
A uniform rod of flexural rigidity EI is bent and loaded as shown. Determine (a) the horizontal deflection of point D, (b) the slope at point D.
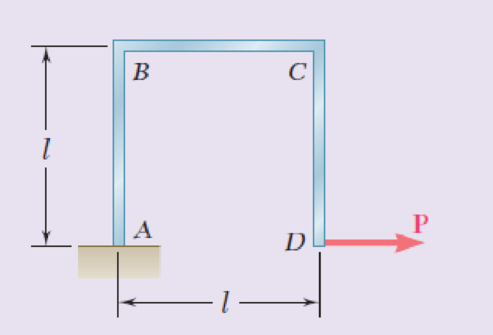
Fig. P11.133
(a)
Find the horizontal deflection of point D.
Answer to Problem 133RP
The horizontal deflection of point D is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The flexural rigidity of the rod is
Calculation:
Apply a couple
Sketch the Free Body Diagram as shown in Figure 1.
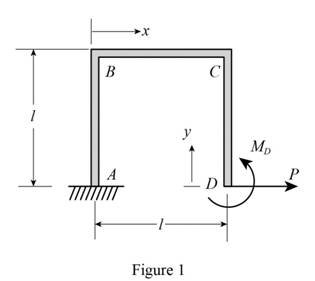
Refer to Figure 1.
Apply the Equations of Equilibrium as shown below.
Summation of forces along vertical direction is Equal to zero.
Summation of forces along horizontal direction is Equal to zero.
Take moment about A is Equal to zero.
Calculate the strain energy
Calculate the deflection of point D
Differentiate both side of the Equation (1) with respect to P as shown below.
Consider the member AB.
The bending moment over portion AB is
Differentiate both side of the Equation (3) with respect to P as shown below.
Differentiate both side of the Equation (3) with respect to
Consider the member BC.
The bending moment over portion BC is
Differentiate both side of the Equation (4) with respect to P as shown below.
Differentiate both side of the Equation (4) with respect to
Consider the member CD.
The bending moment over portion CD is
Differentiate both side of the Equation (5) with respect to P as shown below.
Differentiate both side of the Equation (5) with respect to
Calculate the deflection of point D
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the horizontal deflection of point D is
(b)
Find the slope at point D.
Answer to Problem 133RP
The slope at point D is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The flexural rigidity of the rod is
Calculation:
Calculate the slope at D
Differentiate both side of the Equation (1) with respect to
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the slope of point D is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials, 7th Edition
- Solve the IVP. a. y" 16y 17e* ; = y(0) = 6, y'(0) = -2 b. (D² + 41)y = sin(t) + ½ sin(3t) + sin(t) ; y(0) = 0, y'(0) : = 35 31arrow_forwardFind the general solution. a. y' 5y = 3ex - 2x + 1 - b. y" +4y' + 4y = e¯*cos(x) c. (D² + I)y = cos(wt), w² # 1arrow_forwardhandwritten solutions, please!!arrow_forward
- > Homework 4 - Spring 2025.pdf Spring 2025.pdf k 4 - Spring 2025.pdf (447 KB) Due: Thursday, February 27 Page 1 > of 2 ZOOM 1. A simply supported shaft is shown in Figure 1 with wo = 25 N/cm and M = 20 N cm. Use singularity functions to determine the reactions at the supports. Assume EI = 1000 kN cm². M Wo 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 cm Figure 1 - Problem 1 2. A support hook was formed from a rectangular bar. Find the stresses at the inner and outer surfaces at sections just above and just below O-B. 210 mmarrow_forwardA distillation column with a total condenser and a partial reboiler is separating ethanol andwater at 1.0 atm. Feed is 0.32 mol fraction ethanol and it enters as a saturated liquid at 100mol/s on the optimum plate. The distillate product is a saturated liquid with 80 mol% ethanol.The condenser removes 5615 kW. The bottoms product is 0.05 mol fraction ethanol. AssumeCMO is valid.(a) Find the number of equilibrium stages for this separation. [6 + PR](b) Find how much larger the actual reflux ratio, R, used is than Rmin, i.e. R/Rmin. [3]Note: the heats of vaporization of ethanol and water are λe = 38.58 and λw = 40.645 arrow_forwardWe have a feed that is a binary mixture of methanol and water (60.0 mol% methanol) that issent to a system of two flash drums hooked together. The vapor from the first drum is cooled,which partially condenses the vapor, and then is fed to the second flash drum. Both drumsoperate at 1.0 atm and are adiabatic. The feed to the first drum is 1000 kmol/hr. We desire aliquid product from the first drum that is 35.0 mol% methanol. The second drum operates at afraction vaporized of (V/F)2 = 0.25.(a) Find the liquid flow rate leaving the first flash drum, L1 (kmol/hr). [286 kmol/hr](b) Find the vapor composition leaving the second flash drum, y2. [0.85]arrow_forward
- = The steel curved bar shown has rectangular cross-section with a radial height h = 6 mm and thickness b = 4mm. The radius of the centroidal axis is R = 80 mm. A force P = 10 N is applied as shown. Assume the steel modulus of 207,000 MPa and G = 79.3(103) MPa, repectively. elasticity and shear modulus E = Find the vertical deflection at point B. Use Castigliano's method for a curved flexural member and since R/h > 10, neglect the effect of shear and axial load, thereby assuming that deflection is due to merely the bending moment. Note the inner and outer radii of the curves bar are: r = 80 + ½ (6) = 83 mm, r₁ = 80 − ½ (6) = 77 mm 2 2 Sπ/2 sin² 0 d = √π/² cos² 0 d0 = Π 0 4 大 C R B Parrow_forwardThe steel eyebolt shown in the figure is loaded with a force F = 75 lb. The eyebolt is formed from round wire of diameter d = 0.25 in to a radius R₁ = 0.50 in in the eye and at the shank. Estimate the stresses at the inner and outer surfaces at section A-A. Notice at the section A-A: r₁ = 0.5 in, ro = 0.75 in rc = 0.5 + 0.125 = 0.625 in Ri 200 F FAarrow_forwardI have the fallowing question and solution from a reeds naval arc book. Im just confused as to where this answer came from and the formulas used. Wondering if i could have this answer/ solution broken down and explained in detail. A ship of 7000 tonne displacement has a waterplane areaof 1500 m2. In passing from sea water into river water of1005 kg/m3 there is an increase in draught of 10 cm. Find the Idensity of the sea water. picture of the "answer" is attachedarrow_forward
- Problem A2 long steel tube has a rectangular cross-section with outer dimensions of 20 x 20 mm and a uniform wall thickness of 2. The tube is twisted along its length with torque, T. The tube material is 1045 CD steel with shear yield strength of S,, =315 MPa. Assume shear modulus, G = 79.3GPa. (a) Estimate the maximum torque that can be applied without yielding (b) Estimate the torque required to produce 5 degrees total angle of twist over the length of the tube. (c) What is the maximum torque that can be applied without yielding, if a solid rectangular shaft with dimensions of 20 x 20 is used? You may use the exact solution.arrow_forwardA simply supported beam is loaded as shown. Considering symmetry, the reactions at supports A and B are R₁ = R₂ = wa 2 Using the singularity method, determine the shear force V along the length of the beam as a function of distance x from the support A. A B Ir. 2a За W C R₁₂ x 2. Using the singularity method, determine the bending M along the length of the beam as a function of distance x, from the support A. 3. Using the singularity method, determine the beam slope and deflection along the length of the beam as a function of the distance x, from the support A. Assume the material modulus of elasticity, E and the moment of inertia of the beam cross-section, I are given.arrow_forwardA steel tube, 2 m long, has a rectangular cross-section with outer dimensions of 20 × 30 mm and a uniform wall thickness of 1 mm. The tube is twisted along its length with torque, T. The tube material is 1018 CD steel with shear yield strength of Ssy =185 MPa. Assume shear modulus, G = 79.3GPa. (a) Estimate the maximum torque that can be applied without yielding.- (b) Estimate the torque required to produce 3 degrees total angle of twist over the length of the tube. (c) What is the maximum torque that can be applied without yielding, if a solid rectangular shaft with dimensions of 20 x 30 mm is used? You may use the exact solution:arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





