
(a)
Find the maximum deflection of end C.
(a)
Answer to Problem 46P
The maximum deflection of end C is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The mass of the collar D is
The modulus of elasticity of the steel rod is
The length of the rod AB is
The length of the rod BC is
The diameter of rod AB is
The diameter of rod BC is
Calculation:
Consider the acceleration due to gravity as
Calculate the weight of the collar (m) as shown below.
Substitute
Calculate the cross sectional area
For rod AB.
Substitute
For rod BC.
Substitute
The rod BC has the minimum area
Calculate the deflection
For rod AB.
Substitute
For rod BC.
Substitute
Calculate the maximum deflection
Substitute
Sketch the Free Body Diagram of the rod after deformation as shown in Figure 1.
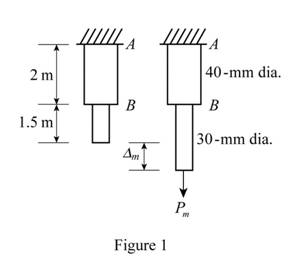
Refer to Figure 1.
Calculate the strain energy
Substitute
Consider that the distance
Calculate the maximum deflection
Substitute
Hence, the maximum deflection of end C is
(b)
The equivalent static load.
(b)
Answer to Problem 46P
The equivalent static load is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The mass of the collar D is
The modulus of elasticity of the steel rod is
The length of the rod AB is
The length of the rod BC is
The diameter of rod AB is
The diameter of rod BC is
Calculation:
Refer to part (a).
The maximum deflection of end C is
Calculate the static load
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the equivalent static load is
(c)
The maximum stress occurs in the rod.
(c)
Answer to Problem 46P
The maximum stress occurs in the rod is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The mass of the collar D is
The modulus of elasticity of the steel rod is
The length of the rod AB is
The length of the rod BC is
The diameter of rod AB is
The diameter of rod BC is
Calculation:
Refer to part (a).
The minimum area of the rod is
Refer to part (b).
The equivalent static load is
Calculate the maximum stress
Substitute
Therefore, the maximum stress occurs in the rod is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials, 7th Edition
- Where on the below beam is the Maxiumum Slope likely to occur? 120 Point A Point B Point C Point B or Point C B сarrow_forwardA very thin metallic sheet is placed between two wood plates of different thicknesses. Theplates are firmly pressed together and electricity is passed through the sheet. The exposed surfaces ofthe two plates lose heat to the ambient fluid by convection. Assume uniform heating at the interface.Neglect end effects and assume steady state.[a] Will the heat transfer through the two plates be the same? Explain.[b] Will the exposed surfaces be at the same temperature? Explainarrow_forwardDesign consideration requires that the surface of a small electronic package be maintained at atemperature not to exceed 82 o C. Noise constraints rule out the use of fans. The power dissipated inthe package is 35 watts and the surface area is 520 cm2 . The ambient temperature and surroundingwalls are assumed to be at 24 o C. The heat transfer coefficient is estimated to be 9.2 W/m2- oC andsurface emissivity is 0.7. Will the package dissipate the required power without violating designconstraints?arrow_forward
- Consider radiation from a small surface at 100 oC which is enclosed by a much larger surface at24 o C. Determine the percent increase in the radiation heat transfer if the temperature of the smallsurface is doubled.arrow_forwardA small electronic package with a surface area of 820 cm2 is placed in a room where the airtemperature is 28 o C. The heat transfer coefficient is 7.3 W/m2 - o C. You are asked to determine if it isjustified to neglect heat loss from the package by radiation. Assume a uniform surface temperature of78 o C and surface emissivity of 0.65 Assume further that room’s walls and ceiling are at a uniformtemperature of 16 o C.arrow_forwardA hollow metal sphere of outer radius or = 2 cm is heated internally with a variable output electricheater. The sphere loses heat from its surface by convection and radiation. The heat transfercoefficient is 22 W/ m2 - o C and surface emissivity is 0.92. The ambient fluid temperature is 20 o C andthe surroundings temperature is 14 oC. Construct a graph of the surface temperature corresponding toheating rates ranging from zero to 100 watts. Assume steady state. Use a simplified model forradiation exchange based on a small gray surface enclosed by a much larger surface at 14 o C.arrow_forward
- 2. A program to make the part depicted in Figure 26.A has been created, presented in figure 26.B, but some information still needs to be filled in. Compute the tool locations, depths, and other missing information to present a completed program. (Hint: You may have to look up geometry for the center drill and standard 0.5000 in twist drill to know the required depth to drill). Dashed line indicates - corner of original stock Intended toolpath-tangent - arc entry and exit sized to programmer's judgment 026022 (Slot and Drill Part) (Setup Instructions. (UNITS: Inches (WORKPIECE MAT'L: SAE 1020 STEEL (Workpiece: 3.25 x 2.00 x0.75 in. Plate (PRZ Location G54: ( XY 0.0 Upper Left of Fixture ( TOP OF PART 2-0 (Tool List: ) ( T04 T02 0.500 IN 4 FLUTE FLAT END MILL) #4 CENTER DRILL ' T02 0.500 TWIST DRILL N010 GOO G90 G17 G20 G49 G40 G80 G54 N020 M06 T02 (0.5 IN 4-FLUTE END MILL) R0.750 N030 S760 M03 G00 x N040 043 H02 2 Y (P1) (RAPID DOWN -TLO) P4 NO50 MOB (COOLANT ON) N060 G01 X R1.000 N070…arrow_forward6–95. The reaction of the ballast on the railway tie can be assumed uniformly distributed over its length as shown. If the wood has an allowable bending stress of σallow=1.5 ksi, determine the required minimum thickness t of the rectangular cross section of the tie to the nearest 18 in. Please include all steps. Also if you can, please explain how you found Mmax using an equation rather than using just the moment diagram. Thank you!arrow_forward6–53. If the moment acting on the cross section is M=600 N⋅m, determine the resultant force the bending stress produces on the top board. Please explain each step. Please explain how you got the numbers and where you plugged them in to solve the problem. Thank you!arrow_forward
- Solving coplanar forcesarrow_forwardComplete the following problems. Show your work/calculations, save as.pdf and upload to the assignment in Blackboard. 1. What are the x and y dimensions for the center position of holes 1,2, and 3 in the part shown in Figure 26.2 (below)? 6.0000 7118 Zero reference point 1.0005 1.0000 1.252 Bore C' bore 1.250 6.0000 .7118 0.2180 deep (3 holes) 2.6563 1.9445 3.000 diam. slot 0.3000 deep. 0.3000 wide 2.6563 1.9445arrow_forwardComplete the following problems. Show your work/calculations, save as.pdf and upload to the assignment in Blackboard. missing information to present a completed program. (Hint: You may have to look up geometry for the center drill and standard 0.5000 in twist drill to know the required depth to drill). 1. What are the x and y dimensions for the center position of holes 1,2, and 3 in the part shown in Figure 26.2 (below)? 6.0000 Zero reference point 7118 1.0005 1.0000 1.252 Bore 6.0000 .7118 Cbore 0.2180 deep (3 holes) 2.6563 1.9445 Figure 26.2 026022 (8lot and Drill Part) (Setup Instructions--- (UNITS: Inches (WORKPIECE NAT'L SAE 1020 STEEL (Workpiece: 3.25 x 2.00 x0.75 in. Plate (PRZ Location 054: ' XY 0.0 - Upper Left of Fixture TOP OF PART 2-0 (Tool List ( T02 0.500 IN 4 FLUTE FLAT END MILL #4 CENTER DRILL Dashed line indicates- corner of original stock ( T04 T02 3.000 diam. slot 0.3000 deep. 0.3000 wide Intended toolpath-tangent- arc entry and exit sized to programmer's judgment…arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





