
(a)
Interpretation:
It is to be explained whether the given transformation would be a result of acid-catalyzed hydration or oxymercuration-reduction.
Concept introduction:
The acid-catalyzed hydration of an
The oxymercuration-reduction is also the reaction of addition of water through the
Answer to Problem 12.44P
The given transformation can be carried out by oxymercuration-reduction. The detailed mechanism is as follows:
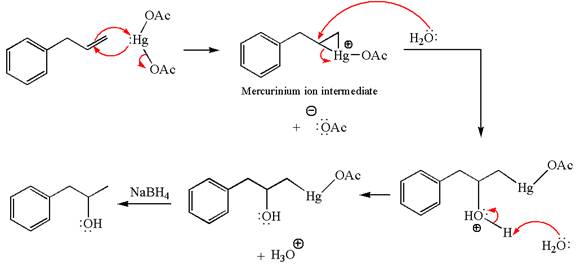
Explanation of Solution
The given equation is
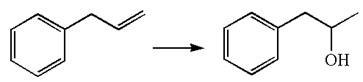
In the substrate, the alkene
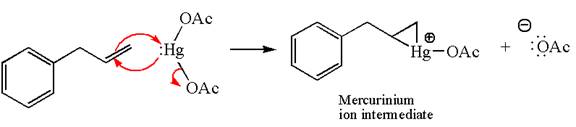
The alkene substrate, on reaction with mercury
In the first step, the electron rich
In the second step, the water molecule acts as a nucleophile on one of the carbons of the three-membered ring to open the ring, followed by deprotonation of the positively charged oxygen atom.
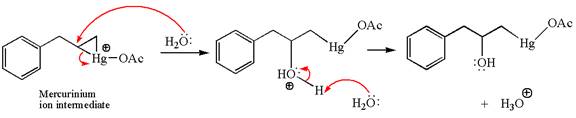
The product formed in the previous step is then subjected to reduction with sodium borohydride,
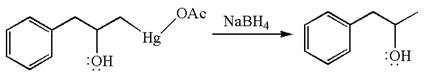
The preparation of the given compound is explained indicating the addition of water across the
(b)
Interpretation:
It is to be explained whether the given transformation would be a result of acid-catalyzed hydration or oxymercuration-reduction.
Concept introduction:
The acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkene is the electrophilic addition of water across the
The oxymercuration-reduction is also the reaction of addition of water through the
Answer to Problem 12.44P
The given transformation can be carried out by acid-catalyzed hydration. The detailed mechanism is as follows:
Explanation of Solution
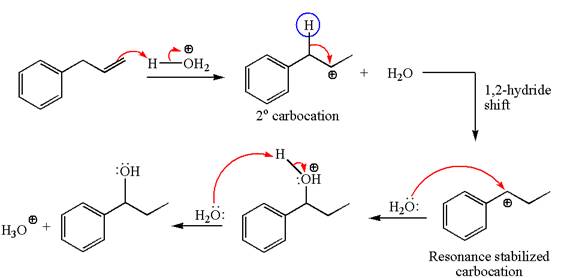
The given equation is
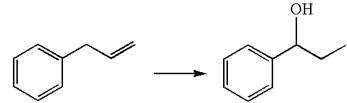
In the substrate, the alkene
The first step is the formation of a secondary carbocation by proton transfer reaction. The proton transfers to the less substituted double bonded carbon.
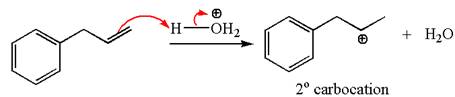
The secondary carbocation can be rearranged to more stable tertiary as well as resonance stabilized carbocation by
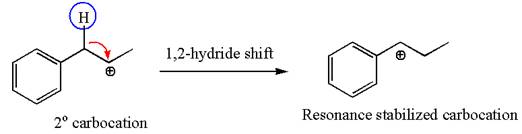
In the second step, the water molecule acts as a nucleophile on one of the carbons of the three-membered ring to open the ring, followed by deprotonation of the positively charged oxygen atom.
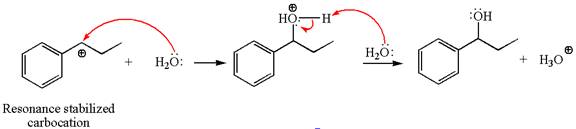
The detailed mechanism for the given reaction is drawn by suggesting that the reaction occurred through carbocation rearrangement.
(c)
Interpretation:
It is to be explained whether the given transformation would be a result of acid-catalyzed hydration or oxymercuration-reduction.
Concept introduction:
The acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkene is the electrophilic addition of water across the
The oxymercuration-reduction is also the reaction of addition of water through the
Answer to Problem 12.44P
The given transformation can be carried out by acid catalyzed hydration. The detailed mechanism is as follows:
Explanation of Solution
The given equation is
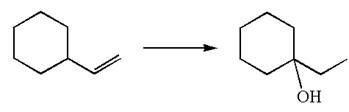
In the substrate, the alkene
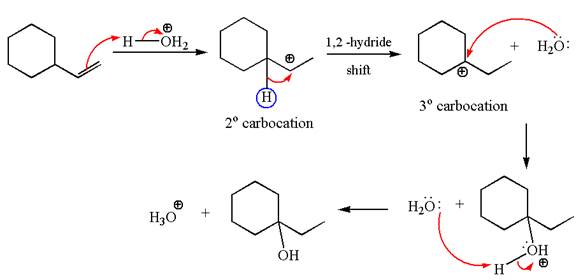
The first step is the formation of a secondary carbocation by proton transfer reaction. The proton transfers to the less substituted double bonded carbon.
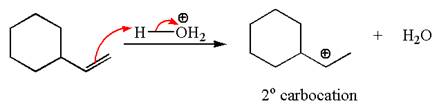
The secondary carbocation can be rearranged to more stable tertiary by
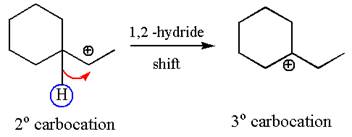
In the second step, the water molecule acts as a nucleophile on one of the carbons of the three-membered ring to open the ring, followed by deprotonation of the positively charged oxygen atom.
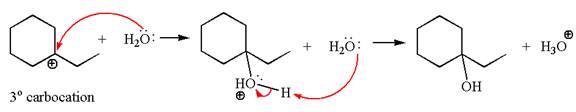
The detailed mechanism for the given reaction is drawn by suggesting that the reaction occurred through carbocation rearrangement.
(d)
Interpretation:
It is to be explained whether the given transformation would be a result of acid-catalyzed hydration or oxymercuration-reduction.
Concept introduction:
The acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkene is the electrophilic addition of water across the
The oxymercuration-reduction is also the reaction of addition of water across the
Answer to Problem 12.44P
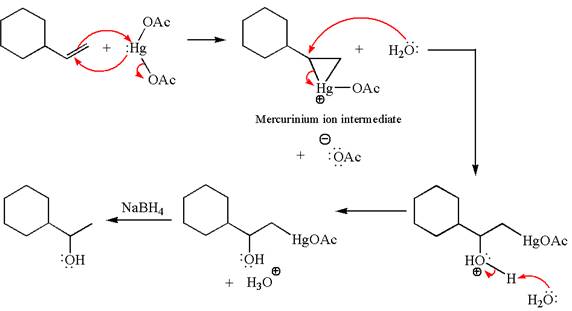
The given transformation can be carried out by oxymercuration-reduction. The detailed mechanism is as follows:
Explanation of Solution
The given equation is
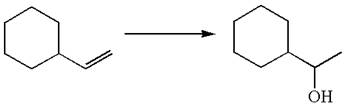
In the substrate, the alkene
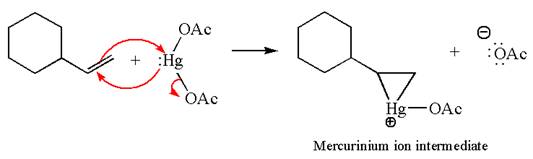
The alkene substrate, on reaction with mercury
In the first step, the electron rich
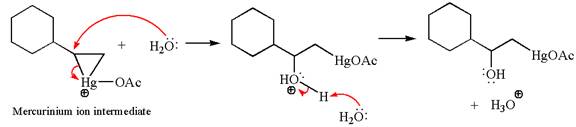
In the second step, the water molecule acts as a nucleophile on one of the carbons of the three-membered ring to open the ring, followed by deprotonation of the positively charged oxygen atom.
The product formed in the previous step is then subjected to reduction with sodium borohydride,
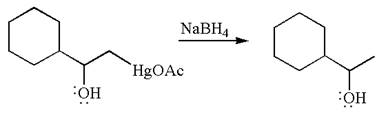
The preparation of the given compound is explained indicating the addition of water across the
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- Write all of Me Possible Products For each Of the Following reactions. In each case identity all pains of enantiomers, all digsterzoners and all Meso compounds 9. 11-60 11-0-11 V-G Η Η H ~ C-11 +HB+ - 1 H b. पन्ना 171-0-11 H-C-H Н C-C=c-call +HBr Perendez ==arrow_forwardHow can i draw the mechanisms for this molecule?arrow_forwarda. Discuss and explain he difference IN Stability between the Chai and Boat Гольцу от судомехане b. For the Following Molecule draw both possible Clain conformations and explain which one is more stable and for what Reason. H. CH₂ CH₂ H "Harrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole


