
(a)
Interpretation:
How the given compound can be produced from an alkene is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Electrophilic addition of carbenes to
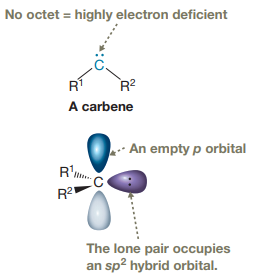
Carbenes are typically highly electrophilic due to the lack of an octet and are
Answer to Problem 12.2P
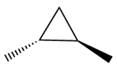
The given compound can be produced from an alkene is shown below:
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is:
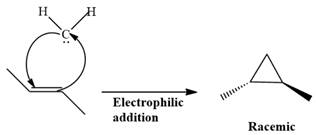
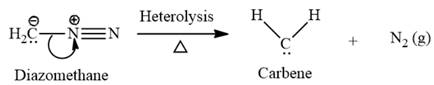
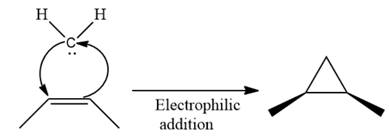
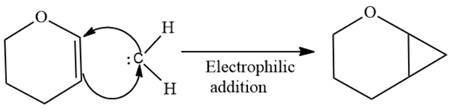
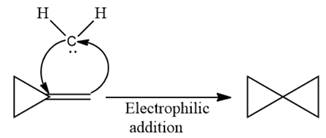
Electrophilic addition of carbenes to alkenes forms cyclopropane rings. Diazomethane (
This carbene intermediate reacts with an alkene in a concerted one-step reaction to form a cyclopropyl ring. The bridge carbon atom in the cyclopropyl ring comes from the carbene while the two carbon atoms are from the original alkene. Two new
![]()
The complete reaction of the addition of carbene to alkene is shown below:
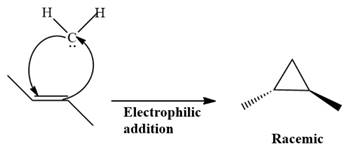
The given compound is produced via an electrophilic addition reaction of a carbene to an alkene.
(b)
Interpretation:
How the given compound can be produced from an alkene is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Electrophilic addition of carbenes to alkenes forms cyclopropane rings. In carbine, the carbon atom has two bonds and a lone pair of electrons.

Carbenes are typically highly electrophilic due to the lack of an octet and are
Answer to Problem 12.2P
The given compound can be produced from an alkene is shown below:

Explanation of Solution
The given compound is:
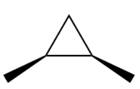
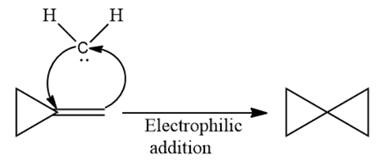
Electrophilic addition of carbenes to alkenes forms cyclopropane rings. Diazomethane (
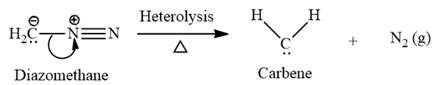
This carbene intermediate reacts with an alkene in a concerted one-step reaction to form a cyclopropyl ring. The bridge carbon atom in the cyclopropyl ring comes from the carbene while the two carbon atoms are from the original alkene. Two new
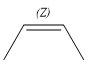
The complete reaction of the addition of carbene to alkene is shown below:
The given compound is produced via an electrophilic addition reaction of a carbene to an alkene.
(c)
Interpretation:
How the given compound can be produced from an alkene is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Electrophilic addition of carbenes to alkenes form cyclopropane rings. In carbine, the carbon atom has two bonds and a lone pair of electrons.

Carbenes are typically highly electrophilic due to the lack of an octet and are
Answer to Problem 12.2P
The given compound can be produced from an alkene is shown below:

Explanation of Solution
The given compound is:
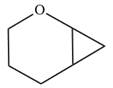
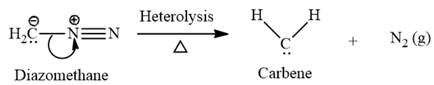
Electrophilic addition of carbenes to alkenes forms cyclopropane rings. Diazomethane (
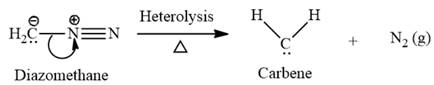
This carbene intermediate reacts with an alkene in a concerted one-step reaction to form a cyclopropyl ring. The bridge carbon atom in the cyclopropyl ring comes from the carbene while the two carbon atoms are from the original alkene. Two new
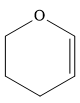
The complete reaction of the addition of carbene to alkene is shown below:
The given compound is produced via an electrophilic addition reaction of a carbene to an alkene.
(d)
Interpretation:
How the given compound can be produced from an alkene is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Electrophilic addition of carbenes to alkenes forms cyclopropane rings. In carbine, the carbon atom has two bonds and a lone pair of electrons.

Carbenes are typically highly electrophilic due to the lack of an octet and are
Answer to Problem 12.2P
The given compound can be produced from an alkene is shown below:
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is:

Electrophilic addition of carbenes to alkenes forms cyclopropane rings. Diazomethane (
This carbene intermediate reacts with an alkene in a concerted one-step reaction to form a cyclopropyl ring. The bridge carbon atom in the cyclopropyl ring comes from the carbene while the two carbon atoms are from the original alkene. Two new
The complete reaction of the addition of carbene to alkene is shown below:
The given compound is produced via an electrophilic addition reaction of a carbene to an alkene.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- PLEASE ANSWER THE QUESTION!!!arrow_forward3. SYNTHESIS. Propose a sequence of synthetic steps (FGI) that convert the starting material (SM) into the Target molecule. For each FGI in your proposed synthesis, specify the reagents / conditions, and draw the product(s) of that FGI. DO NOT INCLUDE the FGI mxn in the answer you submit. If an FGI requires two reagent sets, specify the order in which the reagent sets are added, e.g., i) Hg(OAc)2 / H₂O; ii) NaBH4/MeOH. Indicate the stereochemistry (if any) of the products of each FGI. FGI 1. Me Starting Material Source of all carbons in the Target molecule (can use multiple copies) Me Me Target molecule + enantiomerarrow_forwardcurved arrows are used to illustate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction mechanism stepsarrow_forward
- At 90ºC the vapor pressure of ortho-xylene is 20 kPa and that of meta-xylene is 18 kPa. What is the composition of the vapor in equilibrium with a mixture in which the mole fraction of o-xylene is 0.60?arrow_forwardDraw the products of this reduction of a ketone with sodium borohydride. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate the stereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers, where applicableIgnore any inorganic byproducts. 1) NaBH4 2) HCI/H2O Select to Drawarrow_forwardWhy do you think people who live at high altitudes are advised to add salt to water when boiling food like pasta? What mole fraction of NaCl is needed to raise the boiling point of H2O by 3˚C? Does the amount of salt added to water (typically about one teaspoon to four quarts of water) substantially change the boiling point? (Kb (H2O) = 0.51˚C/molal.)arrow_forward
- pls help asaparrow_forwardpls help asaparrow_forward9. Consider the following galvanic cell: Fe (s) | Fe(NO3)2 (aq) || Sn(NO3)2 (aq) | Sn (s) a. Write an equation for the half reactions occurring at the anode and cathode. b. Calculate the standard cell potential Show all of your work. c. Draw and label the galvanic cell, including the anode and cathode, direction of electron flow, and direction of ion migration.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning

