
Concept explainers
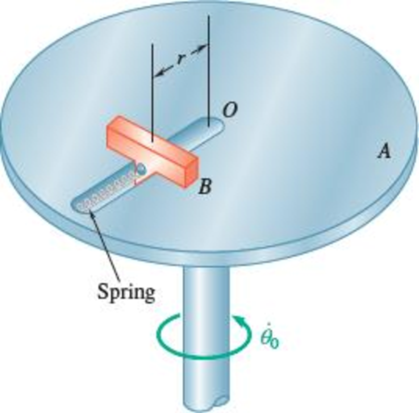
Disk A rotates in a horizontal plane about a vertical axis at the
(a)
Find the position of the slider and horizontal force exerted on the slider by disk at
Answer to Problem 12.133RP
The position of the slider at
The horizontal force exerted on the slider by disk at
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The polar coordinate
The mass
The distance
The spring constant (k) is 100 N/m.
Calculation:
Consider the Position of the slider is in point O
Find the displacement of spring when
Consider distance of the slider (r) from the point O is 500 mm.
Find the displacement of spring when
Substitute 500 mm for r.
Find the restoring force (F) of spring when
Substitute 100 N/m for k and 500 mm for
Sketch the free body diagram and kinetic diagram of forces on disk A and spring as shown in in Figure (1).
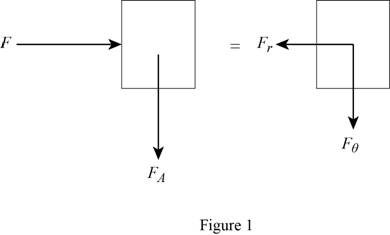
Refer Figure (1).
Write the equation of radial component of acceleration
Apply Newton’s law of equation along radial direction.
The radial force is equal to the restoring force.
Find the equation of restoring force (F).
Substitute
Substitute
Write the equation of
Integrate Equation (1) to find
Use Equation (1) to substitute for
Slider B is at initial position when
Write
Integrate Equation (4) to find
Use Equation (3) to substitute for
Find the position of the slider at
Use Equation (4) to substitute for
Thus, the position of the slider at
Refer Figure 1.
Apply Newton’s law of Equation along transverse direction.
Write the transverse component of acceleration
Here,
The transverse force is the horizontal force exerted on the slider by disk.
The disk is rotating at constant rate. Therefore, the polar coordinate of transverse acceleration,
Find the horizontal force exerted on the slider by disk at
Write the equation of transverse force
Substitute
Substitute 0 for
Substitute Equation (3) in Equation (7).
Thus, the horizontal force exerted on the slider by disk at
(b)
Find the position of the slider and horizontal force exerted on the slider by disk at
Answer to Problem 12.133RP
The position of the slider at
The horizontal force exerted on the slider by disk at
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Consider the Position of the slider is in point O
Find the displacement of spring when
Consider distance of the slider (r) from the point O is 500 mm.
Find the displacement of spring when
Substitute 500 mm for r.
Find the restoring force (F) of spring when
Substitute 200 N/m for k and 500 mm for
Refer Figure (1).
Write the equation of radial component of acceleration
Apply Newton’s law of equation along radial direction.
The radial force is equal to the restoring force.
Find the equation of restoring force (F).
Substitute
Substitute
Write the equation of radial velocity of the slider in terms of r.
Here,
Write equation of the rate of change of position coordinate in terms of differential equation.
Apply differentiation to Equation (8)
Rewrite Equation (10) by multiplying and dividing the right-hand side by dr.
Substitute Equation (10) to rewrite Equation (11).
Substitute Equation (8) to rewrite Equation (12).
Substitute
Apply the limits to integrate the Equation (14).
At the time of instant
Substitute Equation (8) in Equation (15).
Integrate Equation (16).
Use spherical polar coordinates and choose,
Differentiate Equation (18).
Rewrite Equation (18).
Rewrite Equation (20) for
Use Equation (20) and (21) to change the values of limit in Equation (17).
Apply the trigonometric formula of
Use Equation (23) to rewrite Equation (22).
Substitute 0.5m for
Thus, the position of the slider at
Find the radial polar coordinate of velocity using Equation (24).
Differentiate Equation (24) with respect to t.
Substitute 500 mm for
Find the horizontal force exerted on the slider by disk at
Substitute
Substitute 0.1 s for t and
Thus, the horizontal force exerted on the slider by disk at
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
VEC MECH 180-DAT EBOOK ACCESS(STAT+DYNA)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
BASIC BIOMECHANICS
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Modern Database Management
- Access Pearson Mastering Engineering Back to my courses Course Home Course Home Scoresarrow_forwardAccess Pearson Mastering Engineering Back to my courses Course Home Course Home Scores Review Next >arrow_forwardAccess Pearson Course Home Scoresarrow_forwardCan you answer this question?arrow_forwardCan you answer this question?arrow_forwardA gear has a gear wheel with 16 teeth. The gear should be dimensioned for the highest and lowest gear ratio. Looking for output power, torque, speed?nin= 2000 rpmmin = 30Nmn=0,9a max= 450 mmModule 4Gear limitsz1 z213 13-1614 14-2615 15-4516 16-10117 17-131418 18-…..I have calculate but I can’t get the right answers…..√16 =459x60/56x57=1.1 lowest59x60/13x13=20,94 highestnut=2000/1.1= 1818rpmnut=2000/20.94=95.5 rpmMut=1.1x30=33 NmMut=20.94x30=628,2 Nm(Right answer)LowestZ=13, M=24,4Nm, n=2462 rpmHighestZ=92, M=172,5Nm, n=347,8 rpmP=5655W on botharrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





