
EBK PHYSICS
5th Edition
ISBN: 8220103026918
Author: Walker
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 11, Problem 32PCE
In Figure 11-46 two acrobats perform a balancing maneuver. The arms of the top acrobat (in yellow), together with the weight of his head and shoulders, provide a downward force at a distance of 28 cm from the pivot point to balance the torque produced by his lower body. If the lower body of the top acrobat is modeled as a 54-kg mass at a distance of 39 cm from the pivot point, how much force must the arms and upper body produce?
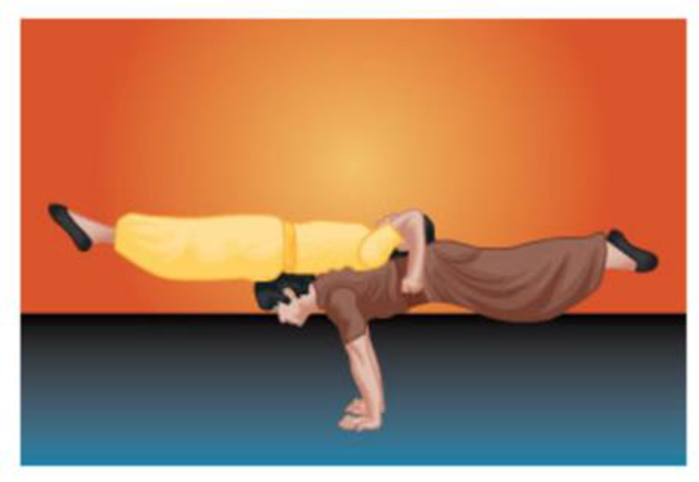
Figure 11-46 Problem 32
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
For each part make sure to include sign to represent direction, with up being positive and down being negative.
A ball is thrown vertically upward with a speed of 30.5 m/s.
A) How high does it rise? y=
B) How long does it take to reach its highest point? t=
C) How long does it take the ball return to its starting point after it reaches its highest point? t=
D) What is its velocity when it returns to the level from which it started? v=
Four point charges of equal magnitude Q = 55 nC are placed on the corners of a rectangle of sides D1 = 27 cm and D2 = 11cm. The charges on the left side of the rectangle are positive while the charges on the right side of the rectangle are negative. Use a coordinate system where the positive y-direction is up and the positive x-direction is to the right.
A. Which of the following represents a free-body diagram for the charge on the lower left hand corner of the rectangle?
B. Calculate the horizontal component of the net force, in newtons, on the charge which lies at the lower left corner of the rectangle.Numeric : A numeric value is expected and not an expression.Fx = __________________________________________NC. Calculate the vertical component of the net force, in newtons, on the charge which lies at the lower left corner of the rectangle.Numeric : A numeric value is expected and not an expression.Fy = __________________________________________ND. Calculate the magnitude of the…
Point charges q1=50.0μC and q2=-35μC are placed d1=1.0m apart, as shown.
A. A third charge, q3=25μC, is positioned somewhere along the line that passes through the first two charges, and the net force on q3 is zero. Which statement best describes the position of this third charge?1) Charge q3 is to the right of charge q2. 2) Charge q3 is between charges q1 and q2. 3) Charge q3 is to the left of charge q1. B. What is the distance, in meters, between charges q1 and q3? (Your response to the previous step may be used to simplify your solution.)Give numeric value.d2 = __________________________________________mC. Select option that correctly describes the change in the net force on charge q3 if the magnitude of its charge is increased.1) The magnitude of the net force on charge q3 would still be zero. 2) The effect depends upon the numeric value of charge q3. 3) The net force on charge q3 would be towards q2. 4) The net force on charge q3 would be towards q1. D. Select option that…
Chapter 11 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS
Ch. 11.1 - A bicycle wheel is mounted on an axle, as shown in...Ch. 11.2 - Consider two objects with the following...Ch. 11.3 - A Physics sign is supported symmetrically by two...Ch. 11.4 - A mobile made from three piggy banks (A, B, C) is...Ch. 11.5 - Prob. 5EYUCh. 11.6 - Consider two objects with the following...Ch. 11.7 - Prob. 7EYUCh. 11.8 - In system 1, a torque of 20 N m acts through an...Ch. 11.9 - The angular velocity of the spinning bicycle wheel...Ch. 11 - Two forces produce the same torque. Does it follow...
Ch. 11 - A car pitches down in front when the brakes are...Ch. 11 - A tightrope walker uses a long pole to aid in...Ch. 11 - When a motorcycle accelerates rapidly from a stop...Ch. 11 - Give an example of a system in which the net...Ch. 11 - Give an example of a system in which the net force...Ch. 11 - Is the normal force exerted by the ground the same...Ch. 11 - Give two everyday examples of objects that are not...Ch. 11 - Give two everyday examples of objects that are in...Ch. 11 - Can an object have zero translational acceleration...Ch. 11 - Stars form when a large rotating cloud of gas...Ch. 11 - What purpose does the tail rotor on a helicopter...Ch. 11 - Is it possible to change the angular momentum of...Ch. 11 - Suppose a diver springs into the air with no...Ch. 11 - To tighten a spark plug, it is recommended that a...Ch. 11 - Pulling a Weed The gardening tool shown in Figure...Ch. 11 - A person slowly lowers a 3.6-kg crab trap over the...Ch. 11 - A squirrel-proof bird feeder has a lever that...Ch. 11 - At one position during its cycle, the foot pushes...Ch. 11 - BIO Predict/Calculate Force to Hold a Baseball A...Ch. 11 - At the local playground, a 21-kg child sits on the...Ch. 11 - Predict/Explain Consider the pulley-block systems...Ch. 11 - Suppose a torque rotates your body about one of...Ch. 11 - A torque of 0.97 N m is applied to a bicycle...Ch. 11 - When a ceiling fan rotating with an angular speed...Ch. 11 - When the play button is pressed, a CD accelerates...Ch. 11 - A person holds a ladder horizontally at its...Ch. 11 - A 0.180-kg wooden rod is 1.25 m long and pivots at...Ch. 11 - Predict/Calculate A wheel on a game show is given...Ch. 11 - The L-shaped object in Figure 11-41 consists of...Ch. 11 - The L-shaped object described in the previous...Ch. 11 - A motorcycle accelerates from rest, and both the...Ch. 11 - Predict/Calculate A torque of 13 N m is applied...Ch. 11 - Predict/Explain Suppose the person in Example...Ch. 11 - A string that passes over a pulley has a 0.321-kg...Ch. 11 - To loosen the lid on a jar of jam 7.6 cm in...Ch. 11 - BIO Predict/Calculate Referring to the person...Ch. 11 - Prob. 24PCECh. 11 - Prob. 25PCECh. 11 - Predict/Calculate A schoolyard teeter-totter with...Ch. 11 - A 0.122-kg remote control 23.0 cm long rests on a...Ch. 11 - Predict/Calculate A 0.16-kg meterstick is held...Ch. 11 - Prob. 29PCECh. 11 - A uniform metal rod, with a mass of 2.0 kg and a...Ch. 11 - Prob. 31PCECh. 11 - In Figure 11-46 two acrobats perform a balancing...Ch. 11 - BIO Forces in the Foot In Figure 11-47 we see the...Ch. 11 - A stick with a mass of 0.214 kg and a length of...Ch. 11 - Prob. 35PCECh. 11 - If the cat in Example 11-9 has a mass of 3.9 kg,...Ch. 11 - Prob. 37PCECh. 11 - Maximum Overhang Three identical, uniform books of...Ch. 11 - A baseball bat balances 71.1 cm from one end. If a...Ch. 11 - A 2.85-kg bucket is attached to a rope wrapped...Ch. 11 - A child exerts a tangential 53 4-N force on the...Ch. 11 - Predict/Calculate You pull downward with a force...Ch. 11 - One elevator arrangement includes the passenger...Ch. 11 - Atwood's Machine An Atwoods machine consists of...Ch. 11 - A 1.4-kg bicycle tire with a radius of 33 cm...Ch. 11 - Jogger 1 in Figure 11-51 has a mass of 65.3 kg and...Ch. 11 - Predict/Calculate Suppose jogger 3 in Figure 11-51...Ch. 11 - A torque of 0.12 N m is applied to an egg beater...Ch. 11 - A windmill has an initial angular momentum of 8500...Ch. 11 - Two gerbils run in place with a linear speed of...Ch. 11 - Predict/Explain A student rotates on a...Ch. 11 - A puck on a horizontal, frictionless surface is...Ch. 11 - A puck on a horizontal, frictionless surface is...Ch. 11 - As an ice skater begins a spin, his angular speed...Ch. 11 - A disk-shaped merry-go-round of radius 2.63 m and...Ch. 11 - A student sits at rest on a piano stool that can...Ch. 11 - Predict/Calculate A turntable with a moment of...Ch. 11 - A student on a piano stool rotates freely with an...Ch. 11 - Walking on a Merry-Go-Round A child of mass m...Ch. 11 - Predict/Explain Two spheres of equal mass and...Ch. 11 - Turning a doorknob through 0.25 of a revolution...Ch. 11 - A person exerts a tangential force of 36.1 N on...Ch. 11 - To prepare homemade ice cream a crank must be...Ch. 11 - Power of a Dental Drill A popular make of dental...Ch. 11 - For a home repair job you must turn the handle of...Ch. 11 - The L-shaped object in Figure 11-40 consists of...Ch. 11 - The rectangular object in Figure 11-41 consists of...Ch. 11 - Predict/Calculate A circular saw blade accelerates...Ch. 11 - CE A uniform disk stands upright on its edge, and...Ch. 11 - CE Consider the two rotating systems shown in...Ch. 11 - CE Predict/Explain A disk and a hoop (bicycle...Ch. 11 - CE A beetle sits at the nm of a turntable that is...Ch. 11 - After getting a drink of water a hamster jumps...Ch. 11 - A 47.0-kg uniform rod 4.25 m long is attached to a...Ch. 11 - Prob. 75GPCh. 11 - BIO The Masseter Muscle The masseter muscle, the...Ch. 11 - Exercising the Biceps You are designing exercise...Ch. 11 - Prob. 78GPCh. 11 - In Example 11-11, suppose the ladder is uniform,...Ch. 11 - When you arrive at Dukes Dude Ranch you are...Ch. 11 - Prob. 81GPCh. 11 - Flats Versus Heels A woman might wear a pair of...Ch. 11 - BIO A young girl sits at the edge of a dock by the...Ch. 11 - BIO Deltoid Muscle A crossing guard holds a STOP...Ch. 11 - BIO Triceps To determine the force a persons...Ch. 11 - Predict/Calculate Suppose partial melting of the...Ch. 11 - A bicycle wheel of radius R and mass M is at rest...Ch. 11 - A 0.101-kg yo-yo has an outer radius R that is...Ch. 11 - BIO Peak Pedaling Torque The downward force...Ch. 11 - A cylinder of mass m and radius r has a string...Ch. 11 - Bricks in Equilibrium Consider a system of four...Ch. 11 - BIO Correcting Torsiversion Torsiversion is a...Ch. 11 - BIO Correcting Torsiversion Torsiversion is a...Ch. 11 - BIO Correcting Torsiversion Torsiversion is a...Ch. 11 - BIO Correcting Torsiversion Torsiversion is a...Ch. 11 - Referring to Example 11-14 Suppose the mass of the...Ch. 11 - Prob. 97PPCh. 11 - Referring to Quick Example 11-22 Suppose the child...Ch. 11 - Referring to Quick Example 11-22 Suppose...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Plants use the process of photosynthesis to convert the energy in sunlight to chemical energy in the form of su...
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
When you rub your cold hands together, the friction between them results in heat that warms your hands. Why doe...
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Another cross in Drosophila involved the recessive, X-linked genes yellow (y), white (w), and cut (ct). A yello...
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
What is the difference between cellular respiration and external respiration?
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Using the South Atlantic as an example, label the beginning of the normal polarity period C that began 2 millio...
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Compare each of the mechanisms listed here with the mechanism for each of the two parts of the acid-catalyzed h...
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The magnitude of the force between a pair of point charges is proportional to the product of the magnitudes of their charges and inversely proportional to the square of their separation distance. Four distinct charge-pair arrangements are presented. All charges are multiples of a common positive charge, q. All charge separations are multiples of a common length, L. Rank the four arrangements from smallest to greatest magnitude of the electric force.arrow_forwardA number of electric charges has been placed at distinct points along a line with separations as indicated. Two charges share a common magnitude, q (lower case), and another charge has magnitude Q (upper case). The signs of the charges are indicated explicitly such that ∣∣+q∣∣∣∣+Q∣∣=∣∣−q∣∣==∣∣−Q∣∣=qQ Four different configurations of charges are shown. For each, express the net electric force on the charge with magnitude Q (upper case) as F⃗E=FE,xî where the positive x direction is towards the right. By repositioning the figures to the area on the right, rank the configurations from the most negative value to the most positive value of FE,x.arrow_forwardA collection of electric charges that share a common magnitude q (lower case) has been placed at the corners of a square, and an additional charge with magnitude Q (upper case) is located at the center of that square. The signs of the charges are indicated explicitly such that ∣∣+q∣∣∣∣+Q∣∣=∣∣−q∣∣==∣∣−Q∣∣=qQ Four unique setups of charges are displayed. By moving one of the direction drawings from near the bottom to the bucket beside each of the setups, indicate the direction of the net electric force on the charge with magnitude Q, located near the center, else indicate that the magnitude of the net electric force is zero, if appropriate.arrow_forward
- In Dark Souls 3 you can kill the Ancient Wyvern by dropping on its head from above it. Let’s say you jump off the ledge with an initial velocity of 3.86 mph and spend 1.72 s in the air before hitting the wyvern’s head. Assume the gravity is the same as that of Earth and upwards is the positive direction. Also, 1 mile = 1609 m. A) How high up is the the ledge you jumped from as measured from the wyvern’s head? B) What is your velocity when you hit the wyvern?arrow_forwardA conducting sphere is mounted on an insulating stand, and initially it is electrically neutral. A student wishes to induce a charge distribution similar to what is shown here. The student may connect the sphere to ground or leave it electrically isolated. The student may also place a charged insulated rod near to the sphere without touching it. Q. The diagrams below indicate different choices for whether or not to include a ground connection as well as the sign of the charge on and the placement of an insulating rod. Choose a diagram that would produce the desired charge distribution. (If there are multiple correct answers, you need to select only one of them.)arrow_forwardA person is making pancakes and tries to flip one in the pan. The person is holding the pan a distance y0 = 1.10 m above the ground when they launch the pancake. The pancake just barely touches the ceiling, which is at a height y = 2.47 m above the ground. A) What must be the initial velocity of the pancake to reach that height? B) This person, shocked that they almost hit the ceiling, does not catch it on the way down and the pancake hits the floor. Assuming up as the positive direction, what is the velocity of the pancake when it hits the floor, ruining breakfast and this person’s day?arrow_forward
- One of Spider-Man’s less talked about powers is that he can jump really high. In the comics Spider-Man can jump upwards 3 stories. A) If Spider-Man leaves the ground at 14.3 m/s, how high can he get? y= B) If Spider-Man jumps directly upwards with the initial velocity used above and then returns to the ground, what total amount of time does he spend airborn? t=arrow_forwardAn insulating rod is positively charged, and an electrically neutral conducting sphere is mounted on an insulating stand. The rod is brought near to the sphere on the right, but they never actually touch. Q. Select the image that best represents the resulting charge distribution on the conducting sphere.arrow_forwardThis is a multi-part problem. For each part make sure to include sign to represent direction, with up being positive and down being negative. A ball is thrown vertically upward with a speed of 30.5 m/s. A) How high does it rise? y= B) How long does it take to reach its highest point? t= C) How long does it take the ball return to its starting point after it reaches its highest point? t= D) What is its velocity when it returns to the level from which it started? v=arrow_forward
- Blue light has a wavelength of 485 nm. What is the frequency of a photon of blue light? Question 13 Question 13 What is the wavelength of radiofrequency broadcast of 104 MHz? Question 14 Question 14 1 Point 3. The output intensity from an x-ray exposure is 4 mGy at 90 cm. What will the intensity of the exposure be at 180 cm? Question 15 Question 15 1 Point What is the frequency of an 80 keV x-ray?arrow_forwardUnder what condition is IA - BI = A + B? Vectors À and B are in the same direction. Vectors À and B are in opposite directions. The magnitude of vector Vectors À and 官 B is zero. are in perpendicular directions.arrow_forwardFor the vectors shown in the figure, express vector 3 in terms of vectors M and N. M S =-M+ Ň == S=м- Ñ S = M +Ñ +Narrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Static Equilibrium: concept; Author: Jennifer Cash;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0BIgFKVnlBU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY