
Concept explainers
(a)
The gravitational force on the particle of mass
(a)
Answer to Problem 64P
The gravitational force on the particle of mass
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Following figure shows the distribution of masses on the semi-circular arc of radius
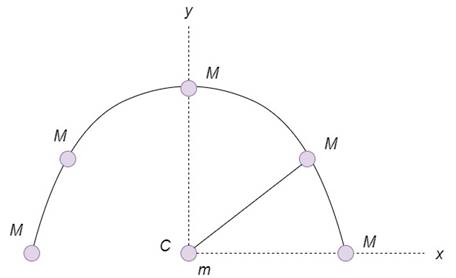
Formula Used:
The expression for the gravitational force between the masses
Here,
Calculation:
Radius of the arc is
Choose the unit vector
The gravitational force between the masses
The gravitational force between the masses
The gravitational force between the masses
The gravitational force between the masses
Hence, net force on the particle of mass
Substitute the values and solve:
Conclusion:
Therefore, the gravitational force on the particle of mass
(b)
The gravitational field at center of curvature of the arc.
(b)
Answer to Problem 64P
The gravitational field at center of curvature of the arc is
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Following figure shows the distribution of masses on the semi-circular arc of radius
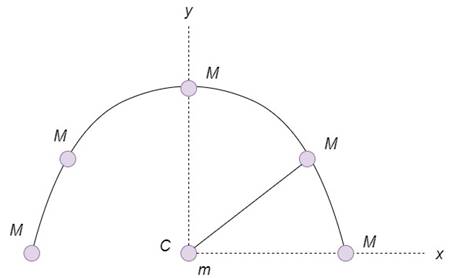
Formula Used:
Gravitational field at a point is:
Here, net gravitational force is
Calculation:
The gravitational field at the center of curvature of the arc can be determined as follows.
Substitute
Conclusion:
The gravitational field at center of curvature of the arc is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers
- Find the wavelength of the photon if a (Li--) electron makes a transition from n=4 to n=3. Findthe Bohr radius for each state.arrow_forwardA photon with wavelength 3000 nm hits a stationary electron. After the collision electron isscattered to 60 degrees. Find the wavelength and frequency of the scattered photon.arrow_forwardA metal has threshold frequency 10^15. Calculate the maximum kinetic energy of the ejectedelectron if a laser beam with wavelength 1.5 10^-7 m is projected on the metal.arrow_forward
- Determine the direction of the vector V, B, or ♬ that is missing from the pair of vectors shown in each scenario. Here, u is the velocity vector of a moving positive charge, B is a constant and uniform magnetic field, and F is the resulting force on the moving charge. 1. 2. 3. B OB F 4. ↑F F 5. 怔 ↑ ↑F Answer Bank 6. ↑ TE Farrow_forwardTwo point charges (+9.80 nC and -9.80 nC) are located 8.00 cm apart. Let U=0 when all of the charges are separated by infinite distances. What is the potential energy if a third point charge q=-4.20 nC is placed at point b? 8.00 cm 8.00 cm 4.00 +4.00 +4.00- cm cm cm HJarrow_forward! Required information Two chloride ions and two sodium ions are in water, the "effective charge" on the chloride ions (CI¯) is −2.00 × 10-21 C and that of the sodium ions (Na+) is +2.00 x 10-21 C. (The effective charge is a way to account for the partial shielding due to nearby water molecules.) Assume that all four ions are coplanar. CT Na+ Na+ 30.0° 45.0% с сг L. where a = 0.300 nm, b = 0.710 nm, and c = 0.620 nm. What is the direction of electric force on the chloride ion in the lower right-hand corner in the diagram? Enter the angle in degrees where positive indicates above the negative x-axis and negative indicates below the positive x-axis.arrow_forward
- A pendulum has a 0.4-m-long cord and is given a tangential velocity of 0.2 m/s toward the vertical from a position 0 = 0.3 rad. Part A Determine the equation which describes the angular motion. Express your answer in terms of the variable t. Express coefficients in radians to three significant figures. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ vec (t)=0.3 cos (4.95t) + 0.101 sin (4.95t) Submit Previous Answers Request Answer × Incorrect; Try Again; 6 attempts remainingarrow_forwardPart A ■Review The uniform 150-lb stone (rectangular block) is being turned over on its side by pulling the vertical cable slowly upward until the stone begins to tip. (Figure 1) If it then falls freely (T = 0) from an essentially balanced at-rest position, determine the speed at which the corner A strikes the pad at B. The stone does not slip at its corner C as it falls. Suppose that height of the stone is L = 1.2 ft. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ? ft VA 10.76 S Submit Previous Answers Request Answer × Incorrect; Try Again; 6 attempts remainingarrow_forwardConsider the circuit shown in the figure. The battery has emf ε = 69 volts and negligible internal resistance. The inductance is L = 0.4 H and the resistances are R 1 = 12 Ω and R 2 = 9.0 Ω. Initially the switch S is open and no currents flow. Then the switch is closed. After leaving the switch closed for a very long time, it is opened again. Just after it is opened, what is the current in R 1?arrow_forward
- A capacitor with a capacitance of C = 5.95×10−5 F is charged by connecting it to a 12.5 −V battery. The capacitor is then disconnected from the battery and connected across an inductor with an inductance of L = 1.55 H . At the time 2.35×10−2 s after the connection to the inductor is made, what is the current in the inductor? At that time, how much electrical energy is stored in the inductor?arrow_forwardCan someone help me with this question. Thanks.arrow_forwardCan someone help me with this question. Thanks.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





