite is placed into a circular orbit about...Ch. 12.2 - The periodic time (see Prob. 12.83) of an earth...Ch. 12.2 - A 500-kg spacecraft first is placed into a...Ch. 12.2 - A space vehicle is in a circular orbit of 2200-km...Ch. 12.2 - Prob. 12.87PCh. 12.2 - Prob. 12.88PCh. 12.2 - Prob. 12.89PCh. 12.2 - A 1-kg collar can slide on a horizontal rod that...Ch. 12.2 - Two 2.6-lb collars A and B can slide without...Ch. 12.2 - A small ball swings in a horizontal circle at the...Ch. 12.3 - A uniform crate C with mass mC is being...Ch. 12.3 - A uniform crate C with mass m is being transported...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.94PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.95PCh. 12.3 - A particle with a mass m describes the path...Ch. 12.3 - A particle of mass m describes the parabola y =...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.98PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.99PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.100PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.101PCh. 12.3 - A satellite describes an elliptic orbit about a...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.103PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.104PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.105PCh. 12.3 - Halleys comet travels in an elongated elliptic...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.109PCh. 12.3 - A space probe is to be placed in a circular orbit...Ch. 12.3 - The Clementine spacecraft described an elliptic...Ch. 12.3 - A space probe is describing a circular orbit of...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.115PCh. 12.3 - A space shuttle is describing a circular orbit at...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.117PCh. 12.3 - A satellite describes an elliptic orbit about a...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.119PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 12.120PCh. 12.3 - Show that the angular momentum per unit mass h of...Ch. 12 - In the braking test of a sports car, its velocity...Ch. 12 - A bucket is attached to a rope of length L = 1.2 m...Ch. 12 - A 500-lb crate B is suspended from a cable...Ch. 12 - The parasailing system shown uses a winch to pull...Ch. 12 - A robot arm moves in the vertical plane so that...Ch. 12 - Telemetry technology is used to quantify kinematic...Ch. 12 - The radius of the orbit of a moon of a given...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.131RPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.132RPCh. 12 - Disk A rotates in a horizontal plane about a...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
A nozzle at A discharges water with an initial velocity of 36 ft/s at an angle with the horizontal. Determine ...
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
17–1C A high-speed aircraft is cruising in still air. How does the temperature of air at the nose of the aircra...
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
How are relationships between tables expressed in a relational database?
Modern Database Management
Porter’s competitive forces model: The model is used to provide a general view about the firms, the competitors...
Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm (16th Edition)
Assume a telephone signal travels through a cable at two-thirds the speed of light. How long does it take the s...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
What types of coolant are used in vehicles?
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question 1. A tube rotates in the horizontal ry plane with a constant angular velocity w about the z-axis. A particle of mass m is released from a radial distance R when the tube is in the position shown. This problem is based on problem 3.2 in the text. R m 2R Figure 1 x a) Draw a free body diagram of the particle if the tube is frictionless. b) Draw a free body diagram of the particle if the coefficient of friction between the sides of the tube and the particle is = k = p. c) For the case where the tube is frictionless, what is the radial speed at which the particle leaves the tube? d) For the case where there is friction, derive a differential equation that would allow you to solve for the radius of the particle as a function of time. I'm only looking for the differential equation. DO NOT solve it. 1 e) If there is no friction, what is the angle of the tube when the particle exits? • Hint: You may need to solve a differential equation for the last part. The "potentially useful…arrow_forwardQuestion 2. A smooth uniform sphere of mass m and radius r is squeezed between two massless levers, each of length 1, which are inclined at an angle with the vertical. A mechanism at pivot point O ensures that the angles & remain the same at all times so that the sphere moves straight upward. This problem is based on Problem 3-1 in the text. P P r Figure 2 a) Draw appropriate freebody diagrams of the system assuming that there is no friction. b) Draw appropriate freebody diagrams of the system assuming that there is a coefficient of friction between the sphere and the right lever of μ. c) If a force P is applied between the ends of the levers (shown in the diagram), and there is no friction, what is the acceleration of the sphere when = 30°arrow_forwardIf you had a matrix A = [1 2 3; 4 5 6; 7 8 9] and a matrix B = [1 2 3], how would you cross multiply them i.e. what is the cross product of AxB. what would be the cross product of a dyadic with a vector?arrow_forward
- Problem 3: The inertia matrix can be written in dyadic form which is particularly useful when inertia information is required in various vector bases. On the next page is a right rectangular pyramid of total mass m. Note the location of point Q. (a) Determine the inertia dyadic for the pyramid P, relative to point Q, i.e., 7%, for unit vectors ₁₁, 2, 3.arrow_forwardCan you solve for v? Also, what is A x uarrow_forwardThe external loads on the element shown below at the free end are F = 1.75 kN, P = 9.0 kN, and T = 72 Nm. The tube's outer diameter is 50 mm and the inner diameter is 45 mm. Given: A(the cross-sectional area) is 3.73 cm², Moment inertial I is 10.55 cm4, and J polar moment inertial is 21.1 cm4. Determine the following. (1) The critical element(s) of the bar. (2) Show the state of stress on a stress element for each critical element. -120 mm- Farrow_forward
- A crate weighs 530 lb and is hung by three ropes attached to a steel ring at A such that the top surface is parallel to the xy plane. Point A is located at a height of h = 42 in above the top of the crate directly over the geometric center of the top surface. Use the dimensions given in the table below to determine the tension in each of the three ropes. 2013 Michael Swanbom ↑ Z C BY NC SA b x B у D Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 30 in b 43 in с 4.5 in The tension in rope AB is lb The tension in rope AC is lb The tension in rope AD is lbarrow_forwardThe airplane weighs 144100 lbs and flies at constant speed and trajectory given by 0 on the figure. The plane experiences a drag force of 73620 lbs. a.) If = 11.3°, determine the thrust and lift forces required to maintain this speed and trajectory. b.) Next consider the case where is unknown, but it is known that the lift force is equal to 7.8 times the quantity (Fthrust Fdrag). Compute the resulting trajectory angle - and the lift force in this case. Use the same values for the weight and drag forces as you used for part a. Уллу Fdrag 10. Ө Fthrust cc 10 2013 Michael Swanbom BY NC SA Flift Fweight The lift force acts in the y' direction. The weight acts in the negative y direction. The thrust and drag forces act in the positive and negative x' directions respectively. Part (a) The thrust force is equal to lbs. The lift force is equal to Part (b) The trajectory angle is equal to deg. The lift force is equal to lbs. lbs.arrow_forwardThe hoist consists of a single rope and an arrangement of frictionless pulleys as shown. If the angle 0 = 59°, determine the force that must be applied to the rope, Frope, to lift a load of 4.4 kN. The three-pulley and hook assembly at the center of the system has a mass of 22.5 kg with a center of mass that lies on the line of action of the force applied to the hook. e ΘΕ B CC 10 BY NC SA 2013 Michael Swanbom Fhook Note the figure may not be to scale. Frope = KN HO Fropearrow_forward
- Determine the tension developed in cables AB and AC and the force developed along strut AD for equilibrium of the 400-lb crate. x. 5.5 ft C 2 ft Z 2 ft D 6 ft B 4 ft A 2.5 ftarrow_forwardA block of mass m hangs from the end of bar AB that is 7.2 meters long and connected to the wall in the xz plane. The bar is supported at A by a ball joint such that it carries only a compressive force along its axis. The bar is supported at end B by cables BD and BC that connect to the xz plane at points C and D respectively with coordinates given in the figure. Cable BD is elastic and can be modeled as a linear spring with a spring constant k = 400 N/m and unstretched length of 6.34 meters. Determine the mass m, the compressive force in beam AB and the tension force in cable BC. Z D (c, 0, d) C (a, 0, b), A e B y f m BY NC SA x 2016 Eric Davishahl Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 8.1 m b 3.3 m C 2.7 m d 3.9 m e 2 m f 5.4 m The mass of the block is The compressive force in bar AB is The tension in cable S is N. kg.arrow_forwardTwo squirrels are sitting on the rope as shown. The squirrel at A has a weight of 1.2 lb. The squirrel at B found less food this season and has a weight of 0.8 lb. The angles 0 and > are equal to 50° and 60° respectively. Determine the tension force in each of the rope segments (T₁ in segment, T₂ in segment Я, and T3 in segment DD) as well as the angle a in degrees. Ө A α B Note the figure may not be to scale. T₁ = lb lb T2 T3 = = lb απ deg A BY NC SA 2013 Michael Swanbomarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Extent of Reaction; Author: LearnChemE;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=__stMf3OLP4;License: Standard Youtube License