
Interpretation:
The molecular shape should be selected for a given molecule that have four shared pair of electrons and no lone pairs of electrons from the given shapes.
Concept introduction:
The geometric shape of the molecule is predicted by VSEPR theory (Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory) from electron pairs surrounding the central atom of the molecule whereas the molecular shape of the molecule is predicted by number of electron pairs as well as lone pairs.
Answer to Problem 14STP
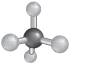
The correct option is (C):
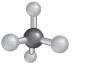
Explanation of Solution
Given:
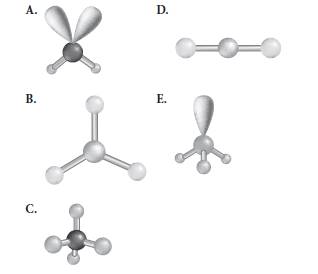
Reason for correct option:
The molecular shape can be determined for a molecule that have four shared pair of electrons and no lone pairs of electrons by taking the example of alkane.
- The structure of
alkanes has single bond between carbon and hydrogen atoms. So, in alkane there is 4 bonded atoms and no lone pair across the carbon atom and thus, according to VESPR the shape of the molecule will be tetrahedral.
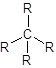
Hence, the correct option is (C):
Reason for correct options:
The geometry A and E have 2 and 1 lone pair respectively whereas geometry B and D both possess less than 4 number of electron pairs.
Chapter 11 Solutions
Chemistry: Matter and Change
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
- Four liters of an aqueous solution containing 6.98 mg of acetic acid were prepared. At 25°C, the measured conductivity was 5.89x10-3 mS cm-1. Calculate the degree of dissociation of the acid and its ionization constant.Molecular weights: O (15.999), C (12.011), H (1.008).Limiting molar ionic conductivities (λ+0 and λ-0) of Ac-(aq) and H+(aq): 40.9 and 349.8 S cm-2 mol-1.arrow_forwardDetermine the change in Gibbs energy, entropy, and enthalpy at 25°C for the battery from which the data in the table were obtained.T (°C) 15 20 25 30 35Eo (mV) 227.13 224.38 221.87 219.37 216.59Data: n = 1, F = 96485 C mol–1arrow_forwardIndicate the correct options.1. The units of the transport number are Siemens per mole.2. The Siemens and the ohm are not equivalent.3. The Van't Hoff factor is dimensionless.4. Molar conductivity does not depend on the electrolyte concentration.arrow_forward
- Ideally nonpolarizable electrodes can1. participate as reducers in reactions.2. be formed only with hydrogen.3. participate as oxidizers in reactions.4. form open and closed electrochemical systems.arrow_forwardIndicate the options for an electrified interface:1. Temperature has no influence on it.2. Not all theories that describe it include a well-defined electrical double layer.3. Under favorable conditions, its differential capacitance can be determined with the help of experimental measurements.4. A component with high electronic conductivity is involved in its formation.arrow_forwardTo describe the structure of the interface, there are theories or models that can be distinguished by:1. calculation of the charge density.2. distribution of ions in the solution.3. experimentally measured potential difference.4. external Helmoltz plane.arrow_forward
- Indicate the correct options when referring to Luther's equation:1. It is not always easy to compare its results with experimental results.2. It depends on the number of electrons exchanged in the species involved.3. Its foundation is thermodynamic.4. The values calculated with it do not depend on temperature.arrow_forwardIndicate which of the unit options correspond to a measurement of current density.1. A s m-22. mC s-1 m-23. Ω m-24. V J-1 m-2arrow_forwardIndicate the options that are true when referring to electrode membranes:1. The Donnan potential, in general, does not always intervene in membranes.2. There are several ways to classify the same membrane.3. Any membrane can be used to determine the pH of a solution.4. Only one solution and one membrane are needed to determine the pH of that solution.arrow_forward
- Calculate the maximum volume of carbon dioxide gasarrow_forwardIn galvanic cells, their potential1. can be measured with a potentiometer2. does not depend on the equilibrium constant of the reaction occurring within them3. is only calculated from the normal potentials of the electrodes they comprise4. can sometimes be considered a variation in a potential differencearrow_forwardIf some molecules in an excited state collide with other molecules in a ground state, this process1. can occur in solution and in the gas phase.2. can be treated as a bimolecular process.3. always results in collisional deactivation.4. does not compete with any other process.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





