
Concept explainers
A rigid, massless rod has three particles with equal masses attached to it as shown in Figure P11.37. The rod is free to rotate in a vertical plane about a frictionless axle perpendicular to the rod through the point P and is released from rest in the horizontal position at t = 0. Assuming m and d are known, find (a) the moment of inertia of the system of three particles about the pivot, (b) the torque acting on the system at t = 0, (c) the
Figure P11.37
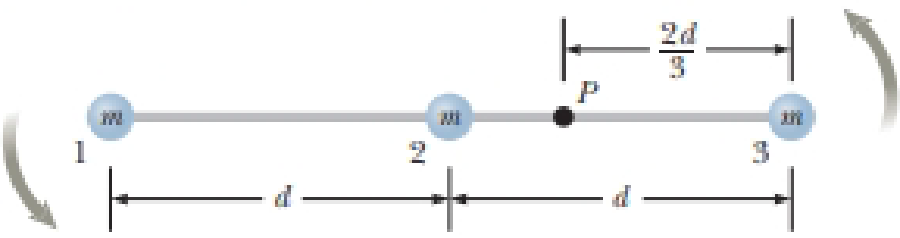
(a)
The moment of inertia of the system of three particles about the pivot.
Answer to Problem 37AP
The moment of inertia of the system of three particles about the pivot is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The mass of three particles is
The formula to calculate moment of inertia is,
The distance of the particle 1 from point P is,
The distance of the particle 2 from point P is,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the moment of inertia of the system of three particles about the pivot is
(b)
The torque acting on the system at
Answer to Problem 37AP
The torque acting on the system at
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The mass of three particles is
Consider that the whole weight,
The formula to calculate torque is,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the torque acting on the system at
(c)
The angular acceleration of the system at
Answer to Problem 37AP
The angular acceleration of the system at
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The mass of three particles is
The formula to calculate angular acceleration is,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the angular acceleration of the system at
(d)
The linear acceleration of the particle 3 at
Answer to Problem 37AP
The linear acceleration of the particle 3 at
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The mass of three particles is
The formula to calculate linear acceleration is,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the linear acceleration of the particle 3 at
(e)
The maximum kinetic energy of the system.
Answer to Problem 37AP
The maximum kinetic energy of the system is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The mass of three particles is
Because the axle is fixed, no external work is performed on the system of the earth and three particles, so the total mechanical energy is conserved.
The rotation kinetic energy is maximum when rod has swung to a vertical orientation with the centre of gravity directly under the axle.
The expression for the energy is,
Conclusion:
Therefore, the maximum kinetic energy of the system is
(f)
The maximum angular speed reached by the rod.
Answer to Problem 37AP
The maximum angular speed reached by the rod is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The mass of three particles is
In the vertical orientation, the rod has the greatest rotational kinetic energy.
The expression for the kinetic energy is,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the maximum angular speed reached by the rod is
(g)
The maximum angular momentum of the system.
Answer to Problem 37AP
The maximum angular momentum of the system is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The mass of three particles is
The expression for the angular momentum is,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the maximum angular momentum of the system is
(h)
The maximum speed of particle 2.
Answer to Problem 37AP
The maximum speed of particle 2 is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The mass of three particles is
The expression for the speed is,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the maximum speed of particle 2 is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
- please answer this asap!!!!arrow_forwardRT = 4.7E-30 18V IT = 2.3E-3A+ 12 38Ω ли 56Ω ли r5 27Ω ли r3 28Ω r4 > 75Ω r6 600 0.343V 75.8A Now figure out how much current in going through the r4 resistor. |4 = unit And then use that current to find the voltage drop across the r resistor. V4 = unitarrow_forward7 Find the volume inside the cone z² = x²+y², above the (x, y) plane, and between the spheres x²+y²+z² = 1 and x² + y²+z² = 4. Hint: use spherical polar coordinates.arrow_forward
- ганм Two long, straight wires are oriented perpendicular to the page, as shown in the figure(Figure 1). The current in one wire is I₁ = 3.0 A, pointing into the page, and the current in the other wire is 12 4.0 A, pointing out of the page. = Find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at point P. Express your answer using two significant figures. VO ΜΕ ΑΣΦ ? Figure P 5.0 cm 5.0 cm ₁ = 3.0 A 12 = 4.0 A B: μΤ You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again. Submit Previous Answers Request Answer 1 of 1 Part B X Express your answer using two significant figures. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ 0 = 0 ? below the dashed line to the right P You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again.arrow_forwardAn infinitely long conducting cylindrical rod with a positive charge λ per unit length is surrounded by a conducting cylindrical shell (which is also infinitely long) with a charge per unit length of −2λ and radius r1, as shown in the figure. What is σinner, the surface charge density (charge per unit area) on the inner surface of the conducting shell? What is σouter, the surface charge density on the outside of the conducting shell? (Recall from the problem statement that the conducting shell has a total charge per unit length given by −2λ.)arrow_forwardA small conducting spherical shell with inner radius aa and outer radius b is concentric with a larger conducting spherical shell with inner radius c and outer radius d (Figure 1). The inner shell has total charge +2q, and the outer shell has charge −2q. What's the total charge on the inner surface of the small shell? What's the total charge on the outer surface of the small shell? What's the total charge on the inner surface of the large shell? What's the total charge on the outer surface of the large shell?arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





