
Concept explainers
For the circuit in Fig. 11.47, find the value of ZL that will receive the maximum power from the circuit. Then calculate the power delivered to the load ZL.
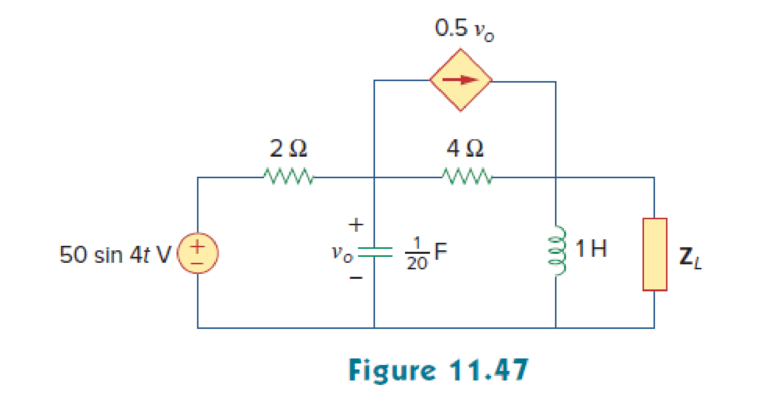
Find the value of the load impedance
Answer to Problem 16P
The value of load impedance
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Refer to Figure 11.47 in the textbook.
The inductance
The capacitance C is
The source voltage is
Formula used:
Write the general expression for the instantaneous voltage.
Write the expression to find the maximum average power.
Here,
Write the expression for
Calculation:
On comparing equation (1) and (2), the angular frequency is,
Write the expression for the reactance of the inductance.
Substitute
Write the expression for the reactance of the capacitance.
Substitute
Refer to Figure 11.47 in the textbook.
To find the Thevenin equivalent the given Figure is modified as shown in Figure 1.
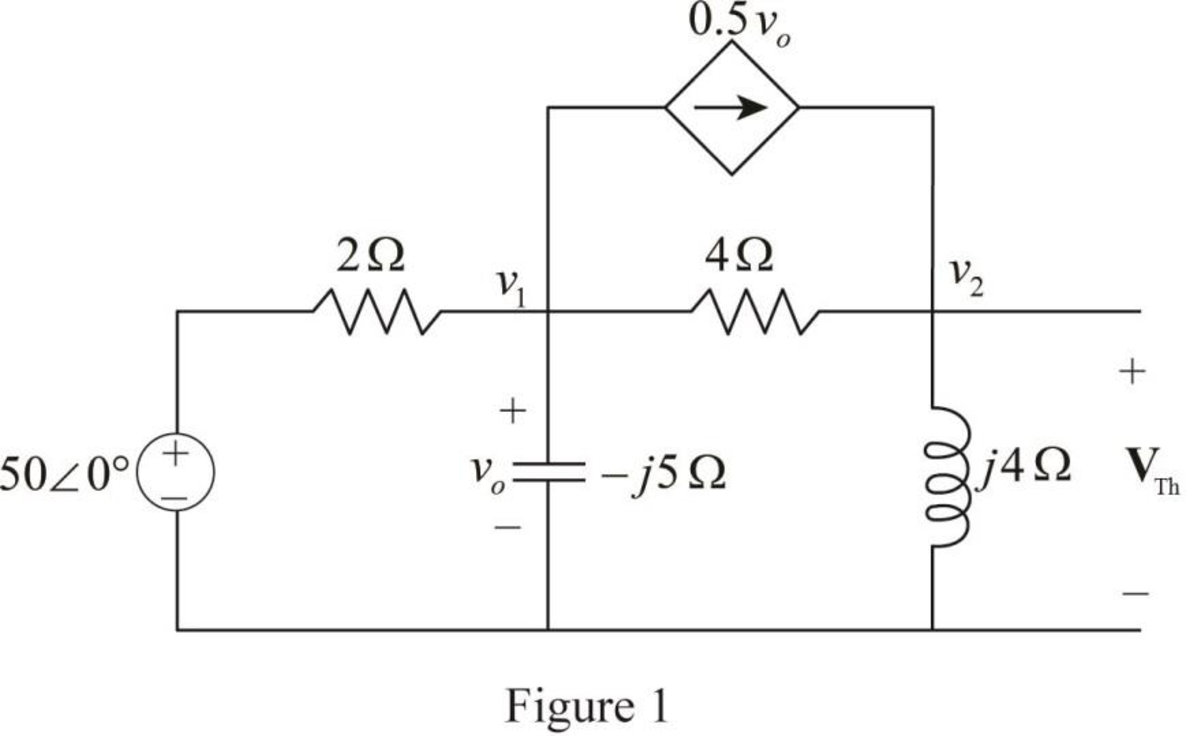
In Figure 1, apply Kirchhoff’s currrent law at node voltage
Rearrange the equation as follows,
In Figure 1, apply Kirchhoff’s currrent law at node voltage
Rearrange the equation as follows,
Substitute equation (6) in equation (5).
Rearrange the equation as follows,
The voltage voltage
Convert the equation from rectangular to polar form.
The Thevenin voltage is,
In Figure 1, to calculate the Thevenin impedance
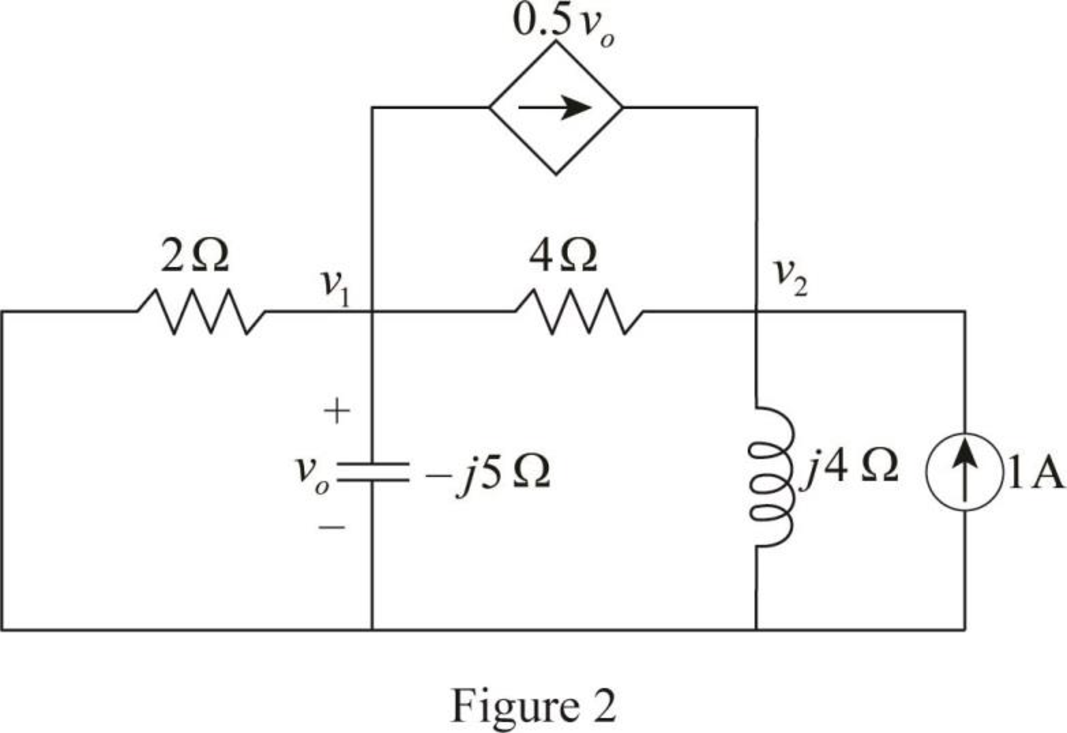
In Figure 2, apply Kirchhoff’current law at node voltage
Rearrange the equation as follows,
In Figure 2, apply Kirchhoff’current law at node voltage
Rearrange the equation as follows,
Substitute equation (7) in equation (8).
Rearrange the equation as follows,
Convert the equation from rectangular to polar form.
The Thevenin impedance
Substitute
Convert the equation from polar to rectangular form.
For maximum average power transfer, the load impedance
Convert the equation from rectangular to polar form.
On comparing the equation (9) with equation (4).
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the value of load impedance
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
- 2. Using the approximate method, hand sketch the Bode plot for the following transfer functions. a) H(s) = 10 b) H(s) (s+1) c) H(s): = 1 = +1 100 1000 (s+1) 10(s+1) d) H(s) = (s+100) (180+1)arrow_forwardQ4: Write VHDL code to implement the finite-state machine described by the state Diagram in Fig. 1. Fig. 1arrow_forward1. Consider the following feedback system. Bode plot of G(s) is shown below. Phase (deg) Magnitude (dB) -50 -100 -150 -200 0 -90 -180 -270 101 System: sys Frequency (rad/s): 0.117 Magnitude (dB): -74 10° K G(s) Bode Diagram System: sys Frequency (rad/s): 36.8 Magnitude (dB): -99.7 System: sys Frequency (rad/s): 20 Magnitude (dB): -89.9 System: sys Frequency (rad/s): 20 Phase (deg): -143 System: sys Frequency (rad/s): 36.8 Phase (deg): -180 101 Frequency (rad/s) a) Determine the range of K for which the closed-loop system is stable. 102 10³ b) If we want the gain margin to be exactly 50 dB, what is value for K we should choose? c) If we want the phase margin to be exactly 37°, what is value of K we should choose? What will be the corresponding rise time (T) for step-input? d) If we want steady-state error of step input to be 0.6, what is value of K we should choose?arrow_forward
- : Write VHDL code to implement the finite-state machine/described by the state Diagram in Fig. 4. X=1 X=0 solo X=1 X=0 $1/1 X=0 X=1 X=1 52/2 $3/3 X=1 Fig. 4 X=1 X=1 56/6 $5/5 X=1 54/4 X=0 X-O X=O 5=0 57/7arrow_forwardQuestions: Q1: Verify that the average power generated equals the average power absorbed using the simulated values in Table 7-2. Q2: Verify that the reactive power generated equals the reactive power absorbed using the simulated values in Table 7-2. Q3: Why it is important to correct the power factor of a load? Q4: Find the ideal value of the capacitor theoretically that will result in unity power factor. Vs pp (V) VRIPP (V) VRLC PP (V) AT (μs) T (us) 8° pf Simulated 14 8.523 7.84 84.850 1000 29.88 0.866 Measured 14 8.523 7.854 82.94 1000 29.85 0.86733 Table 7-2 Power Calculations Pvs (mW) Qvs (mVAR) PRI (MW) Pay (mW) Qt (mVAR) Qc (mYAR) Simulated -12.93 -7.428 9.081 3.855 12.27 -4.84 Calculated -12.936 -7.434 9.083 3.856 12.32 -4.85 Part II: Power Factor Correction Table 7-3 Power Factor Correction AT (us) 0° pf Simulated 0 0 1 Measured 0 0 1arrow_forwardQuestions: Q1: Verify that the average power generated equals the average power absorbed using the simulated values in Table 7-2. Q2: Verify that the reactive power generated equals the reactive power absorbed using the simulated values in Table 7-2. Q3: Why it is important to correct the power factor of a load? Q4: Find the ideal value of the capacitor theoretically that will result in unity power factor. Vs pp (V) VRIPP (V) VRLC PP (V) AT (μs) T (us) 8° pf Simulated 14 8.523 7.84 84.850 1000 29.88 0.866 Measured 14 8.523 7.854 82.94 1000 29.85 0.86733 Table 7-2 Power Calculations Pvs (mW) Qvs (mVAR) PRI (MW) Pay (mW) Qt (mVAR) Qc (mYAR) Simulated -12.93 -7.428 9.081 3.855 12.27 -4.84 Calculated -12.936 -7.434 9.083 3.856 12.32 -4.85 Part II: Power Factor Correction Table 7-3 Power Factor Correction AT (us) 0° pf Simulated 0 0 1 Measured 0 0 1arrow_forward
- electric plants. Prepare the load schedulearrow_forwardelectric plants Draw the column diagram. Calculate the voltage drop. by hand writingarrow_forwardelectric plants. Draw the lighting, socket, telephone, TV, and doorbell installations on the given single-story project with an architectural plan by hand writingarrow_forward
- A circularly polarized wave, traveling in the +z-direction, is received by an elliptically polarized antenna whose reception characteristics near the main lobe are given approx- imately by E„ = [2â, + jâ‚]ƒ(r. 8, 4) Find the polarization loss factor PLF (dimensionless and in dB) when the incident wave is (a) right-hand (CW) An elliptically polarized wave traveling in the negative z-direction is received by a circularly polarized antenna. The vector describing the polarization of the incident wave is given by Ei= 2ax + jay.Find the polarization loss factor PLF (dimensionless and in dB) when the wave that would be transmitted by the antenna is (a) right-hand CParrow_forwardjX(1)=j0.2p.u. jXa(2)=j0.15p.u. jxa(0)=0.15 p.u. V₁=1/0°p.u. V₂=1/0° p.u. 1 jXr(1) = j0.15 p.11. jXT(2) = j0.15 p.u. jXr(0) = j0.15 p.u. V3=1/0° p.u. А V4=1/0° p.u. 2 jX1(1)=j0.12 p.u. 3 jX2(1)=j0.15 p.u. 4 jX1(2)=0.12 p.11. JX1(0)=0.3 p.u. jX/2(2)=j0.15 p.11. X2(0)=/0.25 p.1. Figure 1. Circuit for Q3 b).arrow_forwardcan you show me full workings for this problem. the solution is - v0 = 10i2 = 2.941 volts, i0 = i1 – i2 = (5/3)i2 = 490.2mA.arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





