
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
If the given statement is true or false should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Answer to Problem 12.39P
The statement istrue.
Explanation of Solution
Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons with carbon-carbon double bonds. The combustion reaction takes place in the presence of air. The combustion of alkenes produces carbon dioxide and water.
Hence, the given statement is true.
(b)
Interpretation:
The given statement is true or false should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes or olefins are the unsaturated hydrocarbons. They are organic compounds with one or more carbon-carbon double bonds. Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes. They undergo many characteristic reactions namely Addition reactions, oxidation reactions and combustion reactions.
Answer to Problem 12.39P
The statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
The addition reaction of alkenes is one double bond of alkene and one single bond of a second reactant break, and three new single bonds are formed such that the addition of the second reactant occurs at the carbon atoms of the double bond. Hence, the two new single bonds are formed at the doubly bonded carbon atoms. Therefore, the given statement is true.
(c)
Interpretation:
The given statement is true or false should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes or olefins are the unsaturated hydrocarbons. They are organic compounds with one or more carbon-carbon double bonds. Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes. They undergo many characteristic reactions namely Addition reactions, oxidation reactions and combustion reactions.
Answer to Problem 12.39P
The statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
Regioselectivity means the preference of making or breaking of bonds over all other possibilities. Markovnikov's rule states that in the addition of a halogen acid to an alkene, hydrogen goes to the carbon atom in a double bond that bears a higher number of hydrogen atoms. Thus, it indicates the position of the attack. Hence, Markovnikov's rule refers to the regioselectivity of the carbon-carbon double bond. Therefore, the given statement is true.
(d)
Interpretation:
The given statement is true or false should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes or olefins are the unsaturated hydrocarbons. They are organic compounds with one or more carbon-carbon double bonds. Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes. They undergo many characteristic reactions namely Addition reactions, oxidation reactions and combustion reactions.
Answer to Problem 12.39P
The statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
Markovnikov's rule states that addition of a halogen acid (HX, x = Cl, Br or I) to an alkene, hydrogen goes to the carbon atom in the double bond that bears a higher number of hydrogen atoms. In additionof HCI, HBr, and HI to an alkene, hydrogen attaches to the carbon of the double bond that already has a greater number of hydrogen atoms bonded to it. Therefore, the given statement is true.
(e)
Interpretation:
The given statement is true or false should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes or olefins are the unsaturated hydrocarbons. They are organic compounds with one or more carbon-carbon double bonds. Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes. They undergo many characteristic reactions namely Addition reactions, oxidation reactions and combustion reactions.
Answer to Problem 12.39P
The statement is false.
Explanation of Solution
A carbocation is a carbon atom with three bonds and is deficient in one pair of the electrons, thus, acquiring a positive charge. Therefore, the given statement is false.
(f)
Interpretation:
The given statement is true or false should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes or olefins are the unsaturated hydrocarbons. They are organic compounds with one or more carbon-carbon double bonds. Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes. They undergo many characteristic reactions namely Addition reactions, oxidation reactions and combustion reactions.
Answer to Problem 12.39P
The statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
The carbocation is derived from ethylene by the attack of a proton as depicted in the equation is CH3 CH2 +.
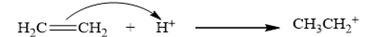
Therefore, the given statement is true.
(g)
Interpretation:
The given statement is true or false should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes or olefins are the unsaturated hydrocarbons. They are organic compounds with one or more carbon-carbon double bonds. Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes. They undergo many characteristic reactions namely Addition reactions, oxidation reactions and combustion reactions.
Answer to Problem 12.39P
The statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
The mechanism of the addition of HX to an alkene is a two-step reaction.
Step 1: The formation of the carbocation. In the first step of the reaction, the proton is added to the double bond, and the carbocation is generated as carbocation intermediate.
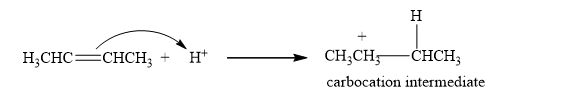
Step 2: The Nucleophilic attack. Then, a halide ion which is a nucleophile attacks the carbocation, forming an additional product.
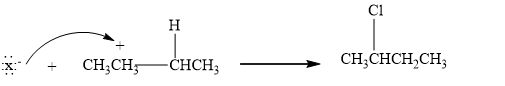
Therefore, the given statement is true.
(h)
Interpretation:
The given statement is true or false should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes or olefins are the unsaturated hydrocarbons. They are organic compounds with one or more carbon-carbon double bonds. Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes. They undergo many characteristic reactions namely Addition reactions, oxidation reactions and combustion reactions.
Answer to Problem 12.39P
The statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
The addition of water is known as hydration. According to Markovnikov's rule, in acid, the catalyzed addition of water to an alkene water molecule is added to the carbon-carbon double bond. Furthermore, in the presence of acid, the alkene is converted to alcohol. Therefore, the given statement is true.
(i)
Interpretation:
The given statement is true or false should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes or olefins are the unsaturated hydrocarbons. They are organic compounds with one or more carbon-carbon double bonds. Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes. They undergo many characteristic reactions namely Addition reactions, oxidation reactions and combustion reactions.
Answer to Problem 12.39P
The statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
The addition of Br2 to a carbon-carbon double bond takes place at room temperature. Thus, if a compound fails to react with Br2, then the compound does not contain a double bond. Therefore, the given statement is true.
(j)
Interpretation:
The given statement is true or false should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes or olefins are the unsaturated hydrocarbons. They are organic compounds with one or more carbon-carbon double bonds. Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes. They undergo many characteristic reactions namely Addition reactions, oxidation reactions and combustion reactions.
Answer to Problem 12.39P
The statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
The addition of H2 is known as reduction. During a reaction with molecular H2, all of the alkenes, are converted to alkanes. Hence, hydrogen is added to the double bond of an alkene. Thus, the given statement is true.
(k)
Interpretation:
The given statement is true or false should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes or olefins are the unsaturated hydrocarbons. They are organic compounds with one or more carbon-carbon double bonds. Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes. They undergo many characteristic reactions namely Addition reactions, oxidation reactions and combustion reactions.
Answer to Problem 12.39P
The statement is false.
Explanation of Solution
Catalytic reduction is the process in which a substance is reduced by hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst. The catalytic reduction of cyclohexene is the addition of H2 across the double bond that is present in the cyclic ring. The resultant product is cyclohexane, not hexane. Thus, the given statement is false.
(l)
Interpretation:
The given statement is true or false should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes or olefins are the unsaturated hydrocarbons. They are organic compounds with one or more carbon-carbon double bonds. Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes. They undergo many characteristic reactions namely Addition reactions, oxidation reactions and combustion reactions.
Answer to Problem 12.39P
The statement is false.
Explanation of Solution
The acid catalyzed hydration of alkene is completed in three steps. The first step includes the addition of a proton (from acid) to the double bond that results in the formation of a carbocation, and hydrogen attaches to one of the doubly bonded carbons. In the second step, an oxygen atom of a water molecule attacks the positively charged carbon, and the water molecule attaches to it, forming an intermediate called an oxonium ion. In the third step, the proton is regenerated again by losing H+ from the oxonium ion, Therefore, in the final product, OH comes from a water molecule, while H comes from the acid used as a catalyst. Thus, the given statement is false.
(m)
Interpretation:
The given statement is true or false should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes or olefins are the unsaturated hydrocarbons. They are organic compounds with one or more carbon-carbon double bonds. Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes. They undergo many characteristic reactions namely Addition reactions, oxidation reactions and combustion reactions.
Answer to Problem 12.39P
The statement is false.
Explanation of Solution
Oxidation is characterized as a gain in oxygen or a loss of hydrogen or a molecule. The alkene on the acid-catalyzed hydration is converted into alcohol. Thus, the conversion of CH2 = CH2 to ethanol is an addition reaction in which a molecule of water is added to the double bond. Thus, there is neither a loss of hydrogen nor a gain of oxygen. Hence, this is an addition reaction and not an oxidation reaction, so, the given statement is false.
(n)
Interpretation:
The given statement is true or false should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Alkenes or olefins are the unsaturated hydrocarbons. They are organic compounds with one or more carbon-carbon double bonds. Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes. They undergo many characteristic reactions namely Addition reactions, oxidation reactions and combustion reactions.
Answer to Problem 12.39P
The statement is false.
Explanation of Solution
According to Markovnikov's rule, in the acid-catalyzed hydration of alkene, water is added to the double bond of alkene such that the addition of the H and OH groups occur. Furthermore, it says that H is added to the carbon with more of the hydrogen atoms. The acid catalyzed hydration of 1-butene and 2-butene both result in the formation of 2-butanol. Hence the given statement is false.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Student Solutions Manual for Bettelheim/Brown/Campbell/Farrell/Torres' Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry, 11th
- Please correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forward(11pts total) Consider the arrows pointing at three different carbon-carbon bonds in the molecule depicted below. Bond B Bond A Bond C a. (2pts) Which bond between A-C is weakest? Which is strongest? Place answers in appropriate boxes. Weakest Bond Strongest Bond b. (4pts) Consider the relative stability of all cleavage products that form when bonds A, B, AND C are homolytically cleaved/broken. Hint: cleavage products of bonds A, B, and C are all carbon radicals. i. Which ONE cleavage product is the most stable? A condensed or bond line representation is fine. ii. Which ONE cleavage product is the least stable? A condensed or bond line representation is fine. c. (5pts) Use principles discussed in lecture, supported by relevant structures, to succinctly explain the why your part b (i) radical is more stable than your part b(ii) radical. Written explanation can be no more than one-two succinct sentence(s)!arrow_forward
- . 3°C with TH 12. (10pts total) Provide the major product for each reaction depicted below. If no reaction occurs write NR. Assume heat dissipation is carefully controlled in the fluorine reaction. 3H 24 total (30) 24 21 2h • 6H total ● 8H total 34 래 Br2 hv major product will be most Substituted 12 hv Br NR I too weak of a participate in P-1 F₂ hv Statistically most favored product will be major = most subst = thermo favored hydrogen atom abstractor to LL Farrow_forwardFive chemistry project topic that does not involve practicalarrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forward
- Q2. Consider the hydrogenation of ethylene C2H4 + H2 = C2H6 The heats of combustion and molar entropies for the three gases at 298 K are given by: C2H4 C2H6 H2 AH comb/kJ mol¹ -1395 -1550 -243 Sº / J K¹ mol-1 220.7 230.4 131.1 The average heat capacity change, ACP, for the reaction over the temperature range 298-1000 K is 10.9 J K¹ mol¹. Using these data, determine: (a) the standard enthalpy change at 800 K (b) the standard entropy change at 800 K (c) the equilibrium constant at 800 K.arrow_forward13. (11pts total) Consider the arrows pointing at three different carbon-carbon bonds in the molecule depicted below. Bond B Bond A Bond C a. (2pts) Which bond between A-C is weakest? Which is strongest? Place answers in appropriate boxes. Weakest Bond Strongest Bond b. (4pts) Consider the relative stability of all cleavage products that form when bonds A, B, AND C are homolytically cleaved/broken. Hint: cleavage products of bonds A, B, and C are all carbon radicals. i. Which ONE cleavage product is the most stable? A condensed or bond line representation is fine. ii. Which ONE cleavage product is the least stable? A condensed or bond line representation is fine. c. (5pts) Use principles discussed in lecture, supported by relevant structures, to succinctly explain the why your part b (i) radical is more stable than your part b(ii) radical. Written explanation can be no more than one-two succinct sentence(s)! Googlearrow_forwardPrint Last Name, First Name Initial Statifically more chances to abstract one of these 6H 11. (10pts total) Consider the radical chlorination of 1,3-diethylcyclohexane depicted below. 4 4th total • 6H total 래 • 4H total 21 total ZH 2H Statistical H < 3° C-H weakest - product abstraction here bund leads to thermo favored a) (6pts) How many unique mono-chlorinated products can be formed and what are the structures for the thermodynamically and statistically favored products? Product 6 Number of Unique Mono-Chlorinated Products Thermodynamically Favored Product Statistically Favored Product b) (4pts) Draw the arrow pushing mechanism for the FIRST propagation step (p-1) for the formation of the thermodynamically favored product. Only draw the p-1 step. You do not need to include lone pairs of electrons. No enthalpy calculation necessary H H-Cl Waterfoxarrow_forward
- 10. (5pts) Provide the complete arrow pushing mechanism for the chemical transformation → depicted below Use proper curved arrow notation that explicitly illustrates all bonds being broken, and all bonds formed in the transformation. Also, be sure to include all lone pairs and formal charges on all atoms involved in the flow of electrons. CH3O II HA H CH3O-H H ①arrow_forwardDo the Lone Pairs get added bc its valence e's are a total of 6 for oxygen and that completes it or due to other reasons. How do we know the particular indication of such.arrow_forwardNGLISH b) Identify the bonds present in the molecule drawn (s) above. (break) State the function of the following equipments found in laboratory. Omka) a) Gas mask b) Fire extinguisher c) Safety glasses 4. 60cm³ of oxygen gas diffused through a porous hole in 50 seconds. How long w 80cm³ of sulphur(IV) oxide to diffuse through the same hole under the same conditions (S-32.0.0-16.0) (3 m 5. In an experiment, a piece of magnesium ribbon was cleaned with steel w clean magnesium ribbon was placed in a crucible and completely burnt in oxy cooling the product weighed 4.0g a) Explain why it is necessary to clean magnesium ribbon. Masterclass Holiday assignmen PB 2arrow_forward
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning





