
Mechanics of Materials, 7th Edition
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780073398235
Author: Ferdinand P. Beer, E. Russell Johnston Jr., John T. DeWolf, David F. Mazurek
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 11.9, Problem 110P
Three rods, each of the same flexural rigidity EI, are welded to form the frame ABCD. For the loading shown, determine the angle formed by the frame at point D.
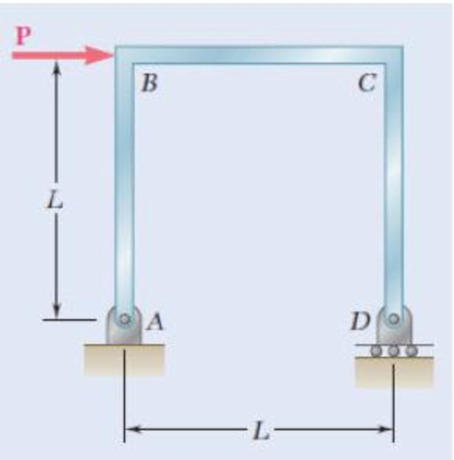
Fig. P11.109 and P11.110
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Qu 1 If crank OA rotates with an angular velocity of ω = 12 rad/s, determine the velocity of piston B and
the angular velocity of rod AB at the instant shown.
please show all work
Q2/ Maria has an online shop where she sells hand made paintings and
cards. She sells the painting for 50 and the card for 20. It takes her 2 hours
to complete 1 painting and 45 minutes to make a single card. She also has
a day job and makes paintings and cards in her free time. She cannot spend
more than 15 hours a week to make paintings and cards. Additionally, she
should make not more than 10 paintings and cards per week.
She makes a profit of 25 on painting and 15 on each card. How many
paintings and cards should she make each week to maximize her profit.
For the beam and loading shown, (a) draw the shear and bending moment diagrams, (b) determine the magnitude and location of the maximum absolute value of the bending momentConsider A = 0please show step by step process, i did something wrong with bending moment diagram( length of beam = 2 + 6 + 2)
Chapter 11 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials, 7th Edition
Ch. 11.3 - Determine the modulus of resilience for each of...Ch. 11.3 - Determine the modulus of resilience for each of...Ch. 11.3 - Determine the modulus of resilience for each of...Ch. 11.3 - Determine the modulus of resilience for each of...Ch. 11.3 - The stress-strain diagram shown has been drawn...Ch. 11.3 - The stress-strain diagram shown has been drawn...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 7PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 8PCh. 11.3 - Using E = 29 106 psi, determine (a) the strain...Ch. 11.3 - Using E = 200 GPa, determine (a) the strain energy...
Ch. 11.3 - A 30-in. length of aluminum pipe of...Ch. 11.3 - A single 6-mm-diameter steel pin B is used to...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 13PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 14PCh. 11.3 - The assembly ABC is made of a steel for which E =...Ch. 11.3 - Show by integration that the strain energy of the...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 17PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 18PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 19PCh. 11.3 - 11.18 through 11.21 In the truss shown, all...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 21PCh. 11.3 - Each member of the truss shown is made of aluminum...Ch. 11.3 - Each member of the truss shown is made of aluminum...Ch. 11.3 - 11.24 through 11.27 Taking into account only the...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 25PCh. 11.3 - 11.24 through 11.27 Taking into account only the...Ch. 11.3 - 11.24 through 11.27 Taking into account only the...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 28PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 29PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 30PCh. 11.3 - 11.30 and 11.31 Using E = 200 GPa, determine the...Ch. 11.3 - Assuming that the prismatic beam AB has a...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 33PCh. 11.3 - The design specifications for the steel shaft AB...Ch. 11.3 - Show by integration that the strain energy in the...Ch. 11.3 - The state of stress shown occurs in a machine...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 37PCh. 11.3 - The state of stress shown occurs in a machine...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 39PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 40PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 41PCh. 11.5 - A 5-kg collar D moves along the uniform rod AB and...Ch. 11.5 - The 18-lb cylindrical block E has a horizontal...Ch. 11.5 - The cylindrical block E has a speed v0 =16 ft/s...Ch. 11.5 - Prob. 45PCh. 11.5 - Prob. 46PCh. 11.5 - The 48-kg collar G is released from rest in the...Ch. 11.5 - Prob. 48PCh. 11.5 - Prob. 49PCh. 11.5 - Prob. 50PCh. 11.5 - Prob. 51PCh. 11.5 - The 2-kg block D is dropped from the position...Ch. 11.5 - The 10-kg block D is dropped from a height h = 450...Ch. 11.5 - Prob. 54PCh. 11.5 - A 160-lb diver jumps from a height of 20 in. onto...Ch. 11.5 - Prob. 56PCh. 11.5 - A block of weight W is dropped from a height h...Ch. 11.5 - 11.58 and 11.59 Using the method of work and...Ch. 11.5 - 11.58 and 11.59 Using the method of work and...Ch. 11.5 - 11.60 and 11.61 Using the method of work and...Ch. 11.5 - 11.60 and 11.61 Using the method of work and...Ch. 11.5 - 11.62 and 11.63 Using the method of work and...Ch. 11.5 - 11.62 and 11.63 Using the method of work and...Ch. 11.5 - Using the method of work and energy, determine the...Ch. 11.5 - Using the method of work and energy, determine the...Ch. 11.5 - The 20-mm diameter steel rod BC is attached to the...Ch. 11.5 - Torques of the same magnitude T are applied to the...Ch. 11.5 - Prob. 68PCh. 11.5 - The 20-mm-diameter steel rod CD is welded to the...Ch. 11.5 - The thin-walled hollow cylindrical member AB has a...Ch. 11.5 - 11.71 and 11.72 Each member of the truss shown has...Ch. 11.5 - 11.71 and 11.72 Each member of the truss shown has...Ch. 11.5 - Each member of the truss shown is made of steel...Ch. 11.5 - Each member of the truss shown is made of steel....Ch. 11.5 - Each member of the truss shown is made of steel...Ch. 11.5 - The steel rod BC has a 24-mm diameter and the...Ch. 11.9 - 11.77 and 11.78 Using the information in Appendix...Ch. 11.9 - 11.77 and 11.78 Using the information in Appendix...Ch. 11.9 - 11.79 through 11.82 For the beam and loading...Ch. 11.9 - 11.79 through 11.82 For the beam and loading...Ch. 11.9 - 11.79 through 11.82 For the beam and loading...Ch. 11.9 - 11.79 through 11.82 For the beam and loading...Ch. 11.9 - 11.83 through 11.85 For the prismatic beam shown,...Ch. 11.9 - 11.83 through 11.85 For the prismatic beam shown,...Ch. 11.9 - 11.83 through 11.85 For the prismatic beam shown,...Ch. 11.9 - 11.86 through 11.88 For the prismatic beam shown,...Ch. 11.9 - 11.86 through 11.88 For the prismatic beam shown,...Ch. 11.9 - 11.86 through 11.88 For the prismatic beam shown,...Ch. 11.9 - For the prismatic beam shown, determine the slope...Ch. 11.9 - For the prismatic beam shown, determine the slope...Ch. 11.9 - For the beam and loading shown, determine the...Ch. 11.9 - For the beam and loading shown, determine the...Ch. 11.9 - 11.93 and 11.94 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 11.9 - 11.93 and 11.94 For the beam and loading shown,...Ch. 11.9 - For the beam and loading shown, determine the...Ch. 11.9 - For the beam and loading shown, determine the...Ch. 11.9 - Prob. 97PCh. 11.9 - For the beam and loading shown, determine the...Ch. 11.9 - 11.99 and 11.100 For the truss and loading shown,...Ch. 11.9 - 11.99 and 11.100 For the truss and loading shown,...Ch. 11.9 - 11.101 and 11.102 Each member of the truss shown...Ch. 11.9 - 11.101 and 11.102 Each member of the truss shown...Ch. 11.9 - 11.103 and 11.104 Each member of the truss shown...Ch. 11.9 - 11.103 and 11 104 Each member of the truss shown...Ch. 11.9 - A uniform rod of flexural rigidity EI is bent and...Ch. 11.9 - For the uniform rod and loading shown and using...Ch. 11.9 - For the beam and loading shown and using...Ch. 11.9 - Two rods AB and BC of the same flexural rigidity...Ch. 11.9 - Three rods, each of the same flexural rigidity EI,...Ch. 11.9 - Three rods, each of the same flexural rigidity EI,...Ch. 11.9 - 11.111 through 11.115 Determine the reaction at...Ch. 11.9 - 11.111 through 11.115 Determine the reaction at...Ch. 11.9 - 11.111 through 11.115 Determine the reaction at...Ch. 11.9 - 11.111 through 11.115 Determine the reaction at...Ch. 11.9 - 11.111 through 11.115 Determine the reaction at...Ch. 11.9 - For the uniform beam and loading shown, determine...Ch. 11.9 - 11.117 through 11.120 Three members of the same...Ch. 11.9 - 11.117 through 11.120 Three members of the same...Ch. 11.9 - 11.117 through 11.120 Three members of the same...Ch. 11.9 - 11.117 through 11.120 Three members of the same...Ch. 11.9 - 11.121 and 11.122 Knowing that the eight members...Ch. 11.9 - 11.121 and 11.122 Knowing that the eight members...Ch. 11 - Rod AB is made of a steel for which the yield...Ch. 11 - Each member of the truss shown is made of steel...Ch. 11 - The ship at A has just started to drill for oil on...Ch. 11 - Collar D is released from rest in the position...Ch. 11 - Each member of the truss shown is made of steel...Ch. 11 - A block of weight W is placed in contact with a...Ch. 11 - Two solid steel shafts are connected by the gears...Ch. 11 - A 160-lb diver jumps from a height of 20 in. onto...Ch. 11 - For the prismatic beam shown, determine the slope...Ch. 11 - A disk of radius a has been welded to end B of the...Ch. 11 - A uniform rod of flexural rigidity EI is bent and...Ch. 11 - The steel bar ABC has a square cross section of...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- CORRECT ANSWER ONLY WITH COMPLETE FBD. PREFERABLY HANDWRITTEN. I WILL UPVOTE 1. The beam shown carries the following loads:Total dead load, wDL = 36 kN/mConcentrated live load, PLL = 240 kNThe beam section is HSS16X12X3/8 with properties:Span, L = 6 mArea, A = 12,100 mm2Moment of inertia about x-axis, Ix = 292 x 106 mm4Fy = 345 MPa 1. Calculate the location of the live load, from the left support, for maximum moment to occur at the fixed support.Answer: 2.536 m2. Calculate the maximum moment. Answer: 439.128 kN-marrow_forwardCORRECT ANSWER AND COMPLETE FBD ONLY. I PREFER HANDWRITTEN BUT ITS OKAY IF NOT. I WILL UPVOTE 2. The space truss shown is supported by ball-and-socket joints at A, B and C. Factored loads P1 and P2 areacting on joints D and E, respectively, towards the negative y-direction. 1. Calculate the stress of member CE, indicate tension or compression. Answer: 23.61 MPa Tension2. Calculate the stress of member AD, indicate tension or compression. Answer: 21.01 MPa Compression3. Calculate the stress of member CD, indicate tension or compression. Answer: 11.03 MPa Tensionarrow_forwardCORRECT ANSWER AND COMPLETE FBD ONLY. I PREFER HANDWRITTEN BUT ITS OKAY IF NOT. I WILL UPVOTE 3. The frame has pin supports at A and E, subject to a wind load. Treat joint C to be an internal hinge. Given:Dimensions, H1 = 3.0 m; H2 = 4.5 m; L = 10.0 mWind loads, wWL (AB) = 4.8 kN/m; wWL (BC) = 3.9 kN/m; wWL (CD) = 1.5 kN/m; wWL (DE) = 1.2 kN/mMembers are made of A36 steel Wide Flange Section with the following properties:Area, A = 64000 mm2Depth, d = 762 mmFlange width, bf = 371 mmThickness of web, tw = 32 mmThickness of flange, tf = 57.9 mmMoment of inertia about x-axis, Ix = 6080 x 106 mm4The wide flange is oriented so that the bending is about the x-axis1. Calculate the stress in member AB, due to the axial load it carries, indicate if tension or compression.Answer: 0.0476 MPa Tension2. Calculate the stress in member DE, due to the axial load it carries, indicate if tension or compression.Answer: 0.2351 MPa Compression3. Calculate the maximum bending stress at B. Answer: 4.282 MPaarrow_forward
- 32 mm 32 mm b' c' C 32 mm 32 mm b PROBLEM 6.41 a The extruded beam shown has a uniform wall thickness of 3 mm. Knowing that the vertical shear in the beam is 9 kN, determine the shearing stress at each of the five points indicated.arrow_forwardIn a structural reliability problem, the resistance (capacity) R and load effect (demand) S random variables associated with a failure mode of the structure of interest are normally distributed and statistically independent with the following probability distribution parameters (or statistics) in consistent units: MR = 12, σR = 3 μs = 5, σs = 2 (a) Determine the exact probability of failure pF ·arrow_forwardThe resistance R and load effect S for a given failure mode are statistically independent random variables with marginal PDF's 1 fR (r) = 0≤r≤100 100' fs(s)=0.05e-0.05s (a) Determine the probability of failure by computing the probability content of the failure domain defined as {rarrow_forwardPlease solve this problem as soon as possible My ID# 016948724arrow_forwardThe gears shown in the figure have a diametral pitch of 2 teeth per inch and a 20° pressure angle. The pinion rotates at 1800 rev/min clockwise and transmits 200 hp through the idler pair to gear 5 on shaft c. What forces do gears 3 and 4 transmit to the idler shaft? TS I y 18T 32T This a 12 x 18T C 48T 5arrow_forwardQuestion 1. Draw 3 teeth for the following pinion and gear respectively. The teeth should be drawn near the pressure line so that the teeth from the pinion should mesh those of the gear. Drawing scale (1:1). Either a precise hand drawing or CAD drawing is acceptable. Draw all the trajectories of the involute lines and the circles. Specification: 18tooth pinion and 30tooth gear. Diameter pitch=P=6 teeth /inch. Pressure angle:20°, 1/P for addendum (a) and 1.25/P for dedendum (b). For fillet, c=b-a.arrow_forward5. The figure shows a gear train. There is no friction at the bearings except for the gear tooth forces. The material of the milled gears is steel having a Brinell hardness of 170. The input shaft speed (n2) is 800 rpm. The face width and the contact angle for all gears are 1 in and 20° respectively. In this gear set, the endurance limit (Se) is 15 kpsi and nd (design factor) is 2. (a) Find the revolution speed of gear 5. (b) Determine whether each gear satisfies the design factor of 2.0 for bending fatigue. (c) Determine whether each gear satisfies the design factor of 2.0 for surface fatigue (contact stress). (d) According to the computation results of the questions (b) and (c), explain the possible failure mechanisms for each gear. N4=28 800rpm N₁=43 N5=34 N₂=14 P(diameteral pitch)=8 for all gears Coupled to 2.5hp motorarrow_forward1. The rotating steel shaft is simply supported by bearings at points of B and C, and is driven by a spur gear at D, which has a 6-in pitch diameter. The force F from the drive gear acts at a pressure angle of 20°. The shaft transmits a torque to point A of TA =3000 lbĘ in. The shaft is machined from steel with Sy=60kpsi and Sut=80 kpsi. (1) Draw a shear force diagram and a bending moment diagram by F. According to your analysis, where is the point of interest to evaluate the safety factor among A, B, C, and D? Describe the reason. (Hint: To find F, the torque Tд is generated by the tangential force of F (i.e. Ftangential-Fcos20°) When n=2.5, K=1.8, and K₁ =1.3, determine the diameter of the shaft based on (2) static analysis using DE theory (note that fatigue stress concentration factors need to be used for this question because the loading condition is fatigue) and (3) a fatigue analysis using modified Goodman. Note) A standard diameter is not required for the questions. 10 in Darrow_forward3 N2=28 P(diametral pitch)=8 for all gears Coupled to 25 hp motor N3=34 Full depth spur gears with pressure angle=20° N₂=2000 rpm (1) Compute the circular pitch, the center-to-center distance, and base circle radii. (2) Draw the free body diagram of gear 3 and show all the forces and the torque. (3) In mounting gears, the center-to-center distance was reduced by 0.1 inch. Calculate the new values of center-to-center distance, pressure angle, base circle radii, and pitch circle diameters. (4)What is the new tangential and radial forces for gear 3? (5) Under the new center to center distance, is the contact ratio (mc) increasing or decreasing?arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Automotive Technology: A Systems Approach (MindTa...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781133612315Author:Jack Erjavec, Rob ThompsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Automotive Technology: A Systems Approach (MindTa...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781133612315Author:Jack Erjavec, Rob ThompsonPublisher:Cengage Learning International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305578296Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill JohnsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305578296Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill JohnsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning

Automotive Technology: A Systems Approach (MindTa...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781133612315
Author:Jack Erjavec, Rob Thompson
Publisher:Cengage Learning

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305578296
Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305387102
Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanical SPRING DESIGN Strategy and Restrictions in Under 15 Minutes!; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dsWQrzfQt3s;License: Standard Youtube License