
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780134319650
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 11.2, Problem 11.13P
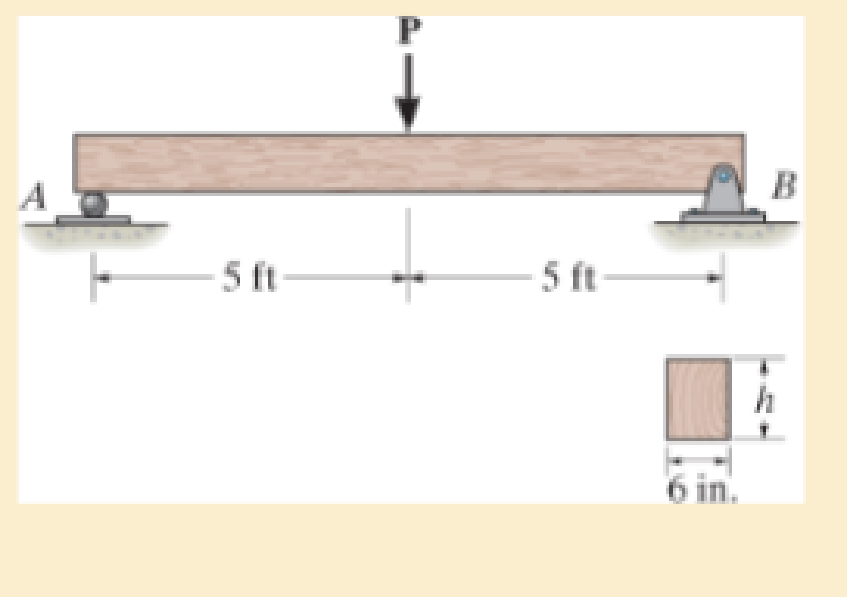
Determine its height h so that it simultaneously reaches its allowable bending stress. σallow = 1.50 ksi and an allowable shear stress of τallow.= 50 psi. Also, what is the maximum load P that the beam can then support?
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
DO NOT COPY SOLUTION
The differential equation of a cruise control system is provided by the following equation:
Find the closed loop transfer function with respect to the reference velocity (vr) .
a. Find the poles of the closed loop transfer function for different values of K. How does the poles move as you change K?
b. Find the step response for different values of K and plot in MATLAB. What can you observe?
c. For the given transfer function, find tp, ts, tr, Mp . Plot the resulting step response. G(s) = 40/(s^2 + 4s + 40)
Aswatan gas occupies a space of 0.3 millike cube at a pressure of 2 bar and temperature of 77 degree Celsius it is indicate at constant volume at pressure of 7 parts determine temperature at the end of process mass of a gas changing internal energy change in enthalpy during the process assume CP is equal to 10 1.005 CV is equal to 0.712 is equal to 287
AUTO CONTROLDNO COPIED ANSWERS, SHOW FULL SOLUTION
The differential equation of a DC motor can be described by the following equation
Find the transfer function between the applied voltage ( Va)and the motor speed (thetadot m).
What is the steady state speed of the motor after a voltage (Va = 10V) has been applied.
Find the transfer function between the applied voltage (Va) and the shaft angle (thetadot m) .
Chapter 11 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Ch. 11.2 - Determine the minimum dimension a to the nearest...Ch. 11.2 - of the rod to safely support the load. The rod is...Ch. 11.2 - The wood has an allowable normal stress of allow =...Ch. 11.2 - of the beam's cross section to safely support the...Ch. 11.2 - Determine the minimum dimension b to the nearest...Ch. 11.2 - The beam is made of steel having an allowable...Ch. 11.2 - Determine its dimensions if it is to be...Ch. 11.2 - Determine the minimum width of the beam to the...Ch. 11.2 - if P=10 kip.Ch. 11.2 - If the allowable bending stress is allow = 22 ksi...
Ch. 11.2 - The allowable bending stress is allow = 24 ksi and...Ch. 11.2 - The allowable bending stress is allow = 22 ksi and...Ch. 11.2 - The allowable bending stress is allow = 24 ksi and...Ch. 11.2 - Select the lightest-weight wide-flange beam from...Ch. 11.2 - The beam has an allowable normal stress of allow =...Ch. 11.2 - The beam has an allowable normal stress of allow...Ch. 11.2 - If each nail can support a shear force of 200 lb....Ch. 11.2 - If each beam is to be designed to carry 90 lb/ft...Ch. 11.2 - Determine its height h so that it simultaneously...Ch. 11.2 - The beam is constructed from four boards. If each...Ch. 11.2 - Prob. 11.15PCh. 11.2 - The beam has an allowable normal stress of allow....Ch. 11.2 - Determine the maximum cable force P that can...Ch. 11.2 - to safely support the load. The wood has an...Ch. 11.2 - and the wood has an allowable normal stress of...Ch. 11.2 - If the glue can support a shear stress of allow, =...Ch. 11.2 - If the allowable bending stress is allow = 6 MPa,...Ch. 11.2 - Determine the width b if the height h=2b.Ch. 11.2 - The allowable bending stress is allow = 24 ksi and...Ch. 11.2 - if allow = 30 ksi and allow = 15 ksi. The journal...Ch. 11.2 - if allow = 30 ksi and allow = 15 ksi. The journal...Ch. 11.2 - Select the lightest-weight wide-flange beam from...Ch. 11.2 - The allowable bending stress is allow = 30 ksi and...Ch. 11.2 - The allowable bending stress is allow = 30 ksi and...Ch. 11.2 - If the maximum bending stress is not to exceed...Ch. 11.2 - Determine the maximum load that can safely be...Ch. 11.4 - Determine the variation in the width was a...Ch. 11.4 - The tapered beam supports a uniform distributed...Ch. 11.4 - The tapered beam supports the concentrated force P...Ch. 11.4 - The beam is made from a plate that has a constant...Ch. 11.4 - Determine the variation in the depth d of a...Ch. 11.4 - Determine the variation of the radius r of the...Ch. 11.4 - Prob. 11.37PCh. 11.4 - Determine the variation in the width b as a...Ch. 11.4 - The tubular shaft has an inner diameter of 15 mm....Ch. 11.4 - Prob. 11.40PCh. 11.4 - Prob. 11.41PCh. 11.4 - The pulleys fixed to the shaft are loaded as...Ch. 11.4 - Prob. 11.43PCh. 11.4 - Prob. 11.44PCh. 11.4 - Prob. 11.45PCh. 11 - The cantilevered beam has a circular cross...Ch. 11 - Select the lightest-weight wide-flange overhanging...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.3RPCh. 11 - Determine the shaft's diameter to the nearest...Ch. 11 - Select the lightest-weight wide-flange beam from...Ch. 11 - The simply supported joist is used in the...Ch. 11 - The simply supported joist is used in the...Ch. 11 - by 4-in. pieces of wood braced as shown. If the...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Auto Controls DONT COPY ANSWERS Perform the partial fraction expansion of the following transfer function and find the impulse response: G(s) = (s/2 + 5/3) / (s^2 + 4s + 6) G(s) =( 6s^2 + 50) / (s+3)(s^2 +4)arrow_forwardDerive the Laplace transform of the following functions. Use the definition of Laplace transform. f(t)=sin4t and f(t)=cos2t Auto Controlsarrow_forwardhelparrow_forward
- any help i dont understandarrow_forwardBattery operated train Mueh Groll CD Af Pair 160,000 kg 0.0005 0.15 19 5m² 1.2kg/m³ 0.98 0.9 Tet neng 0.88 Tesla Prated Tesla Trated Ywheel ng Joyle 2 270 kW 440NM 0,45m 20 8.5kg m Consider a drive cycle of a 500km trip with 3 stops in the middle. Other than the acceleration and deceleration associated with the three stops, the tran maintains. constant cruise speed velocity of 324 km/hr. The tran will fast charge at each stop for 15 min at a rate Peharge = 350 kW Εμ (MN 15MIN Stop w charging (350kW) GMIJ t 6MM 6AW 1) calculate the battery power required to mantain. constant velocity of 324km/hr 2) determine the battery energy, energy required to constant velocity portion of this drive. Cover the 3) calculate the battery energy required to accelerate the train to 324/04/hr. 4) calculate the battery energy that is either fost in deceleration or recovered due to regenerative breaking etcarrow_forwardA 22-lb block B rests as shown on a 28-lb bracket A. The coefficients of friction are μs=0.30μs=0.30 and μk=0.25μk=0.25 between block B and bracket A, and there is no friction in the pulley or between the bracket and the horizontal surface. solved in a previous part. max weight of block C if block B is not to slide on bracket A is 5.045 lbs. Please solve for the acceleration of each Blockarrow_forward
- Test 1 .DOCX * A File Edit View Tools Help INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING PROGRAMME IMB 411-INDUSTRIAL LOGISTICS TEST 1- SEPTEMBER 12, 2012 Instructions: Answer all questions. Time allowed is 1.5 hours. Identify your script with your student number ONLY (Do not write your name). 1. Define the following terms (i) Logistics management (ii) Supply chain management (iii) Vertical integration in a supply chain (3 Marks) (3 Marks) (3 Marks) 2. (a) Using examples of your choice, briefly discuss the following levels of customer service (1) Pre-transaction elements (ii) Transaction elements (4 Marks) (4 Marks) (iii) Post-transaction elements (4 Marks) (b) "The challenge facing Dumelang Enterprise (Pty) Ltd is to establish the real profitability of their customers and to develop service strategies that will improve the profitability of all customers". As a logistics consultant, briefly discuss how you can advise Dumelang's customer service management. 3. (a) List the three main forms of inventory in a…arrow_forwardIt is decided to install several single-jet Pelton wheels to produce a total power of 18 MW. The available head is 246 m. The wheel rotational speed is 650 rpm and the speed ratio (❤) = 0.46. The diameter of the nozzle (jet) is limited to be 0.167 m with a Cv of 0.95. The efficiency of each turbine is 87%. Determine: (1) The number of Pelton wheels to be used, and (2) The bucket angle.arrow_forwardPlease show All work and fill it in thermodynamicsarrow_forward
- Quick solution required. My request, Don't use Ai. Mechanical engineeringarrow_forwardPlease give handwritten solution, don't use chatgpt. Fbd should be includedarrow_forward(I) [40 Points] Using centered finite difference approximations as done in class, solve the equation for O: d20 dx² + 0.010+ Q=0 subject to the boundary conditions shown in the stencil below. Do this for two values of Q: (a) Q = 0.3, and (b) Q= √(0.5 + 2x)e-sinx (cos(5x)+x-0.5√1.006-x| + e −43*|1+.001+x* | * sin (1.5 − x) + (cosx+0.001 + ex-1250+ sin (1-0.9x)|) * x - 4.68x4. For Case (a) (that is, Q = 0.3), use the stencil in Fig. 1. For Case (b), calculate with both the stencils in Fig. 1 and Fig 2. For all the three cases, show a table as well as a plot of O versus x. Discuss your results. Use MATLAB and hand in the MATLAB codes. 1 0=0 x=0 2 3 4 0=1 x=1 Fig 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 0=0 x=0 0=1 x=1 Fig 2arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Mechanics of Materials Lecture: Beam Design; Author: UWMC Engineering;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-wVs5pvQPm4;License: Standard Youtube License