
Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781305079373
Author: William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 12, Problem 2QAP
The following data are for the system
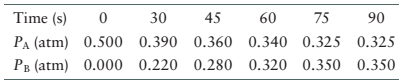
(a) How long does it take the system to reach equilibrium?
(b) How does the rate of the forward reaction compare with the rate of the reverse reaction after 45 s? After 90 s?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Incorrect
Row 2: Your answer is incorrect.
Consider this molecule:
How many H atoms are in this molecule?
22
How many different signals could be found in its 'H NMR spectrum?
12
Note: A multiplet is considered one signal.
13
How many signals would you expect to see in the
Check
O
signal(s)
X
§
'C NMR spectrum for the following compound?
© 2025 McGraw Hill
13
Consider the "C NMR spectrum below.
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
20
PPM
0
The spectrum belongs to which one of the following constitutional isomers of the compound C,H12? Select the single best answer.
Check
✓
G
Save For Later
2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use
Chapter 12 Solutions
Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Ch. 12 - The following data are for the system A(g)2B(g)...Ch. 12 - The following data are for the system A(g)2B(g)...Ch. 12 - Prob. 3QAPCh. 12 - Complete the table below for the reaction...Ch. 12 - Write the equilibrium expressions (K) for the...Ch. 12 - Write the equilibrium expressions (K) for the...Ch. 12 - Write the equilibrium expressions (K) for the...Ch. 12 - Write the equilibrium expressions (K) for the...Ch. 12 - Given the following descriptions of reversible...Ch. 12 - Given the following descriptions of reversible...
Ch. 12 - Write an equation for an equilibrium system that...Ch. 12 - Write a chemical equation for an equilibrium...Ch. 12 - Consider the following reaction at 250C:...Ch. 12 - Consider the following reaction at 1000 C:...Ch. 12 - At 627C, K=0.76 for the reaction...Ch. 12 - At 800C, K=2.2104 for the following reaction...Ch. 12 - Prob. 17QAPCh. 12 - Given the following data at 25C...Ch. 12 - Given the following data at a certain temperature,...Ch. 12 - Consider the following hypothetical reactions and...Ch. 12 - When one mole of carbon disulfide gas reacts with...Ch. 12 - Calculate K for the formation of methyl alcohol at...Ch. 12 - Ammonium carbamate solid (NH4CO2NH2) decomposes at...Ch. 12 - Consider the decomposition at 25C of one mole of...Ch. 12 - Consider the decomposition of ammonium hydrogen...Ch. 12 - A sealed flask has 0.541 atm of SO3 at 1000 K. The...Ch. 12 - A gaseous reaction mixture contains 0.30 atm SO2,...Ch. 12 - For the system PCl5(g)PCl3(g)+Cl2(g)K is 26 at...Ch. 12 - The reversible reaction between hydrogen chloride...Ch. 12 - The reversible reaction between hydrogen chloride...Ch. 12 - A compound, X, decomposes at 131C according to the...Ch. 12 - Consider the following reaction at 75C:...Ch. 12 - Consider the reaction between nitrogen and steam:...Ch. 12 - At 500C, k for the for the formation of ammonia...Ch. 12 - At a certain temperature, K is 4.9 for the...Ch. 12 - At a certain temperature, K=0.29 for the...Ch. 12 - For the reaction N2(g)+2H2O(g)2NO(g)+2H2(g) K is...Ch. 12 - Nitrogen dioxide can decompose to nitrogen oxide...Ch. 12 - Consider the following reaction:...Ch. 12 - Consider the hypothetical reaction at 325C...Ch. 12 - At a certain temperature, the equilibrium constant...Ch. 12 - At 460C, the reaction SO2(g)+NO2(g)NO(g)+SO3(g)...Ch. 12 - Solid ammonium iodide decomposes to ammonia and...Ch. 12 - Consider the following decomposition at 80C....Ch. 12 - Hydrogen cyanide, a highly toxic gas, can...Ch. 12 - At 800 K, hydrogen iodide can decompose into...Ch. 12 - For the following reactions, predict whether the...Ch. 12 - Follow the directions of Question 47 for the...Ch. 12 - Consider the system SO3(g)SO2(g)+12 O2(g)H=98.9kJ...Ch. 12 - Consider the system...Ch. 12 - Predict the direction in which each of the...Ch. 12 - Predict the direction in which each of the...Ch. 12 - At a certain temperature, nitrogen and oxygen...Ch. 12 - Consider the following hypothetical reaction:...Ch. 12 - Iodine chloride decomposes at high temperatures to...Ch. 12 - Sulfur oxychloride, SO2Cl2, decomposes to sulfur...Ch. 12 - For the following reaction C(s)+2H2(g)CH4(g)...Ch. 12 - For the system 2SO3(g)2SO2(g)+O2(g) K=1.32 at 627....Ch. 12 - For a certain reaction, H is +33 kJ. What is the...Ch. 12 - Prob. 60QAPCh. 12 - Hemoglobin (Hb) binds to both oxygen and carbon...Ch. 12 - Mustard gas, used in chemical warfare in World War...Ch. 12 - Prob. 63QAPCh. 12 - For the decomposition of CaCO3 at 900C, K=1.04....Ch. 12 - Isopropyl alcohol is the main ingredient in...Ch. 12 - Consider the equilibrium H2(g)+S(s)H2S(g)When this...Ch. 12 - Prob. 67QAPCh. 12 - The following data apply to the unbalanced...Ch. 12 - Consider the reaction: A(g)+2B(g)+C(s)2D(g)At 25C,...Ch. 12 - For the reaction C(s)+CO2(g)2CO(g) K=168 at 1273...Ch. 12 - Consider the system A(g)+2B(g)+C(g)2D(g)at 25C. At...Ch. 12 - The graph below is similar to that of Figure 12.2....Ch. 12 - Prob. 73QAPCh. 12 - The figures below represent the following reaction...Ch. 12 - Prob. 75QAPCh. 12 - Prob. 76QAPCh. 12 - Consider the following reaction at a certain...Ch. 12 - Prob. 78QAPCh. 12 - Ammonia can decompose into its constituent...Ch. 12 - Hydrogen iodide gas decomposes to hydrogen gas and...Ch. 12 - For the system SO3(g)SO2(g)+12 O2(g)at 1000 K,...Ch. 12 - A student studies the equilibrium I2(g)2I(g)at a...Ch. 12 - At a certain temperature, the reaction...Ch. 12 - Benzaldehyde, a flavoring agent, is obtained by...Ch. 12 - Prob. 85QAPCh. 12 - Prob. 86QAP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The structure of compound 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene (mesitylene) is given below. How many signals would you expect to find in the 'H NMR spectrum of 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene (mesitylene)? Check ×arrow_forward1 How many signals do you expect in the 'H NMR spectrum for this molecule? CI CI Cl Write the answer in the table below. Also, in each of the drawing areas below is a copy of the molecule, with H atoms shown. In each copy, one of the H atoms is highlighted red. Highlight in red all other H atoms that would contribute to the same signal as the H already highlighted red. Note for advanced students: Remember, a multiplet is considered one signal in the 'H NMR spectrum. 1 Number of signals in the 'H NMR spectrum. ☐ For the molecule in the top drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red. If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box at right. No additional H atoms to highlight in top molecule For the molecule in the bottom drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red. If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box at…arrow_forwardwrtie the balanced equation and find the E° when the following half- reactions are combined Zn2+(aq) + 2e---> Zn(s) E°= -0.763V Ag+(aq) + e---> Ag (s) E°=+0.799Varrow_forward
- Consider this molecule: How many H atoms are in this molecule? How many different signals could be found in its 'H NMR spectrum? Note: A multiplet is considered one signal. ☐arrow_forwardStudy this 'H NMR spectrum, and then answer the questions about it in the table below. Check 1.0- 0.5- 0.0 10.0 9.0 8.0 7.0 6.0 5.0 4.0 3.0 2.0 1.0 0.0 What unit symbol should be written on the horizontal axis? What is the chemical shift & of the doublet? If there is no doublet, just check the box instead. Give your answer to 2 significant digits. What is the chemical shift of the signal immediately upfield of the doublet? If there is no doublet, or no signal upfield of it, check the box instead. What is the chemical shift & of the least deshielded proton? If you can't tell without more information, check the box instead. 血 8 = ☐ There is no doublet. 8 = ☐ No such signal. 8 = 0 Need more information.arrow_forwardhow many moles of H2O2 are required to react with 11g of N2H4 according to the following reaction? (atomic weights: N=14.01, H=1.008, O= 16.00) 7H2O2 + N2H4 -> 2HNO3 + 8H20arrow_forward
- calculate the number of moles of H2 produced from 0.78 moles of Ga and 1.92 moles HCL? 2Ga+6HCL->2GaCl3+3H2arrow_forwardan adult human breathes 0.50L of air at 1 atm with each breath. If a 50L air tank at 200 atm is available, how man y breaths will the tank providearrow_forwardWhat are the advantages and/or disadvantages of using the MOHR titration method & AOEC method?arrow_forward
- Are there any alternative methods better than the MOHR titration to quantitatively determine salt in a sample?arrow_forwardhybridization of nitrogen of complex moleculesarrow_forwardUsing reaction free energy to predict equilibrium composition Consider the following equilibrium: 2NO2 (g) = N2O4(g) AGº = -5.4 kJ Now suppose a reaction vessel is filled with 4.53 atm of dinitrogen tetroxide (N2O4) at 279. °C. Answer the following questions about this system: Under these conditions, will the pressure of N2O4 tend to rise or fall? Is it possible to reverse this tendency by adding NO2? In other words, if you said the pressure of N2O4 will tend to rise, can that be changed to a tendency to fall by adding NO2? Similarly, if you said the pressure of N2O4 will tend to fall, can that be changed to a tendency to '2' rise by adding NO2? If you said the tendency can be reversed in the second question, calculate the minimum pressure of NO 2 needed to reverse it. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. 00 rise ☐ x10 fall yes no ☐ atm G Ar 1arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079113
Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:9781938168390
Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:OpenStax

General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285853918
Author:H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285869759
Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Chemical Equilibria and Reaction Quotients; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1GiZzCzmO5Q;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY