
Mechanics of Materials, 7th Edition
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780073398235
Author: Ferdinand P. Beer, E. Russell Johnston Jr., John T. DeWolf, David F. Mazurek
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 11.9, Problem 121P
11.121 and 11.122 Knowing that the eight members of the indeterminate truss shown have the same uniform cross-sectional area, determine the force in member AB.
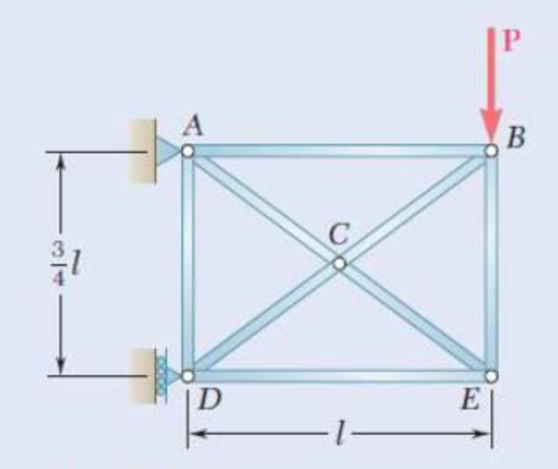
Fig. P11.121
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Using the method of joints, determine the force in each member of the truss shown. State whether each member is in tension or compression.
6.9 Determine the force in each member of the truss shown. State
298 Analysis of Structures
whether each member is in tension or compression.
10 kips
B
C
D
2 kips
7.5 ft
|H
2 kips
2 kips
3.6 ft
G
D
1 kip
1 kip
B
- 6 ft
6 ft
6 ft
6 ft-
9 ft
Fig. P6.9
Н.
PROBLEM No. 2
Determine the smallest safe cross-sectional areas of members BC, CG and GH for the truss shown. The allowable
stress are 100 MPa in tension and 80 MPa in compression. Indicate tension or compression. (answer in mm?)
720 N 1440 N 1440 N 720 N
4 m
4 mt 4 m
4 m
B
D
3 m
6 m
H
Chapter 11 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials, 7th Edition
Ch. 11.3 - Determine the modulus of resilience for each of...Ch. 11.3 - Determine the modulus of resilience for each of...Ch. 11.3 - Determine the modulus of resilience for each of...Ch. 11.3 - Determine the modulus of resilience for each of...Ch. 11.3 - The stress-strain diagram shown has been drawn...Ch. 11.3 - The stress-strain diagram shown has been drawn...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 7PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 8PCh. 11.3 - Using E = 29 106 psi, determine (a) the strain...Ch. 11.3 - Using E = 200 GPa, determine (a) the strain energy...
Ch. 11.3 - A 30-in. length of aluminum pipe of...Ch. 11.3 - A single 6-mm-diameter steel pin B is used to...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 13PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 14PCh. 11.3 - The assembly ABC is made of a steel for which E =...Ch. 11.3 - Show by integration that the strain energy of the...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 17PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 18PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 19PCh. 11.3 - 11.18 through 11.21 In the truss shown, all...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 21PCh. 11.3 - Each member of the truss shown is made of aluminum...Ch. 11.3 - Each member of the truss shown is made of aluminum...Ch. 11.3 - 11.24 through 11.27 Taking into account only the...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 25PCh. 11.3 - 11.24 through 11.27 Taking into account only the...Ch. 11.3 - 11.24 through 11.27 Taking into account only the...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 28PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 29PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 30PCh. 11.3 - 11.30 and 11.31 Using E = 200 GPa, determine the...Ch. 11.3 - Assuming that the prismatic beam AB has a...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 33PCh. 11.3 - The design specifications for the steel shaft AB...Ch. 11.3 - Show by integration that the strain energy in the...Ch. 11.3 - The state of stress shown occurs in a machine...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 37PCh. 11.3 - The state of stress shown occurs in a machine...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 39PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 40PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 41PCh. 11.5 - A 5-kg collar D moves along the uniform rod AB and...Ch. 11.5 - The 18-lb cylindrical block E has a horizontal...Ch. 11.5 - The cylindrical block E has a speed v0 =16 ft/s...Ch. 11.5 - Prob. 45PCh. 11.5 - Prob. 46PCh. 11.5 - The 48-kg collar G is released from rest in the...Ch. 11.5 - Prob. 48PCh. 11.5 - Prob. 49PCh. 11.5 - Prob. 50PCh. 11.5 - Prob. 51PCh. 11.5 - The 2-kg block D is dropped from the position...Ch. 11.5 - The 10-kg block D is dropped from a height h = 450...Ch. 11.5 - Prob. 54PCh. 11.5 - A 160-lb diver jumps from a height of 20 in. onto...Ch. 11.5 - Prob. 56PCh. 11.5 - A block of weight W is dropped from a height h...Ch. 11.5 - 11.58 and 11.59 Using the method of work and...Ch. 11.5 - 11.58 and 11.59 Using the method of work and...Ch. 11.5 - 11.60 and 11.61 Using the method of work and...Ch. 11.5 - 11.60 and 11.61 Using the method of work and...Ch. 11.5 - 11.62 and 11.63 Using the method of work and...Ch. 11.5 - 11.62 and 11.63 Using the method of work and...Ch. 11.5 - Using the method of work and energy, determine the...Ch. 11.5 - Using the method of work and energy, determine the...Ch. 11.5 - The 20-mm diameter steel rod BC is attached to the...Ch. 11.5 - Torques of the same magnitude T are applied to the...Ch. 11.5 - Prob. 68PCh. 11.5 - The 20-mm-diameter steel rod CD is welded to the...Ch. 11.5 - The thin-walled hollow cylindrical member AB has a...Ch. 11.5 - 11.71 and 11.72 Each member of the truss shown has...Ch. 11.5 - 11.71 and 11.72 Each member of the truss shown has...Ch. 11.5 - Each member of the truss shown is made of steel...Ch. 11.5 - Each member of the truss shown is made of steel....Ch. 11.5 - Each member of the truss shown is made of steel...Ch. 11.5 - The steel rod BC has a 24-mm diameter and the...Ch. 11.9 - 11.77 and 11.78 Using the information in Appendix...Ch. 11.9 - 11.77 and 11.78 Using the information in Appendix...Ch. 11.9 - 11.79 through 11.82 For the beam and loading...Ch. 11.9 - 11.79 through 11.82 For the beam and loading...Ch. 11.9 - 11.79 through 11.82 For the beam and loading...Ch. 11.9 - 11.79 through 11.82 For the beam and loading...Ch. 11.9 - 11.83 through 11.85 For the prismatic beam shown,...Ch. 11.9 - 11.83 through 11.85 For the prismatic beam shown,...Ch. 11.9 - 11.83 through 11.85 For the prismatic beam shown,...Ch. 11.9 - 11.86 through 11.88 For the prismatic beam shown,...Ch. 11.9 - 11.86 through 11.88 For the prismatic beam shown,...Ch. 11.9 - 11.86 through 11.88 For the prismatic beam shown,...Ch. 11.9 - For the prismatic beam shown, determine the slope...Ch. 11.9 - For the prismatic beam shown, determine the slope...Ch. 11.9 - For the beam and loading shown, determine the...Ch. 11.9 - For the beam and loading shown, determine the...Ch. 11.9 - 11.93 and 11.94 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 11.9 - 11.93 and 11.94 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 11.9 - For the beam and loading shown, determine the...Ch. 11.9 - For the beam and loading shown, determine the...Ch. 11.9 - Prob. 97PCh. 11.9 - For the beam and loading shown, determine the...Ch. 11.9 - 11.99 and 11.100 For the truss and loading shown,...Ch. 11.9 - 11.99 and 11.100 For the truss and loading shown,...Ch. 11.9 - 11.101 and 11.102 Each member of the truss shown...Ch. 11.9 - 11.101 and 11.102 Each member of the truss shown...Ch. 11.9 - 11.103 and 11.104 Each member of the truss shown...Ch. 11.9 - 11.103 and 11 104 Each member of the truss shown...Ch. 11.9 - A uniform rod of flexural rigidity EI is bent and...Ch. 11.9 - For the uniform rod and loading shown and using...Ch. 11.9 - For the beam and loading shown and using...Ch. 11.9 - Two rods AB and BC of the same flexural rigidity...Ch. 11.9 - Three rods, each of the same flexural rigidity EI,...Ch. 11.9 - Three rods, each of the same flexural rigidity EI,...Ch. 11.9 - 11.111 through 11.115 Determine the reaction at...Ch. 11.9 - 11.111 through 11.115 Determine the reaction at...Ch. 11.9 - 11.111 through 11.115 Determine the reaction at...Ch. 11.9 - 11.111 through 11.115 Determine the reaction at...Ch. 11.9 - 11.111 through 11.115 Determine the reaction at...Ch. 11.9 - For the uniform beam and loading shown, determine...Ch. 11.9 - 11.117 through 11.120 Three members of the same...Ch. 11.9 - 11.117 through 11.120 Three members of the same...Ch. 11.9 - 11.117 through 11.120 Three members of the same...Ch. 11.9 - 11.117 through 11.120 Three members of the same...Ch. 11.9 - 11.121 and 11.122 Knowing that the eight members...Ch. 11.9 - 11.121 and 11.122 Knowing that the eight members...Ch. 11 - Rod AB is made of a steel for which the yield...Ch. 11 - Each member of the truss shown is made of steel...Ch. 11 - The ship at A has just started to drill for oil on...Ch. 11 - Collar D is released from rest in the position...Ch. 11 - Each member of the truss shown is made of steel...Ch. 11 - A block of weight W is placed in contact with a...Ch. 11 - Two solid steel shafts are connected by the gears...Ch. 11 - A 160-lb diver jumps from a height of 20 in. onto...Ch. 11 - For the prismatic beam shown, determine the slope...Ch. 11 - A disk of radius a has been welded to end B of the...Ch. 11 - A uniform rod of flexural rigidity EI is bent and...Ch. 11 - The steel bar ABC has a square cross section of...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- PROBLEM 6.45 Determine the force in members BD and CD of the truss shown. B 36 kN D 36 kN F C E G 4 panels at 2 m = 8 m H 1.5 m ↓arrow_forward(2) Using the method of joints, determine the load in member EG and state whether it is in tension or compression. 9 ft 9 ft -18 ft 18 ft- B F 12 ft A C E 18 ft 18 ft- 18 ft 6 kips 6 kips Fig. P6.15arrow_forwardTruss structure shown is a half of an octagon. Member AD, AE, BG and CG are intersecting, but not connected to each other. Determine the force of member BC. D 45° 45° F B A 24arrow_forward
- Using the method of joints, determine the force in each member of the truss shown. State whether each member is in tension or compression.arrow_forwardB7arrow_forward6.43 Determine the force in members BD and DE of the truss shown. Answer 6.44 Determine the force in members DG and EG of the truss shown. Answer Fig. P6.43 and P6.44 2.4 m 2.4 m 2.4 m 135 KN 135 kN 135 kN A B D F 4.5 m с E Garrow_forward
- Using the method of joints, determine the force in each member of the trussshown. State whether each member is in tension or compression.arrow_forwardSolve Prob. 6.39 for P = 0 and Q = (-900 N)k.(Reference to Problem 6.39):The truss shown consists of nine members and is supported by a ball-and-socket at B , a short link at C , and two short links at D. (a) Check that this truss is a simple truss, that it is completely constrained, and that the reactions at its supports are statically determinate. (b) Determine the force in each member for P= (-1200 N)j and Q = 0.arrow_forwardProblem 10.2: A thin bar of length I is attached to a collar at B and rests at C on a portion of the circular cylinder of radius r. Neglecting friction, determine the value of 0 that corresponds to the equilibrium position given that Q = 2P and r = 0.3, 1 = 200 mm,P = 40N C p. Barrow_forward
- Using the method of joints, determine the force in each member of the truss shown. State whether each member is in tension (T) or compression (C).arrow_forwardProblem 13.1 Two wooden members of 80mm x 120mm uniform rectangular cross section are joined by the simple glued scarf splice shown. The angle of the joint is ß = 30 degrees and the glued joint has a capacity of 410 kPa against tension stresses and 680 kPa against shear stresses. Determine the largest centric load P that can be applied. P 80 mm 120 mm Parrow_forwardA 1-in.-square aluminum strut is maintained in the position shown by a pin support at A and by sets of rollers at B and C that prevent rota-tion of the strut in the plane of the figure. Knowing that LAB=3 ft, determine (a) the largest values of LBC and LCD that can be used if the allowable load P is to be as large as possible, (b) the magnitude of the corresponding allowable load. Consider only buckling in the plane of the figure and use E=10.4 *106 psi.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Solids: Lesson 53 - Slope and Deflection of Beams Intro; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I7lTq68JRmY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY