
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9780134746241
Author: Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. Tasa
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 3.7A, Problem 2A
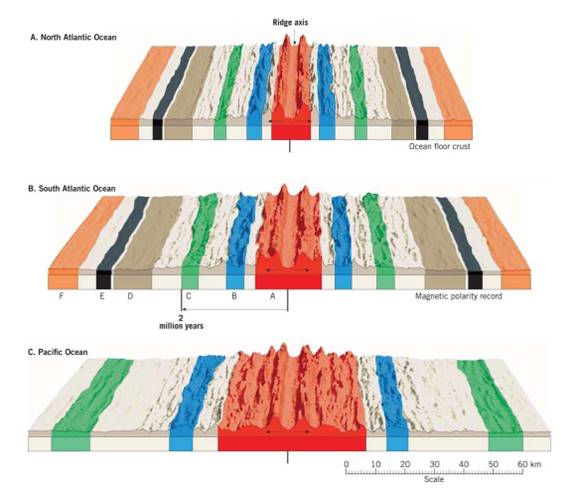
Using the South Atlantic as an example, label the beginning of the normal polarity period C that began 2 million years ago on the left sides of the Pacific and North Atlantic diagrams.
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule06:22
Students have asked these similar questions
Please help as soon as possible. I have an answer for this, but I'm a bit confused, so any extra assistance would be appreciated!
Complete the cross sections on the front and side of the block diagram in Figure 6.6.
Complete the cross-section of the side of the block diagram in Figure 6.7.
Complete the front and side of the block diagram in Figure 6.8
a. Draw four sedimentary layers of equal thickness that have a strike of N90°E. (Hint: Sketch the map view first.)b. Each layer is dipping to the south at an angle of 60°.c. On the block diagram complete the map view and both cross-sectional views.d. Add strike-dip symbols for each rock layer on both parts of Figure 6.9.
There is an old axiom (a self-evident or universally recognized truth) of economics that “There is no such thing as a free lunch”. In the United States, stringent, enforced water quality laws and regulations provide a high level of protection of our waters. This is accomplished at a significant cost. For example, (sewage treatment plants use 2% of the electricity produced in the United States. This high level of protection increases the cost of goods manufactured in the United States compared to other nations such as China where standards are lower, enforcement a bit lax and in some cases, non-existent.
What five (5) things could be done to “level the playing field” so that all manufacturers must provide the same degree of water quality protection no matter where in the world they are located? include how each of your ideas will be implemented (ex: which organization will be provided the power and resources to make sure each idea happens). These should be only about water pollution,…
Chapter 3 Solutions
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Ch. 3.1 - Using an atlas or Figure 3.11 for reference, draw...Ch. 3.1 - Use an atlas or your textbook to label the...Ch. 3.2 - Does Figure 3.3A represent a convergent or...Ch. 3.2 - Does Figure 3.38 represent a convergent,...Ch. 3.2 - Does Figure 3.3e represent a convergent,...Ch. 3.3A - Examine the east coast of South America and the...Ch. 3.3A - Examine the east coast of South America and the...Ch. 3.3A - On separate pieces of tracing paper, sketch the...Ch. 3.3B - Using the same two pieces of tracing paper you...Ch. 3.3B - Reassemble the two continents as you did in...
Ch. 3.5 - Figure 3.8 illustrates an idealized distribution...Ch. 3.5 - Figure 3.8 illustrates an idealized distribution...Ch. 3.5 - On Figure 3.8, outline the zone of earthquakes.Ch. 3.5 - Draw a line on Figure 3.8 at a depth of 100...Ch. 3.5 - The elastic rebound theory predicts that...Ch. 3.6 - How many intervals3, 5, or 7of reverse polarity...Ch. 3.6 - Approximately how many years ago did the current...Ch. 3.6 - Did Earth experience normal or reverse polarity...Ch. 3.6 - Did the period of normal polarity, C, bigin 1, 2,...Ch. 3.6 - During the past 4 million years, has each interval...Ch. 3.6 - Based on the pattern of magnetic reversals shown...Ch. 3.7A - On Figure 3.10, identify and mark the periods of...Ch. 3.7A - Using the South Atlantic as an example, label the...Ch. 3.7A - Using the distance scale at the bottom of Figure...Ch. 3.7A - The distances you obtained in Question 3 are for...Ch. 3.7B - North Atlantic: distance =km100,000cm/km=cm Rate...Ch. 3.7B - Pacific: distance =km100,000cm/km=cm Rate of...Ch. 3.7C - Using Figure 3.2, measure the distance from Point...Ch. 3.7C - Divide the distance in centimeters separating the...Ch. 3.7C - Repeat the procedure above to determine the age of...Ch. 3.7C - Based on your answers to Questions 2 and 3, which...Ch. 3.8 - What are the minimum and maximum ages of the...Ch. 3.8 - What is the approximate distance in kilometers...Ch. 3.8 - Using the data in Questions 1 and 2, calculate the...Ch. 3 - The distribution of earthquakes defines the...Ch. 3 - Prob. 2LRCh. 3 - Prob. 3LRCh. 3 - Prob. 4LRCh. 3 - Prob. 5LRCh. 3 - Prob. 6LRCh. 3 - Prob. 7LRCh. 3 - Prob. 8LRCh. 3 - Complete the block: diagrams in Figure 3.12 to...Ch. 3 - Prob. 10LRCh. 3 - List and explain two lines of evidence from this...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Write a balanced chemical equation for each chemical reaction. a. Solid copper reacts with solid sulfur to form...
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Plants use the process of photosynthesis to convert the energy in sunlight to chemical energy in the form of su...
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Plants use the process of photosynthesis to convert the energy in sunlight to chemical energy in the form of su...
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
2. Define equilibrium population. Outline the conditions that must be met for a population to stay in genetic e...
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
All of the following processes are involved in the carbon cycle except: a. photosynthesis b. cell respiration c...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Describe an example of bioconversion. What metabolic processes can result in fuels?
Microbiology: An Introduction
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Connecticut is the only state in America where treated industrial and municipal wastewater cannot be discharged to a surface water body used downstream as a source of drinking water. It is legal in all 49 other states. For example, New Orleans, Louisiana takes its drinking water from the Mississippi River which receives discharges of many, many treated municipal and industrial wastewater discharges as well as agricultural runoff from the more than 20 states that are upstream of it. Should other states be required to adopt Connecticut's standard? Whyarrow_forwardWhat is thermal pollution? How can it be controlled?arrow_forwardhow can the addition of nutrients such as nitrates and phosphates result in a reduction of the amount of dissolved oxygen in the water?arrow_forward
- Congratulations! You have just been selected to be the ruler of China with absolute power! What are the first five things that you would do to protect the environment and human health from water pollution (not other types of pollution)?arrow_forwardWhy is storm water management more of a problem in an urban area than in a rural area?arrow_forwardwhat is biochemical oxygen demand? how is it related to water quality?arrow_forward
- How are most industrial wastes disposed of? How has this changed over the past 25 years?arrow_forwardThink about natural resource management topics. Which topic or topics, are most interesting?arrow_forwardThink about natural resource management topics. Which topic or topics, if any, are of most interest to you?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Applications and Investigations in Earth Science ...Earth ScienceISBN:9780134746241Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science ...Earth ScienceISBN:9780134746241Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134041360Author:Greg CarbonePublisher:PEARSON
Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134041360Author:Greg CarbonePublisher:PEARSON Environmental ScienceEarth ScienceISBN:9781260153125Author:William P Cunningham Prof., Mary Ann Cunningham ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Environmental ScienceEarth ScienceISBN:9781260153125Author:William P Cunningham Prof., Mary Ann Cunningham ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Earth Science (15th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134543536Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON
Earth Science (15th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134543536Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON Environmental Science (MindTap Course List)Earth ScienceISBN:9781337569613Author:G. Tyler Miller, Scott SpoolmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Environmental Science (MindTap Course List)Earth ScienceISBN:9781337569613Author:G. Tyler Miller, Scott SpoolmanPublisher:Cengage Learning Physical GeologyEarth ScienceISBN:9781259916823Author:Plummer, Charles C., CARLSON, Diane H., Hammersley, LisaPublisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Physical GeologyEarth ScienceISBN:9781259916823Author:Plummer, Charles C., CARLSON, Diane H., Hammersley, LisaPublisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Applications and Investigations in Earth Science ...
Earth Science
ISBN:9780134746241
Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. Tasa
Publisher:PEARSON

Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)
Earth Science
ISBN:9780134041360
Author:Greg Carbone
Publisher:PEARSON

Environmental Science
Earth Science
ISBN:9781260153125
Author:William P Cunningham Prof., Mary Ann Cunningham Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Earth Science (15th Edition)
Earth Science
ISBN:9780134543536
Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. Tasa
Publisher:PEARSON

Environmental Science (MindTap Course List)
Earth Science
ISBN:9781337569613
Author:G. Tyler Miller, Scott Spoolman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physical Geology
Earth Science
ISBN:9781259916823
Author:Plummer, Charles C., CARLSON, Diane H., Hammersley, Lisa
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,